Summary
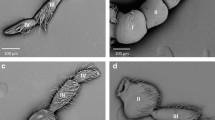
Light and scanning electron microscopic investigations were carried out to map the topography, number, size and configuration of all campaniform sensilla in the exoskeleton of the blowfly Calliphora vicina. We counted a total of about 1,200 campaniform sensilla; sexual dimorphism was not found. The shape, i.e. cap and collar, of most campaniform sensilla is elliptical; only 24 circular sensilla were found. The occurrence of campaniform sensilla is limited to the antennae (pedicels), legs, wings and halteres. Due to their configuration we defined: (a) ‘single sensillum’, (b) ‘sensilla in groups’ and (c) ‘sensilla in fields’. Single sensilla (n=86) occur on all loci mentioned. Sensilla in groups (about 350, in 52 groups) occur on the legs and forewings. The largest group had 32, the smallest 3 sensilla. All sensilla in fields (about 730, in 12 fields) occur on the halteres except for one on the tegula of the wing. A total of about 670 campaniform sensilla, which are more than 55% of all sensilla, are localized in 10 fields on the halteres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert PJ, Zacharuk RY, Wong L (1976) Structure, innervation, and distribution of sensilla on the wings of a grasshopper. Can J Zool 54:1542–1553
Barth FG (1985) Slit sensilla and the measurement of cuticular strains. In: Barth FG (ed) Neurobiology of Arachnids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 162–188
Barth FG, Bohnenberger J (1978) Lyriform slit-sense organ: threshold and stimulus amplitude ranges in a multi-unit mechanoreceptor. J Comp Physiol 125:37–43
Barth FG, Ficker E, Federle HU (1984) Model studies on the mechanical significance of grouping in compound slit sensilla (Chelicerata, Araneida) Zoomorphology 104:204–215
Barth FG, Libera W (1970) Ein Atlas der Spaltsinnesorgane von Cupiennius salei Keys Chelicerata (Araneae). Z Morphol Tiere 68:468
Barth FG, Pickelmann P (1975) Lyriform slit sense organs. Modelling an arthropod mechanoreceptor. J Comp Physiol 103:39–54
Barth FG, Stagl J (1976) The slit sense organs of arachnids. A comparative study of their topography on the walking legs. Zoomorphology 86:1–23
Berlese A (1909) Gli Insetti, Vol 1. Embriologia e Morfologia. Societa editrice libraria, Milano
Bräunig P, Pflüger HJ, Hustert R (1983) The specifity of central nervous projections of locust mechanoreceptors. J Comp Neurol 218:197–207
Bush BM, Laverack MS (1982) Mechanoreception. In: Atwood HL, Sandeman DC (eds) The biology of Crustacea, Vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 399–469
Christophers SR (1960) Aedes aegypti (L) The yellow fever mosquito, University Press, Cambridge, pp 660–663
Cole ES, Palka J (1982) The pattern of campaniform sensilla on the wing and haltere of Drosophila melanogaster and several of its homeotic mutants. J Embryol Exp Morphol 71:41–61
Dumpert K, Gnatzy W (1977) Cricket combined mechanoreceptors and kicking response. J Comp Physiol 122:9–25
Fudalewicz-Niemczyk W (1955) The innervation and sense organs in the wings of the grasshopper Locusta cantans Füssl Pol Pismo Ent 25:127–160
Fudalewicz-Niemczyk W (1963) L'innervation et les organes sensoriels des ailes d'insectes d'autres ordres. Acta Biol Cracov Zool 8:351–462
Fudalewicz-Niemczyk W, Rosciszewska M (1972) The innervation and sense organs of the wings of Gryllus domesticus L. Acta Biol Cracov Zool 15:35–51
Gettrup E (1965) Sensory mechanism in locomotion: the campaniform sensilla of the insect wing and their function during flight. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 30:615–622
Gettrup E (1966) Sensory regulation of wing twisting in locust. J Exp Biol 44:1–16
Gewecke M (1967) Der Bewegungsapparat der Antennen von Calliphora erythrocephala. Z Morphol Ökol Tiere 59:95–133
Gewecke M (1972) Bewegungsmechanismus und Gelenkrezeptoren der Antennen von Locusta migratoria L (Insecta Orthoptera). Z Morphol Ökol Tiere 71:128–149
Ghysen A (1978) Sensory neurones recognize defined pathways in Drosophila central nervous system. Nature 274:869–872
Gnatzy W (1984) ‘Campaniform’ structures on lobster antennae are dermal glands. Cell tissue Res 236:729–731
Gnatzy W, Schmidt M, Römbke J (1984) Are the funnel-canal organs the ‘campaniform sensilla’ of the shore crab Carcinus maenas (Decapoda Crustacea)? I Topography, external structure and basic organization. Zoomorphology 104:11–20
Grünert U, Gnatzy W (1987) Campaniform sensilla of Calliphora vicina (Insecta, Diptera). II Typology. Zoomorphology 106:320–328
Heußlein R, Gnatzy W (1987) Central projections of cercal campaniform sensilla in crickets and cockroaches. Cell Tissue Res 247:591–598
Hicks JB (1857) On a new organ in insects. J Proc Linn Soc (Zool) I:136–140
Honegger HW, Reif H, Müller W (1979) Sensory mechanism of eye cleaning behaviour in the cricket Gryllus campestris. J Comp Physiol 129:247–256
Hooper RL, Pitts CW, Westfall JA (1972) Sense organs on the ovipositor of the face fly Musca autumnalis. Ann Entomol Soc Am 65:577–585
