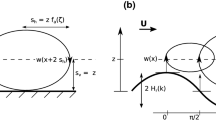
Abstract
The impact of sea waves on sensible heat and momentum fluxes is described. The approach is based on the conservation of heat and momentum in the marine atmospheric surface layer. The experimental fact that the drag coefficient above the sea increases considerably with increasing wind speed, while the exchange coefficient for sensible heat (Stanton number) remains virtually independent of wind speed, is explained by a different balance of the turbulent and the wave-induced parts in the total fluxes of momentum and sensible heat.
Organised motions induced by waves support the wave-induced stress which dominates the surface momentum flux. These organised motions do not contribute to the vertical flux of heat. The heat flux above waves is determined, in part, by the influence of waves upon the turbulence diffusivity.
The turbulence diffusivity is altered by waves in an indirect way. The wave-induced stress dominates the surface flux and decays rapidly with height. Therefore the turbulent stress above waves is no longer constant with height. That changes the balance of the turbulent kinetic energy and of the dissipation rate and, hence the diffusivity.
The dependence of the exchange coefficient for heat on wind speed is usually parameterized in terms of a constant Stanton number. However, an increase of the exchange coefficient with wind speed is not ruled out by field measurements and could be parametrized in terms of a constant temperature roughness length. Because of the large scatter, field data do not allow us to establish the actual dependence. The exchange coefficient for sensible heat, calculated from the model, is virtually independent of wind speed in the range of 3–10 ms-1. For wind speeds above 10 ms-1 an increase of 10% is obtained, which is smaller than that following from the ‘constant roughness length’ parameterization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. J.: 1993, ‘A Study of Wind Stress and Heat Flux Over the Open Ocean by the Inertial-Dissipation Method’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 23, 2153–2161.
Andreas, E. L., Edson, J. B., Monahan, E. C., Rouault, M. R. and Smith, S. D.: 1995, ‘The Spray Contribution to Net Evaporation from the Sea: A Review of Recent Progress’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 72, 3–52.
Belcher, S. E. and Hunt, J. C. R.: 1993, ‘Turbulent Shear Flow Over Slowly Moving Waves’, J. Fluid Mech. 251, 109–148.
Chalikov, D. V. and Belevich, M. Yu.: 1993, ‘One-Dimensional Theory of the Wave Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 63, 65–96.
Chalikov, D. V. and Makin, V. K.: 1991, ‘Models of the Wave Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 56, 83–99.
Charnock, H.: 1955, ‘Wind Stress on a Water Surface’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 639–640.
Caudal, G.: 1993, ‘Self-Consistency between Wind Stress, Wave Spectrum, and Wind-Induced Wave Growth for Fully Rough Air-Sea Interface’, J. Geophys. Res. 98(C12), 22743–22752.
DeCosmo, J.: 1991, ‘Air-Sea Exchange of Momentum, Heat and Water Vapor Over Whitecap Sea States’, Technical Report ONR Grant N00014-85-K-0123, Ph.D. Thesis., University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, p. 212.
DeCosmo, J., Katsaros, K. B., Smith, S. D., Anderson, R. J., Oost, W. A., Bumke, K., and Chadwick, H.: 1996, ‘Air-Sea Exchange of Water Vapor and Sensible Heat: the HEXOS Results’, J. Geophys. Res. in press.
Donelan, M. A.: 1990, ‘Air-Sea Interaction’, in The Sea: Ocean Engineering Science 9, 239–292.
Donelan, M. A. and Pierson, W. J.: 1987, ‘Radar Scattering and Equilibrium Ranges in Wind-Generated Waves with Aplication to Scatterometry’, J. Geophys. Res. 92(C5), 4971–5029.
Donelan, M. A., Hamilton, J., and Hui, W. H.: 1985, ‘Directional Spectra of Wind Generated Waves’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 315, 509–562.
Donelan, M. A., Dobson, F. W., Smith, S. D., and Anderson, R. J.: 1993, ‘On the Dependence of Sea-Surface Roughness on Wave Development’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 23, 2143–2149.
Donelan, M. A., Dobson, F. W., Smith, S. D., and Anderson, R. J.: 1995, ‘Reply’, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 25, 1908–1909.
Fairall, C. W., Kepert, J. D., and Holland, G. J.: 1994, ‘The Effect of Sea Spray on Surface Energy Transports over the Ocean’, The Global Atmos.-Ocean Systems, 2, 121–142.
Friehe, C. A. and Schmitt, K. F.: 1976, ‘Parameterizations of Air-Sea Interface Fluxes of Sensible Heat and Moisture by the Bulk Aerodynamic Formulas’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 6, 801–809.
Garratt, J. R.: 1977, ‘Review of Drag Coefficients Over Oceans and Continents’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 105, 915–929.
Geernaert, G. L.: 1990, ‘Bulk Parameterizations for the Wind Stress and Heat Fluxes’, Surface Waves and Fluxes, Vol. 1, G. L. Geernaert and W. J. Plant, (eds.), Kluwer Academic, 336 pp.
Hasselmann, K.: 1968, ‘Weak-Interaction Theory of Ocean Waves’, Basic Developments in Fluid Dynamics 2, 117–182.
Janssen, P. A. E. M.: 1989, ‘Wave-Induced Stress and the Drag of Air Flow over Sea Waves’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 19, 745–754.
Jones, I. S. F. and Toba, Y.: 1995, ‘Comments on “The Dependence of Sea-Surface Roughness on Wave Development”’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 25, 1905–1907.
