Abstract
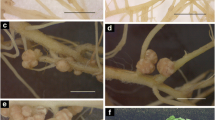
Strains of Bradyrhizobium formed nodule-like structures on Arabidopsis and species of Brassica in pots with sandvermiculite and in glass tubes on a nitrogen-free mineral salts agar. Broad-host-range Rhizobium strains NGR234 from Lablab purpureus and NGR76 from Phaseolus vulgaris formed similar nodule-like structures on Brassica spp. The size of these structures on plants in pots were large, often reaching 10 mm in diameter.
The frequency of inoculated Brassica plants in pots with nodule-like structures was 25–50%, depending on the inoculum strain. The inheritable nature of factors involved in the formation of the nodule-like structures was demonstrated when the structures occurred on 100% of inoculated B. napus seedlings derived from plants with the nodule-like structures.
Nodule-like structures occurred without, but not with, the application of a cellulase-pectolyase-PEG treatment to the roots. Attempts to isolate Bradyrhizobium or Rhizobium from the nodule-like structures failed. Internal infection of these structures could not be detected using either the light or electron microscope. The inoculum strains of root-nodule bacteria were detected in high numbers in the rhizosphere of plants 5 months after inoculation. On agar plates bacterial colonies could be seen, with undiminished growth, over the surface of the agar extending to the root surface. However, ground root tissue of Brassica was toxic to Bradyrhizobium strains. This suggested that Bradyrhizobium strains would not survive after infecting the roots of Brassica spp. Nitrogen fixation was associated with high rhizosphere populations of Azospirillum and not with Bradyrhizobium induced nodule structures of Brassica spp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mallah M K, Davey M R and Cocking E C 1989 Formation of nodular structures on rice seedlings by rhizobia. J. Exp. Bot. 40, 473–478.
Al-Mallah M K, Davey M R and Cocking E C 1990 Nodulation of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by rhizobia. J. Exp. Bot. 41, 1567–1572.
Brewin N J 1991 Development of the legume root nodule. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 191–226.
Bashan Y and Levanony H 1990 Current status Azospirillum inoculation technology: Azospirillum as a challenge for agriculture. Can. J. Microbiol. 591–608.
Cocking E C, Al-Mallah M K, Benson E and Davey M R 1990 Nodulation of non-legumes by rhizobia. In Nitrogen Fixation: Achievements and Objectives. Eds. P MGresshoff, E CRoth, GStacey and W ENewton. pp 813–823 Chapman and Hall, New York.
Francisco P B and Akao S 1993 The 2,4-D-induced wheat paranodules are modified lateral roots with structure enhanced by rhizobial inoculation. Plant and Soil 157, 121–129.
Gland A, Robbelen G and Thies W 1981 Variation of alkenyl glucosinolates in seeds of Brassica species. Z. Pflanzenzuchtg. 87, 96–110.
Jing Y X, Li G S, Shan X Q and Li J G 1990 Rice root nodule with nitrogenase and hemoglobin. In Nitrogen Fixation: Achievements and Objectives. Eds. P MGresshoff, E CRoth, GStacey and W ENewton. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Johsi P A, Caetano-Anolles G, Graham E T and Gresshoff P M 1991 Ontogeny and ultrastructure of spontaneous nodules in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Protoplasma 161, 1–11.
Kraling K, Robbelen G, Thies W, Herrmann M and Ahmadi M R 1990 Variation of seed glucosinolates in lines of Brassica napus. Plant Breeding 105, 33–39.
Li G S, Jing Y X, Shan X Q, Wang H L and Guan C H 1991 Identification of rice nodules that contain Rhizobium bacteria. Chin. J. Bot. 3, 8–17.
Relic B, Perret X, Estrada-Garcia M T, Kopcinska J, Gollinowski W, Krishnan H B, Pueppke S G and Broughton W J 1994 Nod factors of Rhizobium are a key to the legume door. Mol. Microbiol. 13, 171–178.
Sang J P, Minchinton P K and Truscott R J W 1984 Glucosinolate profiles in the seed, root and leaf tissue of cabbage, mustard, rapeseed, radish and swede. Can. J. Plant Sci. 64, 77–93.
Sriskandarajah S, Kennedy I R and Yu D 1993 Effects of plant growth regulators on acetylene-reducing associations between Azospirillum brasilense and wheat. Plant and Soil 153, 165–178.
Tchan Y T and Kennedy I R 1989 Possible N2-fixing root nodule induced in non-legumes. Agric. Sci. (AIAS, Melbourne) 2, 57–59.
Tchan Y T, Zeman A M M and Kennedy I R 1991 Nitrogen fixation in para-nodules of wheat roots by introduced free-living diazotrophs. Plant and Soil 137, 43–47.
Tommerup I C 1984 Development of infection by a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in Brassica napus L. and Trifolium subterraneum L. New Phytol. 98, 487–495.
Trinick M J 1973 Symbiosis between Rhizobium and the non-legume Trema aspera. Nature 244, 459–460.
Trinick M J 1980 Relationships amongst the fastgrowing rhizobia of Lablab purpureus, Leucaena leucocephala, Mimosa spp., Acacia farnesiana and Sesbania grandiflora and their affinities with other rhizobial groups. J. Appl. Bact. 49, 39–53.
Trinick M J, Dilworth M J and Grounds M 1976 Factors affecting the reduction of acetylene by root nodules of Lupinus species. New Phytol. 77, 359–370.
Trinick M J and Hadobas P A 1988 Biology of the Parasponia-Bradyrhizobium symbiosis. Plant and Soil 110, 177–185.
Trinick M J and Hadobas P A 1989 Competition by Bradyrhizobium strains for nodulation of the nonlegume Parasponia andersonii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 1242–1248.
Trinick M J and Hadobas P A 1990a Nodulation of Trifolium repens with modified Bradyrhizobium and the nodulation of Parasponia with Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii. Plant and Soil 125, 49–61.
Trinick M J and Hadobas P A 1990b Symbiotic effectiveness of Bradyrhizobium strains isolated from Parasponia and tropical legumes on Parasponia host species. Plant and Soil 124, 117–126.
Trinick M J, Miller C and Hadobas P A 1991 Formation and structure of root nodules induced on Macroptilium atropurpureum inoculated with various species of Rhizobium. Can. J. Bot. 69, 1520–1532.
Trinick M J, Miller C and Hadobas P A 1992 Internal organisation of nodule-like structures formed on Brassica napus inoculated with Bradyrhizobium. Proceedings of ‘The 1992 Joint Conference on Electron Microscop and Cell Biology.’ (ACEM-12 AND ANZSCB-11). 122p.
Truchet G, Roche P, Lerouge P, Vasse J, Camut S, deBilly F, Prome J C and Denarie J 1991 Sulphated lipo-oligosaccharide signals of Rhizobium meliloti elicit root nodule organogenesis in alfalfa. Nature 351, 670–673.
VanBrussel A A N, Bakhuizen R, vanSpronsen P C, Spaink H P, Tak T, Lugtenberg B J J and Kijne J W 1992 Induction of pre-infection thread structures in the leguminous host plant by mitogenic lipo-oligosaccharides of Rhizobium. Science 257, 70–72.
Vincent J M 1970 A manual for the practical study of the root-nodule bacteria. Int. Biol. Programme Handbook No. 15, Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trinick, M.J., Hadobas, P.A. Formation of nodular structures on the non-legumes Brassica napus, B. campestris, B. juncea and Arabidopsis thaliana with Bradyrhizobium and Rhizobium isolated from Parasponia spp. or legumes grown in tropical soils. Plant Soil 172, 207–219 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011323
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011323