Summary
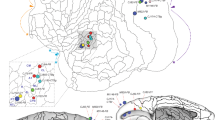
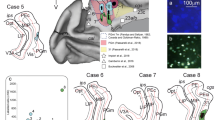
Retrograde and anterograde tracing methods were used to study the connections between the parahippocampal gyrus and the posterior auditory association cortex (area Tpt) in the Old-World monkey. Nine monkeys received injections of tritiated amino acids in different areas of the parahippocampal gyrus, and three monkeys received injections of the retrograde tracer fast blue in area Tpt of the auditory association cortex. It was observed that the medial part of the posterior portion of the parahippocampal gyrus (areaTH) gives rise to projections that terminate in layers I–III of area Tpt. Using complementary retrograde tracing experiments, the cells of origin for this projection were identified in layers V and VI of area TH. The findings reveal a direct structural coupling between auditory association cortices and a temporal region thought to play a role in learning and memory. These connections may form part of a neural system in the monkey that is related to acoustic learning and memory. Homologous systems in humans may be involved in auditory learning and language acquisition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Burton MJ, Passingham RE (1980) Cortical and subcortical afferents to the amygdala of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Brain Res 190: 347–368
Amaral DG, Insausti R, Cowan WM (1983) Evidence for a direct projection from the superior temporal gyrus to the entorhinal cortex in the monkey. Brain Res 275: 263–277
Amaral DG, Price JL (1984) Amygdalo-cortical projections in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Comp Neurol 230: 465–496
Baleydier C, Mauguiere F (1980) The duality of the cingulate gyrus in monkey: neuroanatomical study and functional hypothesis. Brain 103: 535–554
Barnes CL, Maskey KP, Van Hoesen GW (1984) Temporal pole projections to ventromedial temporal lobe structures in the monkey. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10: 287
Bharos TB, Kuypers HGJM, Lemon RN, Muir RB (1981) Divergent collaterals from deep cerebellar neurons to thalamus and tectum and to medulla oblongata and spinal cord: retrograde fluorescent and electrophysiological studies. Exp Brain Res 42: 399–410
Brady DR, Van Hoesen GW (1984) Topographic organization of certain parahippocampal cortical projection neurons in the monkey using retrograde tracers. Soc Neurosci Abstr 10: 287
Celesia GG (1976) Organization of auditory cortical areas in man. Brain 99: 403–414
Chavis DA, Pandya DN (1976) Further observations on cortico-frontal connections in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 117: 369–386
Cowan WM, Gottlieb DI, Hendrickson AE, Price JL, Woolsey TA (1972) The autoradiographic demonstration of axonal connections in the central nervous system. Brain Res 37: 21–51
Damasio AR, Eslinger PJ, Damasio H, Van Hoesen GW, Cornell S (1985) Multimodal amnesic syndrome following bilateral temporal and basal forebrain damage. Arch Neurol 42: 252–259
Galaburda AM, Pandya DN (1982) Role of architectonics and connections in the study of primate brain evolution. In: Armstrong E, Falk D (eds) Primate brain evolution. Plenum Press, New York, pp 203–216
Galaburda AM, Pandya DN (1983) The intrinsic architectonics and connectional organization of the superior temporal region of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 221: 169–181
Galaburda AM, Sanides F (1980) Cytoarchitectonic organization of the human auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol 190: 597–610
Galaburda AM, Sanides F, Geschwind N (1978) Cytoarchitectonic left-right asymmetries in the temporal speech region. Arch Neurol 35: 812–817
Herzog AG, Van Hoesen GW (1976) Temporal neocortical afferent connections to the amygdala in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 115: 57–69
Kosel KC, Van Hoesen GW, Rosene DL (1982) Non-hippocampal cortical projections from the entorhinal cortex in the rat and rhesus monkey. Brain Res 244: 201–213
Mesulam M-M, Van Hoesen GW, Pandya DN, Geschwind N (1977) Limbic and sensory connections of the inferior parietal lobule (area PG) in the rhesus monkey: a study with a new method for horseradish peroxidase histochemistry. Brain Res 136: 393–414
Mishkin M (1978) Memory in monkeys severely impaired by combined but not by separate removal of amygdala and hippocampus. Nature 273: 297–298
Pandya DN, Hallett M, Mukherjee SK (1969) Intra- and interhemispheric connections of the neocortical auditory system in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 14: 49–65
Pandya DN, Kuypers HGJM (1969) Cortico-cortical connections in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 13: 13–36
Pandya DN, Sanides F (1973) Architectonic parcellation of the temporal operculum in rhesus monkey and its projection pattern. Z Anat Entwickl-Gesch 139: 127–161
Pandya DN, Seltzer B (1982) Intrinsic connections and architectonics of posterior cortex in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 204: 196–210
Pandya DN, Van Hoesen GW, Mesulam M-M (1981) Efferent connections of the cingulate gyrus in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res 42: 319–330
Rosene DL, Van Hoesen GW (1977) Hippocampal efferents reach widespread areas of cerebral cortex and amygdala in the rhesus monkey. Science 198: 315–317
Ross ED (1984) Partial and distributed disorders of recent memory in the human. Semin Neurol 4: 245–248
Scoville WB, Milner B (1957) Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 20: 11–21
Seltzer B, Pandya DN (1976) Some cortical projections to the parahippocampal area in the rhesus monkey. Exp Neurol 50: 146–160
Seltzer B, Pandya DN (1978) Afferent cortical connections and architectonics of the superior temporal sulcus and surrounding cortex in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 149: 1–24
Tranel DL, Damasio AR (1985) Knowledge without awareness: an autonomic index of facial recognition by prosopagnosics. Science 228: 1453–1454
Turner BH, Mishkin M, Knapp M (1980) Organization of the amygdalopetal projections from modality-specific association areas in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 191: 515–543
Van Hoesen GW (1982) The parahippocampal gyrus: new observations regarding its cortical connections in the monkey. Trends Neurosci 5: 345–350
Van Hoesen GW, Pandya DN (1975) Some connections of the entorhinal (area 28) and perirhinal (area 35) cortices of the rhesus monkey. I. Temporal lobe afferents. Brain Res 95: 1–24
von Bonin G, Bailey P (1947) The neocortex of Macaca mulatta. University of Illinois Press, Urbana IL
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tranel, D., Brady, D.R., Van Hoesen, G.W. et al. Parahippocampal projections to posterior auditory association cortex (area Tpt) in Old-World monkeys. Exp Brain Res 70, 406–416 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248365
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248365