Abstract
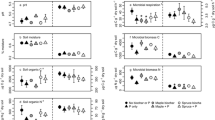
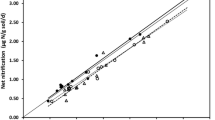
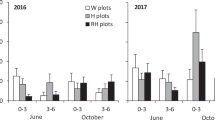
The herbicide glyphosate was sprayed aerially on a section of conifer forest in Atlantic Canada that had been previously clearcut and reforested. Glyphosate was then tested for effects on ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification for a period of 8 months by comparing microbial activity in treated and untreated zones of the clay loam forest soil and the overlying decomposing litter, both with a pH of 3.8. With ammonification, there was generally a stimulation of activity in both the forest litter (FL) and forest soil (FS) that had been exposed to glyphosate during spraying. Nitrification rates in FL and FS were very low and glyphosate had no appreciable stimulatory or inhibitory effect on nitrification. Although glyphosate stimulated denitrification in a few instances, it generally had no significant effect on denitrification activity in FL and FS exposed during spraying. With all processes, microbial activity in FL was significantly greater than that in FS. Laboratory bioassays were also performed with FL and FS, as well as two silt loam (pH 5.8 and 6.4) and one sandy loam (pH 6.8) agricultural soils, using glyphosate concentrations up to 200 times higher than field application rates. With ammonification and denitrification, glyphosate generally stimulated activity at all levels tested and in all soil used. Glyphosate stimulated ammonification by 50% at concentrations ranging from 140 to 550 μg g−1 for the soils and >4000 μg g−1 for FL. With denitrification, the corresponding herbicide levels were approximately 2250 μg g−1 for FS, > 10,000 for FL, and 450 for an agricultural soil. With nitrification, it was estimated that glyphosate concentrations greater than 1000 to 2000 μg g−1 would be required to cause a 50% inhibition of activity. The careful use of glyphosate in forestry should have no toxic effects on N cycling in soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauchamp, E. G., Trevors, J. T., and Paul, J. W.: 1989, Adv. Soil Sci. 10, 113.
Carlisle, S. M. and Trevors, J. T.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 29, 189.
Carlisle, S. M. and Trevors, J. T.: 1988, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 39, 409.
Dhanaraj, P. S.: 1988, in R. Lal and S. Lal (eds.), Pesticides and Nitrogen Cycle, vol. II, CRC Press, Boca Raton, p. 43.
Greaves, M. P. and Malkomes, H. P.: 1980, in R. J. Hance (ed.), Interactions Between Herbicides and the Soil, Academic Press, N.Y., p. 223.
Gundersen, P. and Rasmussen, L.: 1990, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 113, 1.
Haynes, R. J.: 1986, in R. J. Haynes (ed.), Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System, Academic Press, N.Y., p. 127.
Keeney, D. R. and Nelson, D. W.: 1982, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, and D. R. Kenney (eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 2nd ed., Am. Soc. Agronomy, Madison, p. 643.
Klute, A.: 1986, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1, Am. Soc. Agronomy, Madison.
Lal, R.: 1988, in R. Lal and S. Lal (eds.), Pesticides and Nitrogen Cycle, Vol. I, CRC Press, Boca Raton, p. 75.
Lensi, R., Mazurier, S., Goubiere, F., and Josserand, A.: 1986, Soil Biol. Biochem. 18, 239.
Little, T. M. and Hills, F. J.: 1978, Agricultural Experimentation Design and Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, N.Y.
Marsh, J. A. P.: 1985, Pestic. Sci. 16, 93.
Marsh, J. A. P., Davies, H. A., and Grossbard, E.: 1977, Weed Res. 17, 77.
Muller, M. M., Rosenberg, C., Siltanen, H., and Wartiovaara, T.: 1981, Bull Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27,724.
Nakos, G.: 1980, Soil Biol. Biochem. 12, 517.
Page, A. L.: 1982, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Am. Soc. Agronomy, Madison.
Quilty, S. P. and Geoghehan, M. J.: 1976, Proc. Soc. Gen. Microbiol. 3, 128.
Rao, V. V S. N.: 1988, in R. Lal and S. Lal (eds.), Pesticides and Nitrogen Cycle, Vol. II, CRC Press, Boca Baton, p. 1.
Ratnayake, M. and Audus, L. J.: 1978, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol 8, 170.
Ray, R. C. and Sethunathan, N.: 1988, in R. Lal and S. Lal (eds.), Pesticides and Nitrogen Cycle, Vol. II, CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, p. 119.
Robertson, G. P. and Tiedje, J. M.: 1987, Soil Biol Biochem. 19, 187.
Robertson, G. P., Visousek, P. M., Matson, P. A., and Tiedje, J. M.: 1987, Plant and Soil 97, 119.
Stratton, G. W.: 1990a, Toxicity Assessment 5, 319.
Stratton, G. W.: 1990b, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 51, 373.
Vitousek, P. M.: 1983, in B. Bolin and R. B. Cook (eds.), The Major Biogeochemical Cycles and Their Interactions, John Wiley & Sons, N.Y. p. 223.
Wardle, D. A. and Parkinson, D.: 1990, Plant and Soil 122, 29.
Weier, K. L. and Gilliam, J. W.: 1986, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 1210.
Yeomans, J. C. and Bremner, J. M.: 1985, Soil Biol. Biochem. 17, 447.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stratton, G.W., Stewart, K.E. Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on nitrogen cycling in an acid forest soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 60, 231–247 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282625
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282625