Summary
-
1.
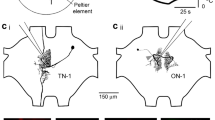
Extracellular HRP injections into the nucleus praeeminentialis dorsalis (NPd) ofApteronotus leptorhynchus retrogradely labeled a population of elec trosensory lateral line lobe (ELL) efferent cells, deep basilar pyramidal cells, that differ morphologically from the previously described basilar and nonbasilar pyramidal cells. These neurons are found deep in the ELL cellular layers; they have small cell bodies and very short sparsely branching apical dendritic trees. The previously described basilar and nonbasilar pyramidal cells are larger, have extensive apical dendrites and are found more superficially.
-
2.
Axon terminals of the deep basilar pyramidal cells were recorded from in the NPd and labeled with lucifer yellow. These NPd afferents have high, regular spontaneous firing rates, and respond tonically to changes in electric organ discharge amplitude.
-
3.
Deep basilar pyramidal cell bodies were recorded from and labeled in the ELL, and these showed the same physiological responses as did the NPd afferent fibers.
-
4.
In addition, basilar pyramidal cells were found which had spontaneous activity patterns and adaptation characteristics intermediate to those typical of the superficial basilar pyramidal cells and the deep basilar pyramidal cells. The size of the pyramidal cells' apical dendritic trees and the placement of their somata within the dorsoventral extent of the ELL cellular layers are highly correlated with the neurons' physiological properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BP :
-
basilar pyramidal cell
- DBP :
-
deep basilar pyramidal cell
- EGp :
-
eminentia granularis posterior
- ELL :
-
electrosensory lateral line lobe
- EOD :
-
electric organ discharge
- GABA :
-
gamma amino butyric acid
- HRP :
-
horseradish peroxidase
- NBP :
-
non basilar pyramidal cell
- NMDA :
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate
- NPd :
-
nucleus praeeminentialis dorsalis
- PSTH :
-
post stimulus time histogram
- TSF :
-
tractus strati fibrosi
References
Bastian J (1981a) Electrolocation I: An analysis of the effects of moving objects and other electrical stimuli on the electroreceptor activity ofApteronotus albifrons. J Comp Physiol 144:465–479
Bastian J (1981b) Electrolocation II: The effects of moving objects and other electrical stimuli on the activities of two categories of posterior lateral line lobe cells inApteronotus albifrons. J Comp Physiol 144:481–494
Bastian J (1986a) Gain control in the electrosensory system mediated by descending inputs to the electrosensory lateral line lobe. J Neurosci 6:553–562
Bastian J (1986b) Gain control in the electrosensory system: a role for the descending projections to the electrosensory lateral line lobe. J Comp Physiol A 158:505–515
Bastian J (1986c) Electrolocation: Behavior, anatomy and physiology. In: Bullock TH, Heiligenberg W (eds) Electroreception. Wiley, New York, pp 577–612
Bastian J (1990) Electroreception. In: Stebbins WC, Berkley MA (eds) Comparative perception, complex signals, vol II. Wiley, New York, pp 35–89
Bastian J, Bratton B (1990) Descending control of electroreception. I. Properties of nucleus praeeminentialis neurons projecting indirectly to the electrosensory lateral line lobe, J Neurosci 10:1226–1240
Bratton B, Bastian J (1990) Descending control of electroreception II: Properties of nucleus praeeminentialis neurons projecting directly to the electrosensory lateral line lobe. J Neurosci 10:1241–1253
Carr CE, Maler L (1986) Electroreception in gymnotiform fish: Central anatomy and physiology. In: Bullock TH, Heiligenberg W (eds) Electroreception. Wiley, New York, pp 319–373
Carr CE, Maler L, Heiligenberg W, Sas E (1981) Laminar organization of the afferent and efferent systems of the torus semicircularis of gymnotiform fish: Morphological substrates for parallel processing in the electrosensory system. J Comp Neurol 203:649–670
Carr CE, Maler L, Sas E (1982) Peripheral and central projections of the electrosensory nerves in gymnotiform fish. J Comp Neurol 211:139–153
Enger PS, Szabo T (1965) Activity of central neurons involved in electroreception in some weakly electric fish (Gymnotidae). J Neurophysiol 28:800–818
Hablitz JJ, Mistry DK (1990) NMDA-evoked outward currents in cultured neocortical neurons using nystatin-perforated patch recordings. Soc Neurosci Abstr 16:1184
Heiligenberg W (1977) Principles of electrolocation and jamming avoidance. In: Braitenberg V (ed) Studies of Brain Function, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–85
