Abstract
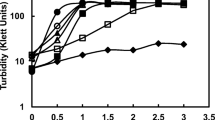
In order to understand the role of the medium osmolality on the metabolism of glumate-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum, effects of saline osmotic upshocks from 0.4 osnol. kg−1 to 2 osmol. kg−1 have been investigated on the growth kinetics and the intracellular content of the bacteria. Addition of a high concentration of NaCl after a few hours of batch culture results in a temporary interruption of the cellular growth. Cell growth resumes after about 1 h but at a specific rate that decreases with increasing medium osmolality. Investigation of the intracellular content showed, during the first 30 min following the shock, a rapid but transient influx of sodium ions. This was followed by a strong accumulation of proline, which rose from 5 to 110 mg/g dry weight at the end of the growth phase. A slight accumulation of intracellular glutamate from 60 to 75 mg/g dry weight was also observed. Accordingly, for Corynebacterium glutamicum an increased osmolality in the glutamate and proline synthesis during the growth phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassit N, Cochet N, Lebeault JM (1993) Influence of water activity on Streptococcus diacetylactis metabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:399–401
Bernard T, Jebbar M, Rassouli Y, Himdi-Kabbab S, Hamelin J, Blanco C (1993) Ectione accumulation and osmotic regulation in Brevibacterium linens. J Gen Microbiol 139:129–136
Csonka LN and Hanson AD (1991) Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol 45:569–606
Dinnbier U, Limpinsel E, Scmid R, Bakker EP (1988) Transient accumulation of potassium glutamate and its replacement by trehalose during adaptation of growing cells Escherichia coli K-12 to elevated sodium chloride concentrations. Arch Microbiol 150:348–357
Frings E, Kunte HJ, Galinski EA (19893) Compatible solutes in representatives of the genera Brevibacterium and Corynebacterium: occurrence of tetrahydropyrimidines and glutamine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 109:25–32
Godel H, Seitz P, Verhoef M (1992) Automated amino acid analysis using combined OPA and FMOC-C1 precolumn derivatization. LC GC Int 5:44–49
Kawahara Y, Ohsumi T, Yoshihara Y Ikeda S (1989) Proline in the osmoregulation of Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Agric Biol Chem 53, 9:2475–2479
Killham K, Firestone MK (1984) Salt stress control of intracellular solutes in Streptomyces indigenous to saline soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:301–306
Krämer R, Graaf A de, Eggeling L, Eikmanns B, Sahm H (1994) Biosynthesis and secretion of amino acids in coryneform bacteria. In: Alberghina L, Frontali L, Sensi P (eds) Procedings of the 6th European Congress in Biotechnology. ELsevier, Amsterdam pp 595–602
Krishna R, Leisinger. (1979) Biosynthesis of proline in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J 181:215–222
Larsson C, Morales C, Gustafsson L, Adler L (1990) Osmoregulation of the salt-tolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii grown in a chemostat at different salinities. J Bacteriol 172:1769–1774
Liebl W, Klamer R, Schleifer KH (1989) Requirements of chelating compounds for the growth of Corynebacterium glutamicum in synthetic media. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:205–210
Marquet M, Uribelarrea JL, Huchenq A, Laneelle G, Goma G (1986) Glutamate excretion by Corynebacterium glutamicum: a study of glutamate accumulation during a fermentation course. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25:220–223
Mondain-Monval F (1988) Ph D thesis, INPL, Nancy
Nagata S, Ogawa Y, Mimura H (1991) Internal cation concentrations of the halotolerant bacterium Brevibacterium sp. in response to the concentrations and species of external salts. J Gen Appl Microbiol 37:403–414
Ohwada T, Sagisaka S (1988) The differential roles of K +, proline and betaine in osmoregulation of Escherichia coli B. Agric Biol Chem 52:313–319
Oren A (1986) Intracellular salt concentrations of the anaerobic eubacteria Haloanaerobium praevalens and Halobacterium halobius. Can J Microbiol 32:4–9
Rod ML, Alam KY, Cunningham PR, Clark DP (1988) Accumulation of trehalose by Escherichia coli K-12 at high osmotic pressure depends on the presence of amber suppressors. J Bacteriol 170:3601–3610
Walter RP, Morris JG, Kell DB (1987) The roles of osmotic stress and water activity in the inhibition of the growth, glycolysis and glucose phosphotransferase system of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Gen Microbiol 133:259–266
Welsh DT, Reed RH, Herbert RA (1991) The role of trehalose in the osmoadaptation of Escherichia coli NCIB 9484: interaction of trehalose, K + and glutamate during osmoadpatation in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol 137:745–750
Whatmore AM, Chudek JA, Reed RH (1990) The effects of osmotic upshock on the intracellular solutes pools of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol 136:2527–2535
Wojcik F (1992) Ph. D. thesis, Orsay, Paris
Yoshinaga F, Tsuchida T, Okumura S (1975) Purification and properties of glutamyl kinases for l-proline and l-glutamine biosynthesis in Brevibacterium flavum. Agric Biol Chem 39:1269–1273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guillouet, S., Engasser, J.M. Sodium and proline accumulation in Corynebacterium glutamicum as a response to an osmotic saline upshock. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 315–320 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172831
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172831