Abstract
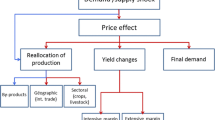
The purpose of this paper is to exemplify a means by which an integrated assessment can be made of global and regional effects on land use of climate change. This is achieved by use of data on the effects of climate change on world food prices as inputs to a regional land use allocation model.
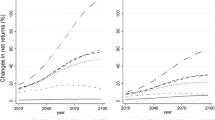
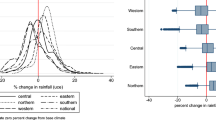
Data on world prices are drawn from a recent global study of climate change and crop yields. In a case study of England and Wales a land allocation model is used to infer changes of land use that are the product of the integrated effect of climate-induced global price changes and climate-related changes of yield in England and Wales. This combination of changed prices and yield potential is used to calculate the land use providing the highest returns for each of 155,235 1 km2 cells of land in England and Wales for a future assumed for the year 2060 (without climate change) and then for that same environment with climate change. The difference between these two is then treated as an estimated effect resulting from climate change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. M., Rosenzweig, C., Peart, R. M., Ritchie, R. T., McCarl, B. A, Glyer, J. D., Curry, R. B., Jones, J. W., Boote, K. J., and Allen, Jr. L. H.: 1990, ‘Global Change and US Agriculture’, Nature 345 (6272), 219–224.
Barr, C. J., Bunce, R. G. H., Clarke, R. T., Fuller, R. M., Furse, M. T., Gillespie, M. K., Groom, G. B., Hallam, C. J., Hornung, M., Howard, D. C., and Ness, M. J.: 1994, Countryside Survey 1990 Main Report, Department of the Environment, London.
Carter, T. R., Parry, M. L., and Porter, J. H.: 1991, ‘Climatic Change and Future Agroclimatic Potential in Europe’, Internat. J. Climatol. 11, 251–269.
FAO: 1991, Agrostat/PC, United Nations, Rome.
Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change: 1990, in Houghton, J. H., Jenkins, G. J., and Ephraums, J. J. (eds.), Climate Change: The IPCC Scientific Assessment, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: 1990, Climate Change 1992 - The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K.
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/World Bank: 1990, World Population Projections, John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore.
Parry, M. L.: 1990, Climate Change and World Agriculture, Earthscan, London.
Rosenzweig, C. and Parry, M. L.: 1994, ‘Potential Impact of Climate Change on World Food Supply’, Nature 367, 133–138.
Rowntree, R. R., Callender, B. A., and Cochrane, J.: 1989, ‘Modelling Climate Change and Some Potential Effects on Agriculture in the UK’, J. Roy. Soc. England 149, 120–126.
UK DoE: 1991, The Potential Effects of Climate Change in the United Kingdom, U.K. Climate Change Impacts Review Group First Report. Department of the Environment, HMSO, London.
United Nations: 1989, World Population Prospects 1988, UN, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parry, M.L., Hossell, J.E., Jones, P.J. et al. Integrating global and regional analyses of the effects of climate change: A case study of land use in England and Wales. Climatic Change 32, 185–198 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143709
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143709