Kader, B. A. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1972, ‘Heat and Mass Transfer Laws for Fully Turbulent Wall Flows’, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 15, 2329–2353.
Kitaigorodskii, S. A. and Donelan, M. A.: 1984, ‘Wind-Wave Effects on Gas Transfer’, in Gas Transfer at Air-Water Surface, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 147–170.
Komen, G. J., Cavaleri, L., Donelan, M., Hasselmann, K., and Janssen, P. A. E. M.: 1994, Dynamics and Modelling of Ocean Waves, Cambridge University Press, 540 pp.
Large, W. G. and Pond, S.: 1982, ‘Sensible and Latent Heat Flux Measurements Over the Ocean’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 12, 464–482.
Launder, B. E., Reece, G. J., and Rodi, W.: 1975, ‘Progress in the Development of a Reynolds-Stress Turbulent Closure’, J. Fluid Mech., 68, 537–566.
Liu, W. T., Katsaros, K. B., and Businger, J. A.: 1979, ‘Bulk Parametrization of Air-Sea Exchanges of Heat and Water Vapor Including the Molecular Constrains at the Interface’, J. Atmos. Sci. 36, 1722–1735.
Makin, V. K.: 1987, ‘Wavelike Momentum Fluxes in Boundary Layer Above Sea Waves’, Oceanology 27, 128–132.
Makin, V. K.: 1989, ‘The Dynamics and Structure of the Boundary Layer above Sea’, Senior doctorate thesis, Inst. of Oceanology, Acad. of Sci. USSR, Moscow, 417 pp.
Makin, V. K.: 1990, ‘Deviation of the Mean Wind Speed Profile Above Waves from the Logarithmic Distribution’, Izv. Atmos. Ocean Phys. 26, 322–324.
Makin, V. K. and Chalikov, D. V.: 1986, ‘Calculating Momentum and Energy Fluxes Going into Developing Waves’, Izv. Atmos. Ocean Phys. 22, 1015–1019.
Makin, V. K. and Mastenbroek, C.: 1996, Fluxes of Momentum and Heat Above Waves, in: M. A. Donelan, W. H. Hui, and W. J. Plant (eds.), The Air-Sea Interface, The University of Toronto Press, Toronto.
Makin, V. K., Kudryavtsev, V. N., and Mastenbroek, C.: 1995, ‘Drag of the Sea Surface’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 73, 159–182.
Mastenbroek, C., Makin, V. K., Garat, M. H., and Giovanangeli, J. P.: 1996, ‘Experimental Evidence of the Rapid Distortion of Turbulence in the Air Flow Over Water Waves’, J. Fluid Mech., in press.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971, Statistical Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 1, Cambridge: MIT Press, 769 pp.
Panchenko, E. G. and Chalikov, D. V.: 1984, ‘Energy Structure of the Surface Layer Above the Sea Ws’, Izv. Atmos. Ocean Phys. 20, 1015–1019.
Phillips, O. M.: 1977, Dynamics of the Upper Ocean, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press, 336 pp.
Plant, W. J.: 1982, ‘A Relationship between Wind Stress and Wave Slope’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 1961–1967.
Pond, S., Phelps, G. T., Paquin, J. E., McBean, G., and Stewart, R. W.: 1971, ‘Measurements of the Turbulent Fluxes of Momentum, Moisture and Sensible Heat Over the Ocean’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 901–917.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flannery, B. P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in Fortran: The An of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, 963 pp.
Rodi, W.: 1984, ‘Turbulence Models and their Application in Hydraulics — A State of the Art Review’, Institut fur Hydromechanik, University of Karlsruhe, 2nd ed., Karlsruhe: International Association for Hydraulic Research, 104 pp.
Smith, S. D.: 1980, ‘Wind Stress and Heat Flux Over the Ocean in Gale Force Winds’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 10, 709–726.
Smith, S. D.: 1988, ‘Coefficients for Sea Surface Wind Stress, Heat Flux and Wind Profiles as a Function of Wind Speed and Temperature’, J. Geophys. Res. 93(C12), 15467–15472.
Smith, S. D. and Anderson, R. J.: 1988, ‘Bedford Institute of Oceanography Eddy Flux Measurements During HEXMAX’, in W. A. Oost, S. D. Smith, and K. B. Katsaros (eds.), Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Workshop: Humidity Exchange Over the Sea: Main Experiment (HEXMAX), Analysis and Interpretation, Dellenhove, Epe, The Netherlands, pp. 14–21.
Smith, S. D., Anderson, R. J., Oost, W. A., Kraan, C., Maat, N., DeCosmo, J., Katsaros, K. B., Davidson, K. L., Bumke, K., Hasse, L., and Chadwick, H. M.: 1992, ‘Sea Surface Wind Stress and Drag Coefficients: The HEXOS Results’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 60, 109–142.
Stewart, R. W.: 1961, ‘The Wave Drag of Wind Over Water’, J. FluidMech. 10, 189–194.
Toba, Y, Iida, N., Kawamura, N., and Jones, I. S. F.: 1990, ‘The Wave Dependence of Sea-Surface Wind Stress’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 20, 705–721.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The investigation was in part supported by the Netherlands Geosciences Foundation (GOA) with financial aid from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makin, V.K., Mastenbroek, C. Impact of waves on air-sea exchange of sensible heat and momentum. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 79, 279–300 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00119442
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00119442