Hustert R, Pflüger HJ, Bräunig P (1981) Distribution and specific central projections of mechanoreceptors in the thorax and proximal leg joints of locusts. III The external mechanoreceptors: The campaniform sensilla. Cell Tissue Res 216:97–111
Knyazeva NI (1976) Wing receptors in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol 12:551–555
Knyazeva NI, Fudalewicz-Niemczyk W, Rosciszewska M (1975) Proprioceptors of the house cricket (Gryllus domesticus L) (Orthoptera). Acta Biol Cracov Ser Zool 18:33–44
Krämer K, Markl H (1978) Flight-inhibition on ground contact in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. I Contact Receptors and a model for their central connections. J Insect Physiol 24:577–586
Kutsch W, Hanloser H, Reinecke M (1980) Light- and electronmicroscopic analysis of a complex sensory organ: The tegula of Locusta migratoria. Cell Tissue Res 210:461–478
Lee RMKW, Craig DA (1983) The labrum and labral sensilla of moquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae): a scanning electron microscopy study. Can J Zool 61:1568–1579
Markl H (1970) Die Verständigung durch Stridulationssignale bei Blattschneiderameisen. III Die Empfindlichkeit für Substrativibrationen. Z Vergl Physiol 69:6–37
Melin D (1941) Contributions to the knowledge of the flight of insects. Uppsala Universitets Arsskrift 4:3–245
Moran DT, Rowley JC III (1975) High voltage and scanning electron microscopy of the site of stimulus reception of an insect mechanoreceptor. J Ultrastruct Res 50:38–46
Moran DT, Rowley JC III, Zill SN, Varela FG (1976) The mechanism of sensory transduction in a mechanoreceptor. Functional stages in campaniform sensilla during the molting cycle. J Cell Biol 71:832–847
Nässel DR, Högmo O, Hallberg E (1983) Antennal receptors in the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala. I. The giant central projection of the pedicellar campaniform sensillum. J Morphol 180:159–169
Palka J, Lawrence PA, Hart HS (1979) Neural projection pattern from homeotic tissue of Drosophila studied in bithorax mutants and mosaics. Develop Biol 69:549–575
Pflugstaedt H (1912) Die Halteren der Dipteren. Z Wiss Zool 100:1–58
Prashad B (1916) The halteres of mosquitoes and their function. Ind J Med Res 3:503–509
Pringle JWS (1938) Proprioception in insects. II The action of the campaniform sensilla on the legs. J Exp Biol 15:114–131
Pringle JWS (1948) The gyroscopic mechanism of the halteres of Diptera. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser B 233:347–384
Pringle JWS (1955) The function of the lyriform organs of arachnids. J Exp Biol 32:270–278
Pringle JWS (1957) Insect Flight. University Press, Cambridge
Rice MJ (1976) Contact chemoreceptors on the ovipositor of Lucilia cuprina (Wied) the Australian sheep blowfly. Austral J Zool 24:353–360
Schafer R, Sanchez TV (1973) Antennal sensory system of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana: Postembryonic development and morphology of the sense organs. J Comp Neurol 149:335–354
Schmidt M, Gnatzy W (1984) Are the funnel-canal organs the ‘campaniform sensilla’ of the shore crab Carcinus maenas (Decapoda Crustacea)? II. Ultrastructure. Cell Tissue Res 237:81–93
Smith DS (1969) The fine structure of haltere sensilla in the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala (Meig) with scanning electron microscopic observations on the haltere surface. Tissue Cell 1:443–484
Völker W (1982) Lebendbeobachtungen an kutikulären Reizübertragungsstrukturen campaniformer Sensillen und Hochauflösungs-Elektronenmikroskopie der reizaufnehmenden Sinneszellregionen. Dissertation Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster
Weinland E (1890) Über die Schwinger (Halteren) der Dipteren. Z Wiss Zool 51:55–166
Wendler G (1978) Lokomotion: das Ergebnis zentral-peripherer Interaktion. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 1978:80–96
Zaćwilichowski MJ (1933) Über die Innervierung und die Sinnesorgane der Flügel der Honigbiene (Apis mellifica L). Bull Acad Pol Cl Math Nat Ser B:275–289
Zaćwilichowski MJ (1934a) Über die Innervierung und die Sinnesorgane der Flügel der Schabe Phyllodromia germanica L. Bull Acad Pol Cl Math Nat Ser B:84–103
Zaćwilichowski MJ (1934b) Über die Innervierung und die Sinnesorgane der Flügel der Feldheuschrecke Stauroderus biguttulus (L). Bull Acad Pol Cl Math Nat Ser B:187–196
Zill SN, Moran DT (1981a) The exoskeleton and insect proprioception. I Responses of tibial campaniform sensilla to external and muscle-generated forces in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. J Exp Biol 91:1–24
Zill SN, Moran DT (1981b) The exoskeleton and insect proprioception. III Activity of tibial campaniform sensilla during walking in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. J Exp Biol 94:57–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnatzy, W., Grünert, U. & Bender, M. Campaniform sensilla of Calliphora vicina (Insecta, Diptera). Zoomorphology 106, 312–319 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312005
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312005