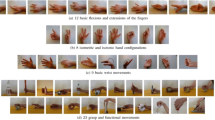
Abstract
In the field of hand gesture recognition based on electromyography, the selection of features is still a matter of research because the accuracy of feature evaluation techniques depends on the distribution underling a feature space. Currently, there are a lot of kinds of features, so a selection method is required in order to find an optimal feature subset. The selection of features can be done based on either classifier methods or statistical measurement indexes. On one hand, the use of classifier methods takes considerable time, consequently, they are computationally expensive. On the other hand, the use of a statistical index allows to select features based on properties, and they are less expensive in terms of time and computational costs. In this context, this study analyzed different statistical indexes to discover optimal feature subsets and predicts which one may have the best performance in terms of classification and recognition accuracy. For this purpose, four indexes were analyzed: the sum of RES (separation and compactness index), the sum of Fuzzy Entropies, and both of these indexes divided by the mutual information of feature subset. These index values were calculated for 10 different feature subsets obtained from nineteen time-domain features which have been investigated by many researchers for extracting useful information from an electromyography signal. The feature subsets were implemented in four classifiers (Artificial Neural Network, k-nearest Neighbors Algorithm, Support Vector Machine, and decision trees) to find the best statistical index which tries to quantify the suitableness of the feature space. Each tested index in this work was analyzed in terms of classification and recognition accuracy for each machine learning algorithm.
This work has been supported by the Corporación Ecuatoriana para el Desarrollo de la Investigación y la Academia (CEDIA) and Escuela Politécnica Nacional.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceves-Fernandez, M., Ramos-Arreguin, J., Gorrostieta-Hurtado, E., Pedraza-Ortega, J.: Methodology proposal of emg hand movement classification based on cross recurrence plots. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019 (2019)
Al-Angari, H.M., Kanitz, G., Cipriani, C.: Distance and mutual information methods for emg feature and channel subset selection for classification of hand movements. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 27, 24–31 (2016)
Al Omari, F., Hui, J., Mei, C., Liu, G.: Pattern recognition of eight hand motions using feature extraction of forearm emg signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A: Phys. Sci. 84(3), 473–480 (2014)
Ameur, S., Khalifa, A.B., Bouhlel, M.S.: A comprehensive leap motion database for hand gesture recognition. In: 2016 7th International Conference on Sciences of Electronics, Technologies of Information and Telecommunications, SETIT 2016, pp. 514–519. IEEE (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/SETIT.2016.7939924
Arief, Z., Sulistijono, I.A., Ardiansyah, R.A.: Comparison of five time series emg features extractions using myo armband. In: 2015 International Electronics Symposium (IES), pp. 11–14. IEEE (2015)
Arjunan, S.P., Kumar, D.K.: Fractal theory based non-linear analysis of semg. In: 2007 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information, pp. 545–548 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSNIP.2007.4496901
Benalcázar, M.E., Anchundia, C.E., Zea, J.A., Zambrano, P., Jaramillo, A.G., Segura, M.: Real-time hand gesture recognition based on artificial feed-forward neural networks and emg. In: 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 1492–1496. IEEE (2018)
Bhingarkar, S., Shah, D.: Fuzzy entropy based feature selection for website user classification in edos defense. In: Bhattacharyya, P., Sastry, H.G., Marriboyina, V., Sharma, R. (eds.) Smart and Innovative Trends in Next Generation Computing Technologies, pp. 440–449. Springer, Singapore (2018)
Caiza, G., Garcia, C., Naranjo, J., Garcia, M.: Flexible robotic teleoperation architecture for intelligent oil fields. Heliyon 6(4) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03833
Caiza, G., Saeteros, M., Oñate, W., Garcia, M.: Fog computing at industrial level, architecture, latency, energy, and security: a review. Heliyon 6(4) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03706
Das, A.K., Pati, S.K., Ghosh, A.: Relevant feature selection and ensemble classifier design using bi-objective genetic algorithm. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 62(2), 423–455 (2020)
