Abstract
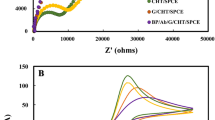
In this paper, how hepatitis B virus is being operated via NFC using a smartphone-controlled electrochemical sensor. Despite the advances in technology, HBV has always been a crucial global health issue. Due to late detection of HBV, there were so many people who died. All the techniques we have to detect HBV are made up of huge device. So, developing smallest devices to detect the HBV has been clearly more important for convenience and growth. Variety of approaches has been used to develop better miniaturized device. This system consists of small-sized NFC sensor tag incorporated with a smartphone and antibody-modified electrode sensor. By EIS and CV, moderations and motion restriction process were verified (Kanchi et al. in Biosens Bioelectron 102:136–149, 2018 [1]). A user-friendly electrochemical device which is portable, economical is the most requiring element in electrochemical sensing to use in point-of-care approach. To make measuring units easier, connection which is wireless has been configured between smartphone and potentiostat called NFC interface that makes the potentiostat into passive operated device running without battery. Using amperometric detection, the hepatitis B antigen (HBsAg) was qualified with the help of NFC-based electrochemical immunosensor by measuring current from the redox couple before and after HBsAg usage. The proposed approach has shown a better performance with long-established immunoassays when the recurring HBV infected serum tested by sensor. The approach has shown a satisfying performance for rapid and reliable portable detection device of HBsAg.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanchi S, Sabela MI, Mdluli PS, Bisetty IK (2018) Smartphone based bio-analytical and diagnosis applications: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 102:136–149
Zhu H, Yaglidere O, Su TW, TSeng D, Ozcan A (2011) Cost-effective and compact wide-field fluorescent imaging on a cell phone. Lab Chip 11:315–322
Teengam P, Siangproh W, Tontisirin S, Amornkun AJ, Chuaypen N, Tangkijvanich P, Henry CS, Ngamrojanavanich N, Chailapakul O (2021) NFC-enabling smartphone-based portable amperometric immunosensor for hepatitis B virus detection: a review. Sense Actuators B: Chem, Elsevier, Thailand, pp 128–825
Tyas AA, Raeni SF, Sakti SP, Sabarudin A (2021) Recent advances of hepatitis B detection towards paper-based analytical devices. vol 21. pp 11, 6643–573
Coskun V, Ozdenizci B, Ok K (2013) A survey on near field communication technology. Wireless Personal Commun 71:2259–2294
Zhang R, