Summary
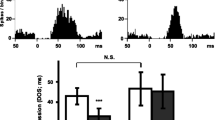
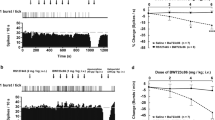
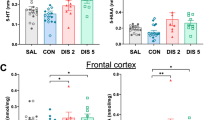
5-HT-containing terminals possess autoreceptors which modulate the release of 5-HT into the synaptic cleft. Tritiated imipramine ([3H]IMI), and more specifically [3H]citalopram and [3H]paroxetine, bind to a site associated with the 5-HT reuptake carrier on the 5-HT terminals. The function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors is decreased following long-term treatment with the 5-HT reuptake blocker citalopram. The present study was undertaken to determine whether an increased synaptic availability of 5-HT or, the occupation of the [3H]IMI site, were responsible for this modification. Unitary extracellular recordings were obtained from CA3 dorsal hippocampus pyramidal neurons under chloral hydrate anesthesia in rats treated daily with fluoxetine (10 mg/kg/day × 14 days), a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, or clorgyline (1 mg/kg/day × 21 days), an inhibitor of type A monoamine oxidase. The function of the terminal 5-HT autoreceptors was assessed by comparing the effectiveness of the electrical stimulation of the ascending 5-HT pathway on the firing activity of hippocampus pyramidal neurons prior to, and following, the administration of methiothepin, an antagonist of the terminal 5-HT autoreceptor, and, by determining the ratio of effectiveness of 0.8 Hz (S1) and 5 Hz (S2) stimulations. Long-term administration of fluoxetine or clorgyline both increased the efficacy of the stimulation of the 5-HT pathway. However, the enhancing effect of methiothepin on the efficacy of the stimulation was attenuated by the fluoxetine, but not by the clorgyline, treatment. The reduction of the function of the terminal 5-HT autoreceptor by the long-term fluoxetine treatment was further indicated by the decreased ratio of effectiveness of the 0.8 and 5 Hz stimulations as compared to that of control rats. To verify that the reuptake blockade per se could not account for the increased synaptic efficacy of 5-HT projections following long-term fluoxetine, the drug was administered acutely to naive rats. It did not increase the efficacy of the stimulation of the 5-HT pathway. Two conclusions are drawn from these results: 1) the increased efficacy of 5-HT synaptic transmission by long-term treatment with antidepressant 5-HT reuptake blockers is not directly due to 5-HT reuptake blockade, but rather, to a reduced function of the terminal 5-HT autoreceptor; 2) the latter phenomenon cannot be ascribed to an increased availability of 5-HT in the synaptic cleft as it was not produced by long-term clorgyline treatment. Hence, these results suggest that long-term occupation of the [3H]IMI site might result in a decreased function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurons. Evidence from single-cell recording studies. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenburg W, Sharman DF, Lagnado JR (eds) Essays in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology. Wiley, New York, pp 1–32
Andrade R, Nicoll RA (1987) Pharmacologically-distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurons of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 394:99–124
Blier P, de Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological investigations on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1275
Blier P, de Montigny C, Tardif D (1984) Effects of two antidepressant drugs mianserin and indalpine on the serotonergic system: single-cell studies in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84:242–249
Blier P, de Montigny C (1985a) Short-term lithium administration enhances serotonergic neurotransmission: Electrophysiological evidence in the rat CNS. Eur J Pharmacol 113:69–77
Blier P, de Montigny C (1985b) Serotoninergic but not noradrenergic neurons in rat central nervous system adapt to long-term treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Neuroscience 16:949–955
Blier P, de Montigny C, Azzaro AJ (1986) Modification of serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission by repeated administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:987–994
Blier P, de Montigny C (1987) Modifications of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone: An electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Synapse 1:470–480
Blier P, de Montigny C, Tardif D (1987) Short-term lithium treatment enhances responsiveness of postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors without altering 5-HT autoreceptor sensitivity: An electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Synapse 1:225–232
Briley M (1985) Imipramine binding: Its relationship with 5-HT reuptake and depression. In: Green AR (ed) Neuropharmacology of serotonin. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 50–78
Brunel S, de Montigny C (1987) Diurnal rhythms in the responsiveness of hippocampal pyramidal neurons to serotonin, norepinephrine, Γ-aminobutyric acid and acetylcholine. Brain Res Bull 18:205–212
Brunel S, de Montigny C (1988) Validation of the I · T50 method for assessing neuronal responsiveness to microiontophoretic applications: A single-cell recording study. J Pharmacol Methods (in press)
Campbell IC, Robinson DS, Lovenburg W, Murphy DL (1979) The effects of chronic regimens of clorgyline and pargyline on monoamine metabolism in the rat brain. J Neurochem 32: 49–55
Chaput Y, Blier P, de Montigny C (1986a) In vivo electrophysiological evidence for the regulatory role of autoreceptors on serotonergic terminals. J Neurosci 6:2796–2801
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1986b) Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: Electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:342–348
de Montigny C, Aghajanian GK (1977) Preferential action of 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-methoxydimethyltryptamine on presynaptic serotonin receptors: A comparative iontophoretic study with LSD and 5-HT. Neuropharmacology 16:811–818
Engel G, Göthert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Galzin AM, Moret C, Verzier B, Langer SZ (1985) Interaction between tricyclic and nontricyclic 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitors and the presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibitory autoreceptors in the rat hypothalamus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:200–211
Graham D, Tahraoui L, Langer SZ (1987) Effect of chronic treatment with selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors and specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitors on [3H]paroxetine binding to cerebral cortical membranes of the rat. Neuropharmacology 26:1087–1092
Habert E, Graham D, Tahraoui L, Claustre Y, Langer SZ (1985) Characterization of [3H]paroxetine binding to rat cortical membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 118:107–114
Hagan RM, Hugues IE (1983) Lack of effect of chronic methiothepin treatment on 5-hydroxytryptamine autoreceptors. Br J Pharmacol 80:513p
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974) Peripheral serotonin antagonists: Failure to antagonize serotonin in brain areas receiving a prominent serotoninergic input. J Neural Transm 35:257–273
Hwang E, Magnussen I, Woert van MH (1980) Effects of chronic fluoxetine administration on serotonin metabolism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 29:79–98
Johnston JP (1968) Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 17:1285–1297
Kandel ER, Spencer WA (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. Afterpotentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol 24:243–259
Langer SZ, Moret C (1982) Citalopram antagonizes the stimulation by lysergic acid diethylamide of presynaptic inhibitory serotonin autoreceptors in the rat hypothalamus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 222:220–226
Largent BL, D'Amato RJ, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (1986) Characterization of serotonin uptake sites with [3H]citalopram and differentiation of multiple [3H]imipramine binding sites. Neurosci Abst 12:224.10
Maura G, Raiteri M (1984) Functional evidence that chronic drugs induce adaptative change of central autoreceptors regulating serotonin release. Eur J Pharmacol 97:309–313
Maura G, Roccatagliata E, Raiteri M (1986) Serotonin autoreceptor in rat hippocampus: Pharmacological characterization as a subtye of the 5-HT1 receptor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 334:323–326
Middlemiss DN (1984) Stercoselective blockade at [3H]5-HT binding sites at the 5-HT autoreceptor by propranolol. Eur J Pharmacol 101:289–293
Moret C (1985) Pharmacology of the serotonin autoreceptor. In: Green AR (ed) Neuropharmacology of serotonin. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 21–49
Offord SJ, Warwick RO (1987) Differential effects of nialamide and clomipramine on serotonin efflux and autoreceptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:593–600
Olpe HR, Schellenburg A (1984) The sensitivity of hippocampal pyramidal neurons to serotonin in vitro: Effect of prolonged treatment with clorgyline or chlorimipramine. J Neural Transm 60:265–271
Palfreyman MG, Mir AK, Kubina M, Middlemis DN, Richards M, Tricklebank MD, Fozard JR (1986) Monoamine receptor sensitivity changes following chronic administration of MDL 72394, a site-directed inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. Eur J Pharmacol 130:73–89
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse 1:3–9
Steinberg S, de Montigny C, Blier P (1987) Electrophysiological assessment of the effect of the serotonin (5-HT) antagonists methiothepin, (−)propranolol and TR 2515 on the somatodendritic 5-HT autoreceptor. Neurosci Abst 12:159.8
Vergé D, Daval G, Patey A, Gozlan H, Elmestikawy S, Hamon M (1985) Presynaptic 5-HT autoreceptors on serotonergic cell bodies and/or dendrites but not terminals are of the 5-HT1A subtype. Eur J Pharmacol 113:463–464
Weissman-Nanopoulous D, Mach E, Magre J, Demassey Y, Pujol JF (1985) Evidence for the localization of 5-HT1A binding sites on serotonin-containing neurons in the raphe dorsalis and raphe centralis nuclei of the rat brain. Neuroscience 17:1061–1072
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Horng JS, Molloy BB (1975) A new selective inhibitor for uptake of serotonin into synaptosomes of rat brain: 3-(p-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-N-methyl-3-phenylpropylamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193:804–811
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Reid LR, Threlkeld PG (1983) Fluoxetine and two other serotonin uptake inhibitors without affinity for neuronal receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 32:1287–1293
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Reid LR, Perry KW (1985) Inhibition of serotonin uptake by optical isomers of fluoxetine. Drug Dev Res 6:397–403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to Claude de Montigny
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blier, P., Chaput, Y. & de Montigny, C. Long-term 5-HT reuptake blockade, but not monoamine oxidase inhibition, decreases the function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors: an electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337, 246–254 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168834
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168834