Summary
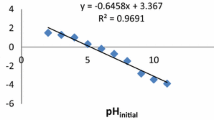
Uptake of the pesticide parathion from aqueous solution by uni-cellular green algae has been investigated. The removal of parathion from solution by Chlorococcales does not occur through passive or by active permeation into the cells but by adsorption, which can be described by the. Freundlich-adsorption-isotherm equation. Investigations of partially purified cell walls phow that neither mucus, cellulose walls nor plasmamembranes adsorb parathion. The lipid containing trilaminar sheath (TLS) adsorbs the pesticide. The relevance of these results to ecological problems is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MK, Casida JE (1958) Metabolism of some organophosphates insecticides by microorganisms. J Econ Entomol 51:59
Cole DR, Plapp FW (1974) Inhibition of growth and photosynthesis in Chlorella pyrenoidosa by a polychlorinates biphenyl and several insecticides. J Environ Entom 3:217
Gregory WW, Reed JK, Priester LE (1969) Accumulation of parathion and DDT by some algae and protozoa. J Protozool 16:69
Ketelaar JAA, Hellingman JE (1951) Chemical studies on insecticides: determination of parathion and dimethylparathion. Anal Chem 23:646
Kipling JJ (1965) Adsorption from solution of non-electrolytes. Academic Press, London
Loosanoff VL, Hanks JE, Ganaros AE (1957) Control of certain forms of zooplankton in Mass algae cultures. Science 125:1092
Moore RB, Dorward DA (1968) Accumulation and metabolism of pesticides by algae. J Phycol 4:7
Pringsheim EA, Pringsheim O (1959) Die Ernährung koloniebildender der Volvocales. Biol Zentralbl 78:937
Saltzman S, Yaron B, Mingelgrin U (1974) The surface catalyzed hydrolysis of parathion on kaolinite. Proc Soil-Sci Soc Amer 38:231
Saltzman S, Mingelgrin U (1977) Montmorillonite-parathion interactions in aqueous suspensions as affected by the mode of preparation. In: Banin A (ed) Agrochemical in Soil. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Staehelin LA, Pickett-Heaps JD (1975) The ultrastructure of Scenedesmus (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 11:163
Veber K, Zahradnik J, Breyl J (1980) Efficiency and rate of elimination of polychlorinated biphenyls from waste waters by means of algae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 25:841
Wahid PA, Sethunathan N (1978) Soprtion — desorption of parathion in soils. J Agric Food chem 26:101
Werner D, Pawlitz H (1978) Differential elimination of phenol by diatoms and other unicellular algae from low concentrations. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 20:303
Yaron B, Saltzman S (1972) Influence of water and temperature on adsorption of parathion in soil. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 36:583
Yaron B, Saltzman S (1978) Soil-parathion surface interactions. Residue Reviews 69:1
Zuckerman BM, Deubert K, Mackiewicz M, Gunner H (1970) Studies on the biodegradation of parathion. Plant Soil 33:273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lohmann, E., Hagedorn, H. The effect of parathion on green algae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 268–272 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252029
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252029