Summary
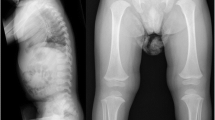
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) type I is a generalized connective tissue disorder, the major manifestations of which are soft, velvety hyperextensible skin and moderately severe joint hypermobility. The gene defect or defects causing EDS type I have not yet been defined, but previous observations suggested that the syndrome may be caused by mutations in the genes for type-I collagen (COL1A1 and COL1A2) or type-III collagen (COL3A1). Here, we performed linkage studies for these three genes in large Azerbaijanian family with EDS type I. Three polymorphisms in the COL3A1 gene, two in the COL1A1 gene, and one in the COL1A2 gene were tested using the polymerase chain reaction. The data obtained excluded linkage of any of the three genes to EDS type I in the family.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arneson MA, Hammerschmidt DE, Furcht LT, King RA (1980) A new form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: fibronectin corrects defective platelet function. JAMA 244:144–151.
Beighton P (1970) The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Heinemann. London.
Byers PH (1989) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. In: Scriber CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. 6th edn. Heinemann, London, pp 2805–2842.
Byers PH, Siegel RC, Holbrook KA, Narayanan AS, Bornstein P, Hall JG (1980) X-linked cutis laxa: defective cross-link formation in collagen due to decreased lysyl oxidase activity. N Engl J Med 303:61–65.
Byers PH, Holbrook KA, Barsh GS (1982) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV: disorders of type III collagen metabolism. In: Akeson WH, Bornstein P, Glimcher MJ (eds) American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons symposium on heritable disorders of connective tissue. Mosby, St Louis, pp 76–81.
Carter C, Wilkinson J (1964) Persistent joint laxity and congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 46:40–43.
Cohn DH, Zhang X (1990) PCR-based linkage strategies for the type I collagen genes. Matrix 10:236.
Cole WG, Chan D, Chambers GW, Walker ID, Bateman JF (1986) Deletion of 24 amino acids from the proα1(I) chain of type I procollagen in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos synd'rome type VII. J Biol Chem 261:5496–5503.
Constantinou CD, Spotila LD, Zhuang J, Sereda L, Hanning C, Prockop DJ (1990) PvuII polymorphisms at the COL1A2 locus. Nucleic Acids Res 18:5577.
Eyre DR, Shapiro FD, Aldridge JF (1985) Heterozygous collagen defect in a variant of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII: evidence for a deleted amino telopeptide domain in the proα2(I) chain. J Biol Chem 260:11322–11329.
Hata R, Kurata S, Shinkai H (1988) Existence of malfunctioning proα2(I) collagen genes in a patient with a proα2(I)-chain-defective variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Eur J Biochem 174:231–237.
Holbrook KA, Byers PH (1982) Structural abnormalities of the dermal collagen and elastin matrix from the skin of patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J Invest Dermatol 79:7–16.
Ihme A, Risteli L, Krieg T, Risteli J, Feldmann U, Juuse K, Müller PK (1983) Biochemical characterization of variants of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VI. Eur J Clin Invest 13:357–362.
Kozlova SI, Prytkov AN, Blinnikova OE, Sultanova FA, Bochgkova DN (1984) Presumed homozygous Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I in a highly inbred kindred. Am J Med Genet 18:763–767.
Kuivaniemi H, Peltonen L, Kivirikko KI (1985) Type IX Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Menkes syndrome: the decrease in lysyl oxidase activity is associated with a corresponding deficiency in the enzyme protein. Am J Hum Genet 37:798–808.
Kuivaniemi H, Kontusaari S, Tromp G, Zhao M, Sabol C, Prockop DJ (1990) Identical G+1 to A mutations in three different introns of the type III procollagen gene (COL3A1) produce different patterns of RNA splicing in three variants of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV. An explanation for exon skipping with some mutations and not others. J Biol Chem 265:12067–12074.
Kuivaniemi H, Tromp G, Prockop DJ (1991) Mutations in collagen genes: causes of rare and some common diseases in man. FASEB J 5:2052–2060.
Kunkel LM, Smith KD, Boyer SH, Borgaonkar DS, Wachtel SS, Miller OJ, Breg WR, Jones HW, Rang JM (1977) Analysis of human Y chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 1245–1249.
Lazoff SG, Rybak JJ, Parker BR, Luzzatty L (1975) Skeletal dysplasia, occipital horns, diarrhea and obstructure uropathy — a new hereditary syndrome. Birth Defects 11:71–74.
Mays PK, Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Prockop DJ (1992) A 15 basepair AT-rich variable number tandem repeat in the type III procollagen gene (COL3A1) as an informative marker for 2q31–2q32.3. Matrix 12 (in press).
Mensing H, Shaeg G (1984) “Composites” — an aberrant structure of the collagen fibril. Dermatologica 168:1–9.
Ott J (1974) Estimation of a recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet 26:588–597.
Pierard GE, Le T, Pierard-Franchimont C, Lapiere CM (1988) Morphometric study of cauliflower collagen fibrils in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I. Coll Relat Res 8:453–457.
Pinnell SR, Krane SM, Kenzora JE, Glimcher MJ (1972) A heritable disorder of connective tissue: hydroxylysine-deficient collagen disease. N Engl J Med 286:1013–1020.
Prytkov AN, Kozlova SI, Sultanova FA, Blinnikova DE, Garkavtsev IV (1984) Genetic analysis of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in a large family tree. Genetika 20:268–273.
Quinn RS, Krane SM (1976) Abnormal properties of collagen lysyl hydroxylase from skin fibroblasts of siblings with hydroxylysine-deficient collagen. J Clin Invest 57:83–93.
Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N (1985) Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354.
