Summary
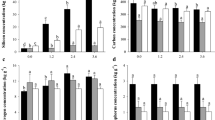
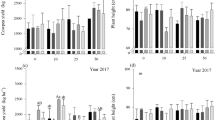
The concentrations of several N fractions, soluble sugars and N/S ratios were determined in Golden Bantam sweet corn and hybrid field corn grown in nutrient solutions and/or soil with various SO4-S levels provided. When the level of SO4-S supplied was less than that needed for maximum growth, higher-than-normal concentrations of amide (asparagine) N and lower-than-normal soluble sugar concentrations were found in the plants. An inadequate S supply appears to limit the plants capacity to synthesize protein to a much greater extent than it inhibits the nitrogen uptake mechanism.
Total N/total S ratios (grammole basis) varying from over 100 to less than 15 were found in plants grown with different levels of sulfate supplied. When SO4-N, NO3-N, and the large amount of amide-N which accumulates under conditions of S deficiency are excluded, the ratio in young corn plants is generally between 22–50. The precision of the N/S ratio as an indicator of S adequacy for growing crops might be improved by a better understanding of the nature of the forms in which N and S occur in plants, and the effects of soil and plant factors other than S level. The percentage of amide-N shows promise as an indicator of S nutrient status. Data available indicates that added S will increase yields of corn plants if their amide-N level exceeds 500 ppm. Amide-N concentration correlates with N/S ratios, and it is much more readily determined than the latter. Its usefulness as a S nutrition indicator should be checked under field conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, C. A. and Sheard, R. W., Alterations in the nitrogen metabolism of Medicago sativa and Dactylis glomerata as influenced by potassium and sulfur nutrition. Can. J. Plant Sci. 46, 671–680 (1966).
Allaway, W. H. and Thompson, J. F., Sulfur in the nutrition of plants and animals. Soil Sci. 101, 204–247 (1966).
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 9th Ed. Washington, D.C. (1960).
Barrien, B. S. and Wood, J. G., Studies on the sulphur metabolism of plants II. The effect of nitrogen supply on the amounts of protein sulphur, sulphate sulphur, and on the value of the ratio of protein nitrogen to protein sulphur at different stages during the life cycle of the plant. New Phytologist 38, 257–264 (1939).
Baszynski, T., Brand, J., Barr, R., Krogman, D. W. and Crane, F. L., Some biochemical characteristics of chloroplasts from mineral-deficient maize. Plant Physiol. 50, 410–411 (1972).
Caldwell, A. C., Seim, E. C. and Rehn, G. W., Sulfur effects on the elemental composition of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and corn (Zea Mays L.). Agron. J. 61, 632–634 (1969).
Coic, Y., Fancouneau, G., Pion, R., Lesaint, C. and Godefroy, S., Influence de la deficience en soufre sur l'absorption des substances minerales et le metabolisme de l'azote et des acides organiques chez l'orge. Ann. Physiol. Veg. 4, 295–306 (1962).
Daigger, L. A. and Fox, R. L., Nitrogen and sulfur nutrition of sweet corn in relation to fertilization and water composition. Agron. J. 63, 729–730 (1971).
Dijkshoorn, W., Lampe, J. E. M. and van Burg, P. J. F., A method of diagnosing the sulfur nutrition status of herbage. Plant and Soil 13, 227–241 (1960).
Dijkshoorn, W. and van Wijk, A. L., The sulphur requirements of plants as evidenced by the sulfur-nitrogen ratio in the organic matter. A review of published data. Plant and Soil 26, 129–157 (1967).
Ergle, D. R. and Eaton, F. M., Sulfur nutrition of cotton. Plant Physiol. 26, 639–645 (1951).
Hall, J. D., Barr, R., Al-Abbas, A. H. and Crane, F. L., The ultrastructure of chloroplasts in mineral-deficient maize leaves. Plant Physiol. 50, 404–409 (1972).
Hanson, E. A., Barrien, B. S. and Wood, J. G., Relations between protein-nitrogen, protein-sulphur and chlorophyll in leaves of sudan grass. Australian J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 19, 231–234 (1941).