Elamvazuthi, I., Ling, G., Nurhanim, K.R.K., Vasant, P., Parasuraman, S.: Surface electromyography (semg) feature extraction based on daubechies wavelets. In: 2013 IEEE 8th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), pp. 1492–1495. IEEE (2013)
Farina, D., Jiang, N., Rehbaum, H., Holobar, A., Graimann, B., Dietl, H., Aszmann, O.C.: The extraction of neural information from the surface EMG for the control of upper-limb prostheses: Emerging avenues and challenges. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabilit. Eng. 22(4), 797–809 (2014)
Gokgoz, E., Subasi, A.: Comparison of decision tree algorithms for emg signal classification using dwt. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 18, 138–144 (2015)
Hu, G.C.A.P.H., Limsakul, P.P.C.: Evaluation of emg feature extraction for classification of exercises in preventing falls in the elderly. In: The 10th International PSU Engineering Conference (2012)
Huang, Y., Wu, H., Liu, H., Yin, Z.: Intelligent Robotics and Applications: 10th International Conference, ICIRA 2017, Wuhan, China, Proceedings, vol. 10462. Springer (2017). Accessed 16–18 Aug 2017
Hudgins, B., Parker, P., Scott, R.N.: A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 40(1), 82–94 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/10.204774
Jali, M.H., Ibrahim, I.M., Sulaima, M.F., Bukhari, W., Izzuddin, T.A., Nasir, M.N.: Features extraction of emg signal using time domain analysis for arm rehabilitation device. In: AIP Conference Proceedings. vol. 1660, p. 070041. AIP Publishing LLC (2015)
Khushaba, R.N., Al-Jumaily, A., Al-Ani, A.: Novel feature extraction method based on fuzzy entropy and wavelet packet transform for myoelectric control. In: 2007 International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies, pp. 352–357 (2007)
Küçük, H., Eminoğlu, İ.: Classification of emg signals by k-nearest neighbor algorithm and support vector machine methods. In: 2013 21st Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2013)
Liang, S., Ma, A., Yang, S., Wang, Y., Ma, Q.: A review of matched-pairs feature selection methods for gene expression data analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 16, 88–97 (2018)
Montalvo, W., Escobar-Naranjo, J., Garcia, C., Garcia, M.: Low-cost automation for gravity compensation of robotic arm. Appl. Sci. (Switzerland) 10(11) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113823
Montalvo, W., Garcia, C., Naranjo, J., Ortiz, A., Garcia, M.: Tele-operation system for mobile robots using in oil & gas industry [sistema de tele-operación para robots móviles en la industria del petróleo y gas]. RISTI - Revista Iberica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informacao 2020(E29), 351–365 (2020)
Nilsson, N., Håkansson, B., Ortiz-Catalan, M.: Classification complexity in myoelectric pattern recognition. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 14(1), 68 (2017)
Phinyomark, A., Hirunviriya, S., Limsakul, C., Phukpattaranont, P.: Evaluation of emg feature extraction for hand movement recognition based on euclidean distance and standard deviation. In: ECTI-CON2010: The 2010 ECTI International Confernce on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, pp. 856–860 (May 2010)
Phinyomark, A., Hirunviriya, S., Nuidod, A., Phukpattaranont, P., Limsakul, C.: Evaluation of emg feature extraction for movement control of upper limb prostheses based on class separation index. In: 5th Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biomedical Engineering 2011, pp. 750–754. Springer Berlin Heidelberg (2011)
Phinyomark, A., Chujit, G., Phukpattaranont, P., Limsakul, C., Hu, H.: A preliminary study assessing time-domain emg features of classifying exercises in preventing falls in the elderly. In: 2012 9th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2012)
Phinyomark, A., Khushaba, R.N., Ibáñez-Marcelo, E., Patania, A., Scheme, E., Petri, G.: Navigating features: a topologically informed chart of electromyographic features space. J. R. Soc. Interface 14(137), 20170734 (2017)
Phinyomark, A., Limsakul, C., Phukpattaranont, P.: Application of wavelet analysis in emg feature extraction for pattern classification. Meas. Sci. Rev. 11(2), 45–52 (2011)
Phinyomark, A., N Khushaba, R., Scheme, E.: Feature extraction and selection for myoelectric control based on wearable emg sensors. Sensors 18(5), 1615 (2018)
Pothirat, T., Chatpun, S., Phukpattaranont, P., Vongjandaeng, D.: The optimal electromyography feature for oral muscle movements. In: The 6th 2013 Biomedical Engineering International Conference, pp. 1–5. IEEE (2013)
