Summary
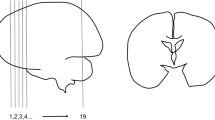
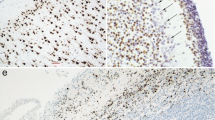
Scanning electron microscopy was used to assess the ultrastructural differences exhibited by the varigated ependymal lining of the near-term human fetal 4th ventricle. The central portion of the fourth ventricular floor, including the median sulcus is punctuated by numerous clumps of cilia. The density of cilia here is not as great as that described for other regions of the human cerebral ventricular system; accordingly, underlying substructure can be noted. There are distinct differences between ependymas that line the floor of the fourth ventricle with those of the adjacent area postrema. The latter region possesses not cilia, but instead exhibits a dense knap of microvilli. The ultra-architecture of the choroid plexus is relatively similar to that of other circumventricular organs with the exception that it possesses small isolated groups of cilia as well as microvilli. These findings are discussed with respect to the dynamics of local CSF movement and flow, ependymoabsorption and ependymosecretion
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. F.: Techniques for the preservation of three dimensional structures in preparing specimens for the electron microscope. Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 13, 130–133 (1951).
Borison, H. L., Brizee, K. R.: Morphology of emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone in cat medulla oblongata. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 77, 38–42 (1951).
Bruni, J. E., Montemurro, D. G., Clattenburg, R. E., Singer, R. P.: A scanning electron microscopic study of the ependymal surface of the third ventricle of the rabbit, rat, mouse and human brain. Anat. Rec. 174, 407–419 (1972).
Clementi, F., Marini, D.: The surface fine structure of the walls of cerebral ventricles and of choroid plexus in cat. Z. Zellforsch. 123, 82–95 (1972).
Coates, P.: (Personal Communication).
Friede, R. L.: Surface structures of the aqueduct and the ventricular walls: a morphologic, comparative and histochemical study. J. comp. Neurol. 116, 229–247 (1961).
Knigge, K. M., Scott, D. E.: Structure and function of the median eminence. Amer. J. Anat. 129, 223–244 (1970).
Kobayashi, H., Matsui, T.: Fine structure of the median eminence and its functional significance, p. 3–46. In: Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, W. F. Ganong and L. Martini (eds.) New York: Oxford University Press 1969.
Kozlowski, G. P., Scott, D. E., Krobisch Dudley, G.: Scanning electron microscopy of the third ventricle of sheep. Z. Zellforsch., 136, 169–176 (1973).
Kozlowski, G. P., Scott, D. E., Murphy, J.: Scanning electron microscopy of the lateral ventricles of sheep. Amer. J. Anat. 135, 561–566 (1972).
Kroidl, R.: Die arterielle und venöse Versorgung der Area postrema der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 89, 430–452 (1968).
Leveque, T. F.: The median prechiasmatic area in the rat and LH secretion, p. 298–305. In: Brain-Endocrine Interaction. The Median Eminence: Structure and Function. Int. Symp. Munich 1971, K. M. Knigge, D. E. Scott and A. Weindl (eds.) Basel: Karger 1972.
Lindner, E., Leonhardt, H.: Cytosomen mit Zylindroiden und fünfschichtigen Membranen. Untersuchungen an den Nerven und Gliazellen der Area postrema im Kaninchengehirn. Z. Zellforsch. 86, 453–474 (1968).
Scott, D. E., Knigge, K. M., Krobisch-Dudley, G.: The mammalian median eminence; a neuroendocrine transducer. Sci. Amer., in press (1971).
Scott, D. E., Kozlowski, G., Krobisch-Dudley, G.: A comparative ultrastructural analysis of the third cerebral ventricle of the North American Mink (Mustela vision). Anat. Rec., 175, 155–168 (1973).
Scott, D. E., Krobisch-Dudley, G., Gibbs, F. P., Brown, G. M.: The mammalian median eminence, a comparative and experimental model, p. 30–49. In: Brain-Endocrine Interaction. Median Eminence: Structure and Function. Int. Symp. Munich 1971, K. M. Knigge D. E. Scott and A. Weindl (eds.). Basel: Karger 1972.
Scott, D. E., Paull, W. K., Krobisch-Dudley, G.: A comparative scanning electron microscopic analysis of the human cerebral ventricular system. I. The third ventricle. Z. Zellforsch. 132, 203–215 (1972a).
Streeter, G. L.: Anatomy of the floor of the fourth ventricle. Amer. J. Anat. 2, 299–324 (1903).
Sulzmann, R.: Zur Morphologie des Ependyms im Zentralkanal des Hundes. Anat. Anz. 109, 351–357 (1961).
Talanti, S., Kivalo, E.: Studies on the area postrema of the bovine fetus. Annales Academiae Scientarium Fennial. Series A.-V. Medica. 83, 1–6 (1961).
Torack, R. M., Finke, E. H.: Evidence for a sequestration of function within the area postrema based on scanning electron microscopy and the penetration of horseradish peroxidase. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 85–96 (1971).
Weindl, A.: Zur Morphologie und Histochemie von Subfornical-Organ, Organum vasculosum laminae terminalis und Area postrema bei Kaninchen und Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 67, 740–775 (1965).
Wilson, J. T.: On the anatomy of the calamus region in the human bulb; with an account of a hitherto undescribed “Nucleus postremus”. J. Anat. Physiol. 40, 210–241, 357–386 (1906).
Wislocki, G. B., Putnam, T. J.: Note on the anatomy of the area postrema. Anat. Rec. 19, 281–285 (1920).
Wittkowski, W.: Zur funktionellen Morphologie ependymaler und extraependymaler Glia im Rahmen der Neurosekretion. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Neurohypophyse an der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 86, 111–128 (1968a).
Wittkowski, W.: Elektronenmikroskopische Studien zur intraventrikularen Neurosekretion in den Recessus infundibularis der Maus. Z. Zellforsch. 92, 207–216 (1968b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by U.S.P.H.S. Grant NS 08171.
Career Development Awardee GM K04 70001.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, D.E., Kozlowski, G.P., Paull, W.K. et al. Scanning electron microscopy of the human cerebral ventricular system. Z. Zellforsch 139, 61–68 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307461
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307461