Heiligenberg W (1986) Jamming avoidance systems: Model systems for neuroethology. In: Bullock TH, Heiligenberg W (eds) Electroreception. Wiley, New York, pp 613–649
Heiligenberg WH, Dye J (1982) Labelling of electroreceptor afferents in a gymnotoid fish by intracellular injection of HRP: The mystery of multiple maps. J Comp Physiol 148:287–296
Hill RH, Brodin L, Grillner S (1989) Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors augments repolarizing responses in lamprey spinal neurons. Brain Res 499:388–392
Larkman A, Mason A (1990) Correlations between morphology and electrophysiology of pyramidal neurons in slices of rat visual cortex. I. Establishment of cell classes. J Neurosci 10:1407–1414
Maler L (1979) The posterior lateral line lobe of certain gymnotoid fish: Quantitative light microscopy. J Comp Neurol 183:323–364
Maler L, Monoghan D (1989) Distribution of glutamate receptors in the electrosensory system of gymnotiform fish. Soc Neurosci Abstr 15:1135
Maler L, Mugnaini E (1986) Immunohistochemical identification of GABAergic synapses in the electrosensory lateral line lobe of a weakly electric fish (Apteronotus leptorhynchus). Soc Neurosci Abstr 12:312
Maler L, Sas EKB, Rogers J (1981) The cytology of the posterior lateral line lobe of high-frequency weakly electric fish (Gymnotidae): Dendritic differentiation and synaptic specificity in a simple cortex. J Comp Neurol 195:87–139
Maler L, Sas E, Carr C, Matsubara J (1982) Efferent projections of the posterior lateral line lobe in gymnotiform fish. J Comp Neurol 211:154–164
Mason A, Larkman A (1990) Correlations between morphology and electrophysiology of pyramidal neurons in slices of rat visual cortex. II. Electrophysiology. J Neurosci 10:1415–1428
Mathieson WB, Maler L (1988) Morphological and electrophysiological properties of a novel in vitro preparation: The electrosensory lateral line lobe brain slice. J Comp Physiol A 163:489–506
Metcalf WK (1985) Wsensory neuron growth cones comigrate with posterior lateral line lobe primordial cells in zebrafish. J Comp Neurol 238:218–224
Nadi S, Maler L (1987) The laminar distribution of amino acids in the caudal cerebellum and electrosensory lateral line lobe of weakly electric fish (Gymnotidae). Brain Res 425:218–224
Réthelyi M, Szabo T (1973) Neurohistological analysis of the lateral line lobe in a weakly electric fish,Gymnotus carapo (Gymnotidae, Pisces). Exp Brain Res 18:323–339
Sas E, Maler L (1983) The nucleus praeeminentialis: A Golgi study of a feedback center in the electrosensory system of gymnotid fish. J Comp Neurol 221:127–144
Sas E, Maler L (1987) The organization of afferent input to the caudal lobe of the cerebellum of the gymnotid fishApteronotus leptorhynchus. Anat Embryol 177:55–79
Saunders J, Bastian J (1984) The physiology and morphology of two types of electrosensory neurons in the weakly electric fishApteronotus leptorhynchus. J Comp Physiol A 154:199–209
Schwindt PC, Spain WJ, Foehring RC, Stafstrom CE, Chubb MC, Crill WE (1988a) Multiple potassium conductances and their functions in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol 59:424–449
Schwindt PC, Spain WJ, Foehring RC, Chubb MC, Crill WE (1988b) Slow conductances in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro and their role in slow excitability changes. J Neurophysiol 59:450–467
Shumway CA (1990a) Multiple electrosensory maps in the medulla of weakly electric gymnotiform fish. I: Physiological differences. J Neurosci 9:4388–4399
Shumway CA (1990b) Multiple electrosensory maps in the medulla of weakly electric gymnotiform fish. II: Anatomical differences. J Neurosci 9:4400–4415
Shumway CA, Maler L (1989) GABAergic inhibition shapes temporal and spatial response properties of pyramidal cells in the electrosensory lateral line lobe of gymnotiform fish. J Comp Physiol A 164:391–407
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1981) Biometry. W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, pp 114–117
Turner RW, Maler L (1989) Synaptic plasticity in the cerebellar parallel fiber projection to the electrosensory lateral line lobe of gymnotiform fish. Soc Neurosci Abstr 15:1135
Zakon HH (1986) The electroreceptive periphery. In: Bullock TH, Heiligenberg W (eds) Electroreception. Wiley, New York, pp 103–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bastian, J., Courtright, J. Morphological correlates of pyramidal cell adaptation rate in the electrosensory lateral line lobe of weakly electric fish. J Comp Physiol A 168, 393–407 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199600
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199600