Rhodes, C., Allmendinger, R., Climent, R.: New interfaces for classifying performance gestures in music. In: International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, pp. 31–42. Springer (2019)
Scherer, R., Rao, R.: Non-Manual Control Devices. In: Handbook of Research on Personal Autonomy Technologies and Disability Informatics, pp. 233–250. IGI Global (2011). https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-60566-206-0.ch015
She, H., Zhu, J., Tian, Y., Wang, Y., Yokoi, H., Huang, Q.: Semg feature extraction based on stockwell transform improves hand movement recognition accuracy. Sensors 19(20), 4457 (2019)
Shi, W.T., Lyu, Z.J., Tang, S.T., Yang, C.Y.: A bionic hand controlled by hand gesture recognition based on surface emg signals: a preliminary study. Biocybernet. Biomed. Eng. 38(1), 126–135 (2018)
Szabó, Z.: Information theoretical estimators toolbox. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15(1), 283–287 (2014)
Tkach, D., Huang, H., Kuiken, T.A.: Study of stability of time-domain features for electromyographic pattern recognition. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 7(1), 21 (2010)
Too, J., Abdullah, A.R., Zawawi, T.T., Musa, H.: Classification of emg signal based on time domain and frequency domain features. Int. J. Hum. Technol. Interaction (IJHaTI) 1(1), 25–30 (2017)
Too, J., Abdullah, A.R., Mohd Saad, N., Tee, W.: Emg feature selection and classification using a pbest-guide binary particle swarm optimization. Computation 7(1), 12 (2019)
Too, J., Abdullah, A.R., Saad, N.M.: Classification of hand movements based on discrete wavelet transform and enhanced feature extraction. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 10(6) (2019). https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2019.0100612
Trigili, E., Grazi, L., Crea, S., Accogli, A., Vitiello, N., Panarese, A.: Detection of movement onset using emg signals for upper-limb exoskeletons in reaching tasks. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 16(1), 45 (2019)
Villarejo, J., Frizera, A., Bastos, T.F., Sarmiento, J.: Pattern recognition of hand movements with low density semg for prosthesis control purposes. In: 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2013)
Vimos, V.H., Benalcázar, M., Oña, A.F., Cruz, P.J.: A novel technique for improving the robustness to sensor rotation in hand gesture recognition using semg. In: International Conference on Computer Science, Electronics and Industrial Engineering (CSEI), pp. 226–243. Springer (2019)
Xi, X., Tang, M., Luo, Z.: Feature-level fusion of surface electromyography for activity monitoring. Sensors 18(2), 614 (2018)
Xi, X., Tang, M., Miran, S.M., Luo, Z.: Evaluation of feature extraction and recognition for activity monitoring and fall detection based on wearable semg sensors. Sensors 17(6), 1229 (2017)
Xing, K., Yang, P., Huang, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, Q.: A real-time emg pattern recognition method for virtual myoelectric hand control. Neurocomputing 136, 345–355 (2014)
Young, A.J., Smith, L.H., Rouse, E.J., Hargrove, L.J.: Classification of simultaneous movements using surface emg pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(5), 1250–1258 (2012)
Zea, J.A., Benalcázar, M.E.: Real-time hand gesture recognition: A long short-term memory approach with electromyography. In: International Conference on Computer Science, Electronics and Industrial Engineering (CSEI), pp. 155–167. Springer (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Corporación Ecuatoriana para el Desarrollo de la Investigación y la Academia (CEDIA) and by the Escuela Politécnica Nacional (EPN) for the development of the research project PIE-CEPRA-2019-13-Reconocimiento de Gestos.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Barona-Lopez, L.I., Valdivieso-Caraguay, A.L., Benalcazar, M.E., Aguas, X., Zea, J.A. (2021). Feature Evaluation of EMG Signals for Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Mutual Information, Fuzzy Entropy and RES Index. In: García, M.V., Fernández-Peña, F., Gordón-Gallegos, C. (eds) Advances and Applications in Computer Science, Electronics and Industrial Engineering. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1307. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4565-2_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4565-2_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-4564-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-4565-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)