Summary
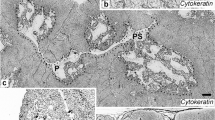
To evaluate interrelationships among epithelial cells, and between morphology and function in the microenvironment, we studied the ultrastructural morphology of epithelial cells in sections of human thymus from donors aged 2 months to 31 years. Six types of epithelial cells were observed: “subcapsular-perivascular” (type 1); “pale” (type 2); “intermediate” (type 3); “dark” (type 4); “undifferentiated” (type 5); and “large-medullary” (type 6). Cells of types 2, 3 and 4 were found throughout the organ. The type-2 to -4 epithelial cells may represent various stages in a differentiation process. In this, type-2 cells are very active and type-4 cells are possibly degenerating elements. Type-4 cells can also contribute to Hassall's corpuscles. Type-5 cells were located mainly in the cortico-medullary region and showed the morphological characteristics of undifferentiated elements. Type-6 cells were located exclusively in the medulla and displayed characteristics of cellular activity. Small Hassall's corpuscles consisted of type-6 epithelial cells; in larger corpuscles many nuclei of type-6 cells were found. Cells of types 2 and 6 contained tubular structures (diameter approximately 20 nm).
Concerning the function of thymus epithelial cells, the features associated with protein synthesis observed in cellular types 2 and 6 make them likely candidates for humoral factor-producing and/or secreting elements. In addition, type-2 and -3 cells in the cortex appear to contribute to a special pattern of epithelium-lymphocyte interaction (“thymic nurse cells”), as demonstrated by the intracytoplasmic location of lymphocytes in the epithelial cells. The various steps in intrathymic T-cell maturation occur at locations in a microenvironment composed of morphologically distinct epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Ito T (1974) Tubular complex of small lymphocytes in lymphatic tissue of the mouse. Arch Histol Jpn 37:133–142.
Arya S, Gilbert EF, Hong R, Bloodworth JMB Jr (1982) The thymus. In: Bloodworth JMB Jr (ed) Endocrine pathology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, chapter 19.
Bearman RM, Levine GD, Bensch KG (1978) The ultrastructure of the normal human thymus: a study of 36 cases. Anat Rec 190:755–781.
Clark SJ Jr (1963) The thymus in mice of strain 129/J, studied with the electron microscope. Am J Anat 112:1–33.
Duijvestijn AM, Hoefsmit EC (1981) Ultrastructure of the rat thymus: the micro-environment of T-lymphocyte maturation. Cell Tissue Res 218:279–292.
Frazier JA (1973) Ultrastructure of the chick thymus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 135:191–205.
Gaudecker B von (1978) Ultrastructure of the age-involuted adult human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 186:507–525.
Gaudecker B von, Müller-Hermelink HK (1980) Ontogeny and organization of the stationary non-lymphoid cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res 207:287–306.
Gelfand EW, Dosch H-M, Shore A, Limatibul S, Lee JWW (1980) The role of the thymus in human T-cell differentiation. In: Gelfand EW, Dosch H-M (eds) The biological basis for immunodeficiency disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 39–56.
Gorgollon P, Ottone-Anaya M (1978) Fine structure of canine thymus. Acta Anat 100:136–152.
Haar JL (1974) Light and electron microscopy of the human fetal thymus. Anat Rec 179:463–476.
Haelst U van (1967) Light and electron microscopic study of the normal and pathological thymus of the rat. I. The normal thymus. Z Zellforsch 77:534–553.
Hay ED, Revel JP (1963) Autoradiographic studies of the origin of the basement lamella in Ambystoma. Dev Biol 7:152–168.
Haynes BF, Shimizu K, Eisenbarth G (1983) Identification of human and rodent thymic epithelium using tetanus toxin and monoclonal antibody A2B5. J Clin Invest 71:9–14.
Hirokawa K (1969) Electron microscopic observation of the human thymus of the fetus and the newborn. Acta Pathol Jpn 19:1–13.
Hirokawa K, McClure JE, Goldstein AL (1982) Age-related changes in localization of thymosin in the human thymus. Thymus 4:19–29.
Hoshino T (1963) Electron microscopic studies of the epithelial reticular cells of the mouse thymus. Z Zellforsch 59:513–529.
Hwang WS, Ho TY, Luk SC, Simon GT (1974) Ultrastructure of the rat thymus. A transmission, scanning electron microscope, and morphometric study. Lab Invest 31:473–487.
Ito T, Hoshino T (1966) Fine structure of the epithelial reticular cells of the medulla of the thymus in the golden hamster. Z Zellforsch 69:311–318.
Janossy G, Bofill M, Trejdosiewicz LK, Chilosi M (1983) Cellular differentiation of lymphoid subpopulations and their microenvironments in the human thymus. In: Müller-Hermelink HK (ed) The thymus: histophysiology and pathology. Springer, Berlin, in press.
Järplid B (1974) Dark reticular cells in the thymus of mice. Acta Radiol 13:319–328.
Kameya T, Watanabe Y (1965) Electron microscopic observations on human thymus and thymoma. Acta Pathol Jpn 15:223–246.
Kater L (1973) A note on Hassall's corpuscles. Contemp Top Immunobiol 2:101–109.
Kater L, Oosterom R, McClure J, Goldstein AL (1979) Presence of thymosin-like factors in human thymic epithelium conditioned medium. Int J Immunopharmaco 1:273–284.
Kendall MD (1980) Avian thymus glands: a review. Dev Comp Immunol 4:191–209.
Kendall MD, Blackett NM (1983) Ultrastructural studies on the thymus gland after administration of phenylhydrazine to bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus). Cell Tissue Res 232:201–219.
Le Douarin NM, Jotereau FV (1981) The ontogeny of the thymus. In: Kendall MD (ed) the thymus gland. Academic Press, London, pp 37–62.
Mandel T (1968) Ultrastructure of epithelial cells in the cortex of guinea pig thymus. Z Zellforsch 92:159–168.
Pereira G, Clermont Y (1971) Distribution of cell web-containing epithelial reticular cells in the rat thymus. Anat Rec 169:613–626.
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212.
Richardson KC, Jarrett L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323.
Ritter MA, Sauvage CA, Cotmore SF (1981) The human thymus micro-environment: in vitro identification of the thymic nurse cells and other antigenetically-distinct subpopulations of epithelial cells. Immunology 44:439–446.
Sato T, Shamoto M (1973) A simple rapid polychrome stain for epoxy embedded tissue. Stain Technol 48:223–227.
Savino W, Santa-Rosa GL (1982) Histophysiology of thymic epithelial reticular cells. Arch Histol Jpn 45:139–144.
Schmitt D, Monier JC, Dardenne M, Pleau JM, Bach JF (1982) Location of FTS (facteur thymique sérique) in the thymus of normal and auto-immune mice. Thymus 4:221–231.
Shier KJ (1981) The thymus according to Schambacher: medullary ducts and reticular epithelium of thymus and thymomas. Cancer 48:1183–1199.
Singh J (1981) The ultrastructure of epithelial reticular cells. In: Kendall MD (ed) The thymus gland. Academic Press, London, pp 133–150.
Wijngaert FP van de, Rademakers LHPM, Schuurman H-J, De Weger RA, Kater L (1983) Identification and in situ localization of the thymic nurse cell in man. J Immunol 130:2348–2351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van de Wijngaert, F.P., Kendall, M.D., Schuurman, HJ. et al. Heterogeneity of epithelial cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res. 237, 227–237 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217140
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217140