Sartoris DJ, Luzzatti L, Weaver DD, Macfarlane JD, Hollister DW, Parker BR (1984) Type IX Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Radiology 152:665–670.
Shamban A, Uitto J (1989) Hereditary diseases of connective tissue. In: Ruiz-Maldonado R, Parish LC, Beare JM (eds) Textbook of pediatric dermatology. Grune & Stratton, Philadelphia, pp 117–141.
Shinkai H, Hirabayashi O, Tamereki A, Matsubayashi S, Seno S (1976) Connective tissue metabolism in cultred fibroblasts of a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I. Arch Dermatol Res 257:113–123.
Sokolov BP, Sher BM, Lomova TY, Kukharenko VI, Blinnikova OI, Kozlova SI, Kalinin VN (1987) Some characteristics of structure and synthesis of procollagens produced by the cultural skin fibroblasts from patients with type I Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol 1:19–23.
Sokolov BP, Sher BM, Kozlov EA, Tsvetkova TA, Rudakov SS, Delvig AA, Kalinin VN (1990) Structural characteristics of collagens from skin and rib cartilage of patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type II. Vopr Med Khim 36:90–93.
Steinmann B, Gitzelmann R, Vogel A, Grant ME, Harwood R, Seou CHJ (1975) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in two siblings with deficient lysyl hydroxylase activity in cultured skin fibroblasts but only mild hydroxylysine deficient skin. Helv Paediatr Acta 30:255–274.
Steinmann B, Tuderman L, Peltonen L, Martin GR, McKusick VA, Prockop DJ (1980) Evidence for a structural mutation of procollagen type I in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem 255:8887–8893.
Stolle CA, Pyeritz RE, Myers JC, Prockop DJ (1985) Synthesis of an altered type III procollagen in a patient with type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J Biol Chem 260:1937–1944.
Superti-Furga A, Gugler E, Gitzelmann R, Steinmann B (1988) A multi-exon deletion in one of the two COL3A1 alleles affecting structure, stability, and processing of type III procollagen. J Biol Chem 263:6226–6232.
Sykes B, Ogilvie D, Wordsworth P, Anderson J, Jones N (1986) Osteogenesis imperfecta is linked to both the type I collagen structural genes. Lancet II: 69–72.
Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Shikata H, Prockop DJ (1989a) A single base mutation that substitutes serine for glycine 790 of the α1(III) chain of type III procollagen causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV. J Biol Chem 264:1349–1352.
Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Stolle C, Pope FM, Prockop DJ (1989b) Single base mutation in the type III procollagen gene that converts the codon for glycine 883 to aspartate in a mild variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV. J Biol Chem 264:19313–19317.
Tromp G, Kleinert C, Kuivaniemi H, Prockop DJ (1991) C to T polymorphism in exon 33 of the COL3A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 19:681.
Tsipouras P, Schwartz RC, Liddel AC, Salkeld CS, Weil D, Ramirez F (1988) Genetic distance of two fibrillar collagen loci, COL3A1 and COL5A2, located on the long arm of human chromosome 2. Genomics 3:275–277.
Vasan NS, Kuivaniemi H, Vogel BE, Minor RR, Wootton JAM, Tromp G, Weksberg R, Prockop DJ (1991) A mutation in the proα2(I) gene (COL1A2) for type I procollagen in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII: evidence suggesting that skipping of exon 6 in RNA splicing may be a common cause of the phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 48:305–317.
Vogel A, Holbrook KA, Steinmann B, Gitzelmann R, Byers PH (1979) Abnormal collagen fibril structure in the gravis form (type I) of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Lab Invest 40:201–206.
Weil D, Bernard M, Combata N, Wirtz MK, Hollister DW, Steinmann B, Ramirez F (1988) Identification of a mutation that causes exon-skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem 263:8561–8564.
Weil D, D'Alessio M, Ramirez F, Wet W de, Cole WG, Chau D, Bateman JF (1989a) A base substitution in the exon of a collagen gene causes alternative splicing and generates a structurally abnormal polypeptide in a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. EMBO J 8:1705–1710.
Weil D, D'Alessio M, Ramirez F, Steinmann B, Wirtz MK, Glanville RW, Hollister DW (1989b) Temperature-dependent expression of a collagen splicing defect in the fibroblasts of a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem 266:16804–16809.
Weil D, D'Alessio M, Ramirez F, Eyre DR (1990) Structural and functional characterization of a splicing mutation in the proα2(I) collagen gene of an Ehlers-Danlos type VII patient. J Biol Chem 265:16007–16011.
Wenstrup RJ, Murad S, Pinnel S (1989) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VI: clinical manifestation of collagen lysyl hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr 115:405–409.
Westerhausen AI, Constantinou CD, Prockop DJ (1990) A sequence polymorphism in the 3′-nontranslated region of the proα1(I) chain of type I procollagen. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4968.
Williams C, Williamson R, Coutelle C, Loeffler F, Smith J, Ivinson A (1988) Same-day, first-trimester antenatal diagnosis for cystic fibrosis by gene amplification. Lancet II:102–103.
Wirtz MK, Glanville RW, Steinmann B, Rao VH, Hollister DW (1987) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB. J Biol Chem 262: 16376–16385.
Zafarullah K, Kleinert C, Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Kontusaari S, Wu Y, Ganguly A, Prockop DJ (1990) G to A polymorphism in exon 31 of the human proα1(III) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res 18:61580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave of absence from Institute of Human Genetics, National Research Center of Medical Genetics, Moskvorechie St., 1. Moscow 115478, USSR
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokolov, B.P., Prytkov, A.N., Tromp, G. et al. Exclusion of COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 genes as candidate genes for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I in one large family. Hum Genet 88, 125–129 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206058
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206058