Abstract
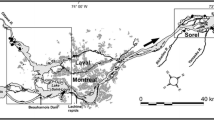
Longitudinal variations of phytoplankton biomass and composition were assessed in a 250 km-long section of the St.Lawrence River, which alternately runs through narrow (< 2 km) river cross sections and wide (up to 10 km) fluvial lakes. In the main river stem, concentrations of suspended matter and total phosphorus increased with distance downstream, whereas light penetration decreased. Seasonal changes in plankton composition and biomass were more important than those resulting from differences in water mass (tributary) of origin. Sampling at three cross river sections and in two fluvial lakes showed a progressive downstream decrease in phytoplankton biomass and changes in size structure and taxonomic composition. River plankton was primarily composed of small (< 10 µm equivalent spherical diameter), truly planktonic cells belonging to Cryptophyceae and diatoms, with Chlorophyceae in summer. Plankton sampled in summer among rooted macrophytes in fluvial lakes exhibited a higher biomass of resuspended periphytic algae than in the main river stem, which contributed slightly to downstream phytoplankton biomass.
Successive river cross sections always shared about 50% of their taxa, indicating a rapid downstream transport of algae within the main water mass. However, the proportion of species common to all cross sections was highest during the spring freshet, and lowest during summer low discharge, likely resulting from the development of a distinct flora in fluvial lakes during summer. Conversely, about 30% of the identified taxa were exclusive to a cross section and were replaced by others occurring downstream. Overall, phytoplankton composition along the St.Lawrence River is primarily controlled by advective forces, which result in a homogeneous flora in the main river stem, with a local contribution of resuspended periphyton from fluvial lakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A., A. Chodorowski & P. Legendre, 1974. Studies of the effects of pollution on the diatom communities of the St.Lawrence River near Montreal. Proc. 9th Can. Symp. Water Pollut. Res. 135–141.
Alaerts-Smeesters, E. & E. Magnin, 1973. Étude préliminaire du phytoplancton du Lac Saint-Louis, élargissement du fleuve Saint-Laurent près de Montréal, Québec. Can. J. Bot. 52: 489–501.
Allan, R. J., 1986. The limnological units of the Lower Great Lakes —St. Lawrence River corridor and their role in the source and aquatic fate of toxic contaminants. Water Pollut. Res. Can. 21: 168–186.
Baker, A. L. & K. K. Baker, 1979. Effects of temperature and current discharge on the concentration and photosynthetic activity of the phytoplankton in the upper Mississippi River. Freshwat. Biol. 9: 191–198.
Bertrand, N. & W. F. Vincent, 1994. Structure and dynamics of photosynthetic picoplankton across the saltwater transition zone of the St-Lawrence River. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51: 161–171.
Bonetto, A. A., 1986. The Paraná River system. In B. R. Davies & K. F. Walker (eds), The ecology of river systems. Dr W. Junk Publishers: 541–555.
Bourelly, P., 1972. Les algues d'eau douce, Initiation à la systématique. Tome I : Les Algues vertes. N. Boubées & Cie éd. Paris. 572 pp.
Bourelly, P., 1981. Les algues d'eau douse, Initiation á la systématique. Tome 11: Les Algues jaunes et brunes Chrysophycées, Phéophycées, Xanthophycées et Diatomées. Boubées & Cie éd. Paris. 515 pp.
Bourelly, P., 1985. Les algues d'eau douse, Initiation á la systématique. Tome III: Les Algues bleues et rouges Les Eugléniens, Péridiniens et Cryptomonadines. N. Boubées & Cie éd. Paris. 606 pp.
Bourelly, P., 1988. Compléments les algues d'eau douse, Initiation á la systématique. Tome I ; les Algues Vertes. Paris. Boubées & Cie éd. 182 pp.
Canadian Hydrographic Service, 1993. Bathymetric charts. St.Lawrence River. Dept. of Fisheries and Oceans.
Cardinal, A., 1961. Etude des variations saisonnière du phytoplancton du Lac Saint-François. M.Sc. thesis, Université de Montreal, Montreal, Quebec. 77 pp.
Cattaneo, A., 1987. Periphyton in lakes of different trophy. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 44: 296–303.
Cloern, J. E., 1987. Turbidity as a control on phytoplankon biomass and productivity in estuaries. Cont. Shelf Res. 7: 1367–1381.
