Abstract
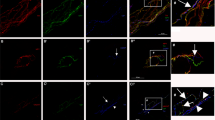
Besides its thermoregulatory role, the sympathetic innervation of the skin is involved in a modulation of sensory processing and trophic functions that has not been fully characterized. To investigate possible sites at which such sympathosensory interactions might occur, a quantitative ultrastructural study of the sympathetic innervation of the skin was attempted. The hairy skin of the guinea pig was studied because the sympathetic and sensory nerve axons in this species can easily be discriminated by the presence of immunoreactivity to the catecholamine-synthesizing enzyme, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). The thermoregulatory role of the sympathetic skin innervation was highlighted by the almost exclusive sympathetic innervation of piloarrector muscles which contained 62% (n = 195) of randomly selected TH-immunoreactive (TH-IR) axon profiles. Of TH-IR pilomotor axons, 53% were filled with vesicles. Vesicle-containing axonal profiles were equally frequent around dermal arterial blood vessels (partly associated with mast cells), hair follicles, and within nerve fibre bundles surrounded by a perineural sheath, in each case accounting for about 3% of all dermal TH-IR axonal profiles. In contrast to piloarrector muscles, at these locations TH-IR (sympathetic) and non-reactive (sensory) axons were found in close association. These findings are in line with the previously reported inhibitory influence of sympathetic stimulation upon hair follicle afferents and perivascular sensory nerve terminals. In addition, they point to a yet underestimated target of sympathetic axon terminals, i. e. preterminal nerve fibre bundles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barasi S, Lynn B (1986) Effects of sympathetic stimulation on mechanoreceptive and nociceptive afferent units from the rabbit pinna. Brain Res 378:21–27
Blennerhassett MG, Bienenstock J (1990) Apparent innervation of rat basophilic leukaemia (RBL-sH3) cells by sympathetic neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett 120:50–54
Blennerhassett MG, Tomioka M, Bienenstock J (1991) Formation of contacts between mast cells and sympathetic neurons in vitro. Cell Tissue Res 265:121–128
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tipins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Coderre TJ, Basbaum AI, Levine JD (1989) Neural control of vascular permeability: interactions between primary afferents, mast cells, and sympathetic efferents. J Neurophysiol 62:48–58
Davies SN (1984) Sympathetic stimulation causes a frequency-dependent excitation and suppression of thermoreceptive cells in the trigeminal nucleus of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 350:22P
Gibbins IL (1990) Target-related patterns of co-existence of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal peptide, enkephalin and substance P in cranial parasympathetic neurons innervating the facial skin and exocrine glands of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 38:541–560
Gibbins IL (1992) Vasoconstrictor, vasodilator and pilomotor pathways in sympathetic ganglia of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 47:657–672
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, MacIntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pig. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
Grundemar L, Håkanson R (1991) Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and C-terminal fragments release histamine from rat peritoneal mast cells. Br J Pharmacol 104:776–778
Hozawa K, Kimura RS (1989) Vestibular sympathetic nervous system in guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 107:171–181
Jänig W, Koltzenburg M (1991) What is the interaction between the sympathetic terminal and the primary afferent fiber? In: Basbaum AI, Besson JM (eds) Towards a new pharmacotherapy of pain. Wiley, Chichester, pp 331–352
Jänig W, Schmidt RE (eds) (1992) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. VCH, Weinheim, Frankfurt
Karanth SS, Springall DR, Kuhn DM, Levene MM, Polak JM (1991) An immunocytochemical study of cutaneous innervation and the distribution of neuropeptides and protein gene product 9.5 in man and commonly employed laboratory animals. Am J Anat 191:369–383
Kawasaki H, Nuki C, Saito A, Takasaki K (1990) Adrenergic modulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-containing nerve-mediated vasodilation in the rat mesenteric resistance vessel. Brain Res 506:287–290
Kummer W, Gleich A (1992) Neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive nerve fibres in guinea-pig hairy skin are of dual (sympathetic and sensory) origin. Neuropeptides 22:38
Kummer W, Gibbins IL, Stefan P, Kapoor V (1990) Catecholamines and catecholamine synthesizing enzymes in guinea-pig sensory ganglia. Cell Tissue Res 261:595–606
Kummer W, Hauser-Kronberger C, Muss WH (1994) Pre-embedding immunohistochemistry in transmission electron microscopy. In: Gu J, Hacker GW (eds) Modern analytical methods in histochemistry. Plenum Press, New York, (in press)
Lassmann G (1977) Lichtmikroskopische Untersuchungen der Innervation der Haut. In: Lassmann G, Jurecka W, Niebauer G (eds) Wiener Symposium: Struktur und Pathologie des Hautnervensystems. Verband der wissenschaftlichen Gesellschaften Österreichs, Wien, pp II/1-II/14
Levine JD, Coderre TJ, Covinsky K, Basbaum AI (1990) Neural influences on synovial mast cell density in rat. J Neurosci Res 26:301–307
Marshall I, Al-Kazwini SJ, Holman JJ, Craig RK (1986) Human and rat α-CGRP but not calcitonin cause mesenteric vasodilation in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 123:217–222
Nilsson BY (1972) Effects of sympathetic stimulation on mechanoreceptors of cat vibrissae. Acta Physiol Scand 85:390–397
Pierce JP, Roberts WJ (1981) Sympathetically induced changes in the responses of guard hair and type II receptors in the cat. J Physiol. (Lond) 314:411–428
Piotrowski W, Foreman JC (1986) Some effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide in human skin and on histamine release. Br J Dermatol 114:37–46
Roberts WJ, Levitt GR (1982) Histochemical evidence for sympathetic innervation of hair receptor afferents in cat skin. J Comp Neurol 210:204–209
Schotzinger RJ, Landis SC (1990) Postnatal development of autonomic and sensory innervation of thoracic hairy skin in the rat. A histochemical, immunocytochemical, and radioenzymatic study. Cell Tissue Res 260:575–587
Schoups AA, Annaert WG, De Potter WP (1990) Presence and subcellular localization of α2-adrenoreceptors in dog splenic nerve. Brain Res 517:308–314
Schreurs J, Seelig T, Schulman H (1986) β2-Adrenergic receptors on peripheral nerves. J Neurochem 46:294–296
Shen GH, Grundemar L, Zukowska-Grojec Z, Håkanson R, Wahlestedt C (1991) C-terminal neuropeptide Y fragments are mast cell-dependent vasodepressor agents. Eur J Pharmacol 204:249–256
Uddman R, Edvinsson L, Jansen I, Stiernholm P, Jensen K, Olesen J, Sundler F (1986) Peptide-containing nerve fibres in human extracranial tissue: a morphological basis for neuropeptide involvement in extracranial pain? Pain 27:391–399
Waris T, Rechardt L (1977) Histochemically demonstrable catecholamines and cholinesterases in nerve fibers of rat dorsal skin. Histochemistry 53:203–216
Zarbin MA, Palacios JM, Wamsley JK, Kuhar MJ (1983) Axonal transport of beta-adrenergic receptors. Antero- and retrogradely transported receptors differ in agonist affinity and nucleotide sensitivity. Mol Pharmacol 24:341–348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth, S., Kummer, W. A quantitative ultrastructural investigation of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive axons in the hairy skin of the guinea pig. Anat Embryol 190, 155–162 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193412
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193412