Johnson, C. M. and Nishita, H., Microestimation of sulfur in plant materials, soils and irrigation water. Anal. Chem. 24, 736–742 (1952).
Johnson, C. M., Stout, P. R., Broyer, T. C. and Carlton, A. B., Comparative chlorine requirements of different plant species. Plant and Soil 8, 337–353 (1957).
Jones, R. K., Robinson, P. J., Haydock, K. P. and Megarrity, R. G., Sulphurnitrogen relationships in the tropical legume Stylosanthes Humilis. Australian J. Agric. Research 22, 885–894 (1971).
Kemper, D. W. and Sorensen, R. C., Comparative effects of nitrogen and sulfur fertilization and liming on three crops grown on four soils. Agron. J. 66, 92–97 (1974).
Mertz, E. T. and Matsumoto, H., Further studies on the amino acids and proteins of sulfur-deficient alfalfa. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 63, 60–63 (1956).
Moir, R. J., Implications of the N:S ratio and differential recycling. In Symposium: Sulfur in Nutrition. eds. O. H.Muth and J. E.Oldfield. pp. 164–181. Avi Publ. Co., Westport, Conn. (1970).
Oaks, A., Asparagine synthesis in Zea mays. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 141, 436–439 (1967).
Pucher, G. W., Vickery, H. B. and Leavenworth, C. S., Determination of ammonia and amide nitrogen in plant tissue. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 7, 152–156 (1935).
Pumphrey, F. V. and Moore, D. P., Diagnosing sulfur deficiency of alfalfa from plant analysis. Agron. J. 57, 364–366 (1965).
Rehm, G. W. and Caldwell, A. C., Sulfur uptake by corn as influenced by ammonium and nitrate nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 34, 327–329 (1970).
Rendig, V. V., Sulfur and nitrogen composition of fertilized and unfertilized alfalfa grown on a S-deficient soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 20, 237–240 (1956).
Rendig, V. V. and McComb, E. A., Effect of nutrition stress on plant composition. I. The interaction of added nitrogen with varying sulfur supply. Soil Sci. Am. Proc. 23, 377–380 (1959).
Sorensen, R. C., Penas, E. J. and Alexander, U. U., Sulfur content and yield of alfalfa in relation to plant nitrogen and sulfur fertilization. Agron. J. 60, 20–24 (1968).
Steinbergs, A., Iismaa, O., Freney, J. R., and Barrow, N. J., Detection of total sulfur in soil and plant material. Ana. Chim. Acta 27, 158–164 (1962).
Stewart, B. A. and Porter, L. K., Nitrogen-Sulfur relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), corn (Zea mays) and beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). Agron. J. 61, 267–271 (1969).
Terman, G. L., Allen, S. E. and Giordano, P. M., Dry matter yield N and S concentration relationships and ratios in young corn plants. Agron. J. 65, 633–636 (1973).
Thomas, M. D., Assimilation of sulfur and physiology of essential S-compounds. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology IX, 37–63 (1958).
Thompson, J. F., Smith, I. K. and Moore, D. P., Sulfur requirement and metabolism in plants. In Sulfur in Nutrition. eds. O. H.Muth and J. E.Oldfield. pp. 80–96. Avi Publ. Co., Westport, Conn. (1970).
Tisdale, S. L., Davis, R. L., Kingsley, A. F. and Mertz, E. T., Methionine and cystine content of two strains of alfalfa as influenced by different concentrations of the sulfate ion. Agron. J. 42, 221–225 (1950).
Warncke, D. D. and Barber, S. A., Ammonium and nitrate uptake by corn (Zea mays L.) as influenced by NH4/NO3 ratio. Agron. J. 65, 950–953 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rendig, V.V., Oputa, C. & McComb, E.A. Effects of sulfur deficiency on non-protein nitrogen, soluble sugars, and N/S ratios in young corn (Zea mays L.) plants. Plant Soil 44, 423–437 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015893
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015893