Cluis, D., G. Bourgeault, C. Laberge, C. Guimont & D. Potvin, 1990. Analyse statlstique des données de qualité de l' eau du fleuve Saint-Laurent (1978–1988). INRS-Eau, Rapport Scientifique No. 289.
Contant, H. & E. Lacoursière, 1978. Contribution á l'étude quantitative du phytoplancton du fleuve Saint-Laurent aux environs du Complexe nucléaire de Gentilly. Groupe Thermopol, Dép. de Biologie, Universite du Quebec a Trois-Rivières, Canada. 85 pp.
del Giorgio, P. A., A. L. Vinocur, R. J. Lombardo & H. G. Tell, 1991. Progressive changes in the structure and dynamics of the phytoplankton community along a pollution gradient in a lowland river — a multivariate approach. Hydrobiologia 224: 129–154.
Descy, J.-P., 1987. Phytoplankron composition and dynamics in the river Meuse (Belgium). Arch. Hydrobiol. 78: 225–245.
De Sève, M. A. & M. E. Goldstein, 1981. The structure and composition of epilithic diatom communities of the St.Lawrence and Des Outaouais Rivers in the Montreal area. Can. J. Bot. 59: 377–387.
Désilets, L. & C. Langlois, 1989. Variabilité spatiale et saisonnière de la qualité de l'eau du fleuve Saint-Laurent, Centre Saint-Laurent, Environnement Canada, Montreal. 112 pp.
Environment Canada, 1993. Manuel des méthodes d'analyse (Annexes B). Laboratoire régional -Région du Québec Section d'écotoxicologie et de chimie environnementale, Centre SaintLaurent, Montréal, Canada.
Environment Canada, 1994. Daily flow values for the St.Lawrence and Ottawa Rivers. Hydrology section, Atmospheric Environment Service, Quebec Region, Montreal, Canada.
Findlay, D. L. & H. J. Kling, 1979. A species list and pictorial reference to the phytoplankton of Central and Northern Canada — Part I & Il. Fish. Mar. Serv. Man. Rep. 1503. Western Region, Fisheries and Marine Service, Department of Fisheries and the Environment. Winnipeg. 619 pp.
Frenette, J.-J., W. F. Vincent, J. J. Dodson & C. Lovejoy, 1995. Sizedependent variations in phytoplankton and protozoan community structure across the St.Lawrence River transition region. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 129: 99–110.
Germain, H., 1981. Flore des Diatomées, Diatomophycdes. Eaux douces et saumâtres du Massif Armoricain et des contrées voisines d'Europes occidentale. Société Nouvelle des Éditions Boubée, Paris. 444 pp. Glooschenko, W. A., J. E. Moore & R. A. Vollenweider, 1972. The seasonal cycle of pheopigments in Lake Ontario with particular emphasis on the role of zooplankton grazing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17:597–605.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970. The ecology of running waters. University of Toronto Press. Toronto, Canada. 555 pp.
Irénée-Marie, F. l. C., 1938. Flore Desmidiale de la région de Montréal. Presse de l'Université de Montréal. 547 pp.
Jones, R. I. & R. J. Barrington, 1985. A study of the suspended algae in the river Derwent, Derbyshire, U.K. Hydrobiologia 128: 255–264.
Lack, T. J., 1971. Quantitative studies on the phytoplankton of the rivers Thames and Kennet at Reading. Freshwat. Biol. 1: 213–224.
Lewis, W. M. Jr., 1988. Primary production in the Orinoco river. Ecology 69: 679–692.
Lorenzen, C. J., 1967. Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments; Spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12: 343–346.
Lund, J. W. G., C. Kipling & E. D. LeCren, 1958. The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimating by counting. Hydrobiologia 11: 143–170.
Mills, E. L. & J. L. Forney, 1982. Response of Lake Ontario plankton entering the international section of the St. Lawrence River. Int. Revue Ges. Hydrobiol. 67: 27–43.
Mills, E. L., S. B. Smith & J. L. Forney, 1981. The St.Lawrence River in winter: population structure, biomass and pattern of its primary and secondary food web components. Hydrobiologia 79: 65–75.
Moore, J. W., 1976. Seasonal succession of algae in rivers. I. Examples from the Avon, a large slow-flowing river. J. Phycol. 12: 342–349.
Moss, B. & H. Balls. 1989. Phytoplankton distribution in a floodplain lake and river system. II. Seasonal changes in the phytoplankton communities and their control by hydrology and nutrient availability. J. Plankton Res. 11: 839–867.
