Abstract
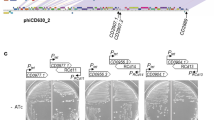
High titered Clostridium sordellii lethal toxin antiserum, cross-reactive with C. difficile cytotoxin B (ToxB), was used to isolate toxB fragments from a C. difficile expression library. Recombinant clones containing toxB fragments of the 5′ and 3′ end were isolate. A 2.5-kb HincII fragment of chromosomal DNA overlaps both groups of clones. A partial restriction map of the total toxB gene is presented. The gene is positioned upstream of utxA and toxA toxB has a size of 6.9kb, corresponding to a 250-kDa polypeptide. A partial sequence of the 5′ end of toxB was determined. The sequence contains 398 bp upstream of toxB with a putative Shine-Dalgarno box (AGGAGA) and 609 bp of the toxB open reading frame. The N-terminal 203 amino acids of ToxB were compared with the N-terminal amino acids of the enterotoxin A (ToxA). A homology of 64% of the residues was detected, which proves the relatedness of ToxA and ToxB of C. difficile.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- ToxA:
-
C. difficile enterotoxin A
- ToxB:
-
C. difficile cytotoxin B
- toxB :
-
gene encoding ToxB
- HT:
-
C. sordellii hemorrhagic toxin
- LT:
-
C. sordellii lethal toxin
References
Bartlett JG, Chang TW, Gurwith M, Gorbach SL, Onderdonk AB (1978) Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med 298:531–534
Chang TW, Gorbach SL, Bartlett JG (1978) Neutralization of Clostridium difficile toxin by Clostridium sordellii antitoxins. Infect Immun 22:418–422
Däubener W, Leiser E, Eichel-Streiber C v, Hadding U (1988) Clostridium difficile toxins A and B inhibit human immune response in vitro. Infect Immun 56:1107–1112
Dove CH, Wang SZ, Price SB, Phelbs CJ, Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD, Johnson JL (1990) Molecular characterization of the Clostridium difficile toxin A gene. Infect Immun 58:480–488
Eichel-Streiber C v, Harperath U, Bosse D, Hadding U (1987) Purification of two high molecular weight toxins of Clostridium difficile which are antigenically related. Microbial Pathogen 2:307–318
Eichel-Streiber C v, Suckau D, Wachter M, Hadding U (1989) Cloning and characterization of overlapping DNA fragments of the toxin A gene of Clostridium difficile. J Gen Microbiol 135:55–64
Eichel-Streiber C v, Laufenberg-Feldmann R, Sauerborn M (1990) The analysis of the Clostridium difficile toxin A reveals the 3′end to be composed of a 2499 bp repetitive structure. Bacterial protein toxins, Fischer, Stuttgart, New York pp 1516–1517
Gill DM (1982) Bacterial toxins: a table of lethal amounts. Microbiol Rev 46:86–94
Johnson JL, Phelps C, Barroso L, Roberts MD, Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD (1990) Cloning and expression of the toxin B gene of Clostridium difficile. Curr Microbiol 20:397–401
Lyerly DM, Carrig PE, Wilkins TD (1989) Nonspecific binding of mouse monoclonal antibodies to Clostridium difficile toxins A and B. Curr Mirobiol 19:303–306
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Meador III J, Tweten RK (1988) Purification and characterization of toxin B from Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun 56:1708–1714
Popoff MR (1987) Purification and characterization of Clostridium sordellii lethal toxin and cross-reactivity with Clostridium difficile cytotoxin. Infect Immun 55:35–43
Pothoulakis C, Barone LM, Ely R, Faris B, Clark ME, Franzblau C, LaMont JT (1986) Purification and properties of Clostridium difficile cytotoxin B. J Biol Chem 261:1316–1321
Rothman SW, Gentry MK, Brown JE, Foret DA, Stone MJ, Strickler MP (1988) Immunochemical and structural similarities in toxin A and toxin B of Clostridium difficile shown by binding to monoclonal antibodies. Toxicon 26:583–599
Sauerborn M, Eichel-Streiber C v (1990) Nucleotide Sequence of Clostridium difficile toxin A. Nucleic Acids Res 18:1629–1630
Schulze J, Eichel-Streiber C v (1990) Cloning and characterization of the Clostridium difficile toxin B gene. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [A] 273:126
Tabor S, Richardson CC (1987) DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4767–4771
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M31mp18 und pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Eichel-Streiber, C., Laufenberg-Feldmann, R., Sartingen, S. et al. Cloning of Clostridium difficile toxin B gene and demonstration of high N-terminal homology between toxin A and B. Med Microbiol Immunol 179, 271–279 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192465
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192465