Abstract
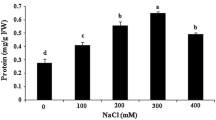
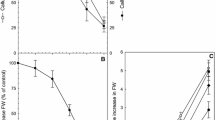
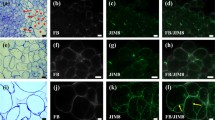
Electron microscopy observations of salt-tolerant embrogenic calli of Citrus limon [(L.) Burm. f.] showed several changes in cell ultrastructure when compared with control calli. Both types of calli comprised clusters of meristematic cells, but salt-tolerant calli had several structural differences: thick cell walls, ring-shaped mitochondria, an increased content of lipid bodies, microbodies and parallel accumulation of rough endoplasmatic reticulum. These structural features seem to be related with salt tolerance in Citrus limon cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Hayyim G & Kochba J (1983) Aspect of salt tolerance in a NaCl selected stable cell line of Citrus sinensis. Plant Physiol. 72: 695–690
Boudier JA, Marchi D, Cataldo C, Massacrier A & Cau P (1981) Origin and fate of autophagic vacuoles in exons and nerve-endings of the rat neurohypophysis. II Relationships with axoplasic reticulum and three dimensional aspects. Biol. Cell. 40: 33–40
Bressan RA, Nelson DE, Iraki NH (1990) Reduced cell expansion and changes in cell walls of plant cells adapted to NaCl. In: Katterman F (Ed) Environmental Injury to Plants (pp 137–139). Academic Press Inc. NY
Button J, Kochba J & Borman CH (1974) Fine structure and embryoid development from embryogenic ovullar callus of ‘Shamouti’ orange (Citrus sinensis Osb). J. Expt. Bot. 25: 446–457
Chandler S & Thorpe TA (1986) Variation from plant tissue cultures: biotechnological application to improving salinity tolerance. Biotechnol. Adv. 4: 157–164
Diaz de Leon JL, Soto H, Merchant MT & Diaz de León L (1982) Biochemical and ultrastructural changes induced by NaCl in cell cultures derived from Bouvardia ternifolia. In: San Pietro A (Ed) Biosaline Research (pp 461–466). Plenum, New York
Dutta PC, Applequist L, Gunnarsson L & Von Hofsten S (1991) Lipid bodies in tissue culture, somatic and zygotic embryo of Daucus carota L.: a qualitative and quantitative study. Plant. Sci. 78: 215–221
Dutta Gupta S, Joshi PA, Hovanesian JC & Conger BV (1992) Ultrastructural characterization of somatic embryos regenerated from NaCl selected and nonselected calli of Dactylis glomerata. Protoplasma 170: 177–185
Ericson JLE (1969) Studies on induced cellular autophagy I. Electron microscopy of cells with in vivo labelled lysosomes. Exp. Cell. Res. 55: 95–106
Fransz PF & Schell JHN (1991) An ultrastructural study of the early development of somatic embryos in maize. Can. J. Bot. 69: 858–865
Halperin W & Jensen WA (1967) Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J. Ultrastructal. Res. 18: 428–443
Hecht-Buchholz C (1983) Light and electron microscopy investigations of the reaction of various genotypes to nutritional disorders. Plant Soil 72: 151–165
Huang CX & van Stevenick RFM (1990) Salinity induced structural changes in meristematic cells of barley roots. New. Phytol. 115: 17–22
Konar RN, Thomas E & Street HE (1986) Origin and structure of embryoids arising from epidermal cells of the stem of Ranunculus sceleratus L. J. Cell Biol. 11: 77–93
Kramer D (1983) Genetically determined adaptations in roots to nutritional stress: correlation of structure and function. Plant Soil 72: 167–173
Kramer D (1984) Cytological aspects of salt tolerance in higher plants. In: Staples RC & Toeniessen GH (Eds) Salinity Tolerance in Plants. Strategies for Crop Improvement (pp 3–15). John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York
Leedale GF, Buetow DE (1976) Observations on cytolysome formation and other cytological phenomena in carbon-starved Euglena gracillis. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell. 25: 149–154
Mesquita F (1972) Ultrastructure de formations comparables aux vacuoles autophagiques dans les cellules des racines de Alium cepa et du Lupinus albus. Cytologie 37: 95–110
Nazarenko LV & Serebryakova VN (1990) Ultrastructural changes in Euglena cells of different nutritional types under the influence of salinity. Sov. Plant Physiol. 76: 142–146
Newcomb W & Wetherell DF (1970) The effects of 2,4,6-trichorophenoxyacetic acid on embryogenesis in wild carrot tissue cultures. Bot. Gaz. 131: 242–245
Nymann LP, Walter RJ, Donovan RD, Berns MV & Arditti J (1987) Effects of artificial seawater on the ultrastructure and morphometry of taro (Colocasia esculenta) cells in vitro. Environ. Expt. Bot. 27: 245–252
Piqueras A & Hellín E (1990) Somatic embryogenesis in Citrus limon. A simple reproducible model for developmental studies in woody plants, In: Puigdomenech P & Nelson T (Eds) Approaches to Plant Development (p 67). Fundación J. March, Madrid
Piqueras A & Hellín E (1992) Selección y caracterización de una línea cellular de limonero (C. limon), tolerante a estrés salino. Suelo y Planta 2: 629–640
Poljakoff-Mayber A (1981) Ultrastructural consequences of drought. In: Paleg LG & Aspinall D (Eds) The Physiology and Biochemistry of Drought Resistance in Plants (pp 389–403). Academic Press. NY
Profumo P, Gastaldo P & Rascio N (1987) Ultrastructural study of different types of callus from leaf explants of Aesculus hipposcastanum L. Protoplasma 138: 89–97
Ramagopal S (1988) Regulation of protein synthesis in root, shoot and embryonic tissues of germinating barley during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ. 11: 501–515
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17: 208–212
Seltzer R, Laüchli A & Kramer D (1975) Interzellulare transportwerge des chlorids in wurzeln intakter gerstepflanzen. Cytobiologie 10: 449–457
Sing NK, LaRosa ChP, Handa AK & Hasegawa PM (1989) Reduced growth rate and changes in cell wall protein in plant cells adapted to NaCl. In: Cherry JH (Ed) Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms Associated with Environmental Stress Tolerance in Plants (pp 173–194). NATO ASI series, Vol G19. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Smith MM, Hodson MJ, Opik H & Wainwright SJ (1982) Salt-induced ultrastructural damage to mitochondria in root tips of a salt sensitive ecotype of Agrostis stolonifera. J. Expt. Bot. 33: 886–895
Spuit AR (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastr. Res. 26: 31–43
Van Steveninck RFM, Van Steveninck ME, Hall TA & Peters PD (1974) X-ray microanalysis and distribution of halides in Nitella transucens. In: Saunders JV & Goodchild DJ (Eds) Electron Microscopy. Vol 2 (pp 602–603). Australian Academy of Sciences, Canberra
Valadimirova MG (1976) Changes of ultrastructural organization during functional reorganization of the cell in Chlorella sp. Fiziol. Rast 23(6): 1180–1185
Whatley JM & Whatley FR (1987) When is a chromoplast? New Phytol. 106: 667–678
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piqueras, A., Olmos, E. & Hellín, E. Cytological changes related with salt tolerance in embryogenic callus of Citrus limon . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 39, 13–18 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037586
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037586