Munawar, M. & I. F. Munawar, 1986. The seasonality of phytoplankton in the North American Great Lakes, a comparative synthesis. Hydrobiologia 138: 85–115.
Munawar, M., I. F. Munawar & L. H. McCarthy, 1987. Phytoplankton ecology of large eutrophic and oligotrophic lakes of North America: Lakes Ontario and Superior. Arch. Hydrobiol. 25: 51–96.
Painchaud, J., J.-C. Therriault & L. Legendre, 1993. Repartition et variabilitd de la chlorophylle et des bactéries de l'estuaire fluvial du Saint-Laurent. Abstract presented at the Association Canadienne Française pour l'Avancement des Sciences meeting (ACFAS), Rimouski.
Paquet, S., V. Jarry & C. Hudon, 1995. Phytoplankton species composition in the St.Lawrence River. Proc. XVIth SIL Congress, 23–29 July 1995, Sao Paulo, Brazil (in press).
Peterson, C. G. & R. J. Stevenson. 1989. Seasonality in river phytoplankton: multivariate analyses of data from the Ohio river and six Kentucky tributaries. Hydrobiologia 182: 99–114.
Prescott, G. W., 1951. Algae of the Western Great Lakes area. Otto Koeltz Science Publishers. Koenigstein. 977 pp.
Provencher, M., 1976. Étude du périphyton et du phytoplancton de la voie maritime du Saint-Laurent. La production primaire phase 1. Le comité d'étude du fleuve Saint-Laurent. 65 pp.
Provencher M., 1977. Étude du phytoplancton du fleuve Saint-Laurent et de ses tributarres. Rapport technique no 9. Comité d'étude sur le fleuve Saint-Laurent. 270 pp.
Reynolds, C. S., 1994. The long, the short and the stalled: on the attributes of phytoplankton selected by physical mixing in lakes and rivers. Hydrobiologia 289: 9–21.
Roche & Associés, 1982. Etudes des communautés planctoniques du Lac Saint-Louis et du Bassin de La Prairie. Projet Lachine. Rapport Final. Rapport prepare pour Hydro-Quebec, Direction de l'environnement. 173 pp.
Rojo, C., M. Alvarez Cobelas & M. Arauzo, 1994. An elementary, structural analysis of river phytoplankton. Hydrobiol. 289: 43–55.
Rondeau, B., 1993. Qualité des eaux du fleuve Saint-Laurent 1985–1990. Tronçon Cornwall-Quebec. Centre Saint-Laurent. Environnement Canada. 150 pp.
Shannon, C. & W. Weaver, 1949. The mathematical theory of communication. University & Illinois Press, Urbana.
Simard, N., 1994. Structure et dynamique de la communauté phytoplanctonique de l' estuaire fluvial du Saint-Laurent (Qúebec). M.Sc. thesis, Universite Laval, Quebec. 85 pp.
Stevenson, R. J. & K. D. White, 1995. A comparison of natural and human determinants of phytoplankton communities in the Kentucky River basin, USA. Hydrobiologia 297: 201–216.
Swale, E. M. F., 1969. Phytoplankton in two English rivers. J. Ecol. 57: 1–23.
Swanson, C. D. & R. W. Bachmann, 1976. A model of algal exports in some Iowa streams. Ecology 57: 1076–1080.
Sylvestre, A., K. W. Kuntz & N. D. Warry, 1987. Qualité de l' eau à son entrée dans le fleuve Saint-Laurent, de 1977 à 1983. Technical Report No. 142. Inland Waters Directorate, Environment Canada, Burlington. 60 pp.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1986. Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67: 1167–1179.
Vollenweider, R. A., M. Munawar & P. Stadelmann, 1974. A comparative review of phytoplankton and primary production in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Fisheries Res. Board Can. 31: 739–762.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. E. Likens, 1991. Limnological analyses, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 391 pp.
Wetzel, R. G., 1983, Limnology, 2nd edn. Saunders College Publishing ed. Chicago. 767 pp.
Whitton, B. A., 1975. River Ecology. In B.A. Whitton (ed.), University of California Press. Berkeley. 725 pp.
Williams, L. G. & C. Scott, 1962. Principal diatoms of major waterways of the United States. Limnol. Oceanogr. 7: 365–379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hudon, C., Paquet, S. & Jarry, V. Downstream variations of phytoplankton in the St.Lawrence River (Québec, Canada). Hydrobiologia 337, 11–26 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028503
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028503