Abstract
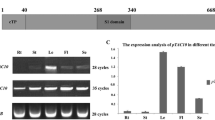
Porphobilinogen deaminase (PBG deaminase) is an early enzyme of the pathway for chlorophyll and heme synthesis. Using degenerate oligonucleotide primers, based on amino acid sequence data for purified PBG deaminase from pea, a fragment was amplified from Arabidopsis genomic DNA by PCR, and then used to isolate both a cDNA and a genomic clone for PBG deaminase from Arabidopsis. The cDNA, shown to be full-length by primer extension, encodes a precursor protein of 382 residues, which can be imported into isolated chloroplasts and processed to the mature size. The genomic clone encodes an identical sequence to the cDNA, except for the presence of four introns within the coding region of the mature protein, and 1.7 kb of upstream sequence. There is no obvious TATA box within 50 bp of the transcription start. Southern blot analysis suggests that PBG deaminase is encoded by a single gene in the Arabidopsis genome, and RNase protection experiments demonstrated that this gene is expressed in both leaves and roots. These results support the conclusion that there is only one form of PBG deaminase in all plant cells, which is located in the plastid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel, FM, Brent, R, Kingston, RE, Moore, DD, Seidman, JG, Smith, JA, Struhl, K: Short Protocols in Molecular Biology, pp. 154–155. John Wiley, New York (1989).
Battersby, AR: Biosynthesis of the pigments of life. J Nat Prod 51: 629–642 (1988).
Beale, SI, Weinstein, J: tetrapyrrole metabolism in photosynthetic organisms. In: Dailey, HA (ed) Biosynthesis of Heme and Chlorophylls, pp. 297–391. McGraw-Hill, New York (1990).
Beaumont, C, Porcher, C, Picat, C, Nordman, Y, Grandchamp B: The mouse porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Structural organization, sequence, and transcriptional analysis. J Biol Chem 264: 14829–14834 (1989).
Cavener, DR, Ray, SC: Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucl Acids Res 19: 3185–3192 (1991).
Chomczynski, P, Sacchi, N: Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate phenol chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159 (1987).
Chretien, S, Dubart, A, Beaupain, D, Raich, N, Grandchamp B, Rosa, J, Goossens, M, Romeo, P-H: Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in house-keeping expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6–10 (1988).
Cohen, Y, Steppuhn, J, Herrmann, RG, Yalovsky, S, Nechushtai, R: Insertion and assembly of the precursor of subunit II into the photosystem I complex may precede its processing. EMBO J 11: 79–85 (1992).
Corden, J, Wasylyk, B, Buchwaler, A, Sassone-Corsi, P, Kedinger, C, Chambon, P: Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science 209: 1406–1414 (1980).
Dean, C, Tamaki, S, Dunsmuir, P, Favreau, M, Katayama C, Dooner, H, Bedbrook, J: Messenger-RNA transcripts of several plant genes are polyadenylated at multiple sites in vivo. Nucl Acids Res 14: 2229–2240 (1986).
Devereux, J, Haeberli, P, Smithies, O: A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1984).
Elder, GH: Acquired disorders of haem synthesis. Essays Med Biochem 2: 75–114 (1976).
Feinberg, AP, Vogelstein, B: A technique for radiolabelling restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1983).
Gavel, Y, vonHeijne, G: A conserved cleavage-site motif in chloroplast transit peptides. FEBS Lett 61: 455–458 (1990).
Huynh, TV, Young, RA, Davis, RW: Constructing and screening cDNA libraries in λgt10 and λgt11. In: Glover DM (ed) DNA Cloning: A Practical Approach, vol 1, pp. 49–78 IRL Press, Oxford (1985).
Jones, RM, Jordan, PM: Purification and properties of porphobilinogen deaminase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 299: 895–902 (1994).
Madueño, F, Napier, JA, Gray, JC: Newly imported Rieske iron-sulfur protein associates with both Cpn60 and Hsp70 in the chloroplast stroma. Plant Cell 5: 1865–1876 (1993).
Pruitt, R, Meyerowitz, E: Characterization of the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Mol Biol 187: 169–183 (1986).
Sambrook, J, Fritsch, EF, Maniatis, T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Shashidhara, LS, Lim, SH, Shackleton, JB, Robinson, C, Smith, AG: Protein targeting across the three membranes of the Euglena chloroplast envelope. J Biol Chem 267: 12885–12891 (1992).
Smith, AG: Enzymes for chlorophyll synthesis in developing peas. In: Akoyunoglou, G, Senger, H (eds) Regulation of Chloroplast Differentiation, pp. 49–54. Alan R. Liss, New York (1986).
Smith, AG: Subcellular localization of two porphyrinsynthesis enzymes in Pisum sativum (pea) and Arum (cuckoo-pint) species. Biochem J 249: 423–428 (1988).
Smith, AG, Marsh, O, Elder, G: Investigation of the subcellular location of the tetrapyrrole biosynthesis enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase in higher plants. Biochem J 292: 503–508 (1993).
Smith AG, Santana MA, Wallace-Cook ADM, Roper J, Labbe-Bois R: Isolation of a cDNA encoding chloroplast ferrochelatase from Arabidopsis thaliana, by functional complementation of a yeast mutant. J Biol Chem, in press (1994).
Witty, M, Wallace-Cook, ADM, Albrecht, H, Spano, AJ, Michel, H, Shabanowitz, J, Hunt, DF, Timko, MP, Smith AG: Structure and expression of chloroplast-localized porphobilinogen deaminase from pea (Pisum sativum L.) isolated by redundant polymerase chain reaction. Plant Physiol 103: 139–147 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, S.H., Witty, M., Wallace-Cook, A.D.M. et al. Porphobilinogen deaminase is encoded by a single gene in Arabidopsis thaliana and is targeted to the chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 26, 863–872 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028854
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028854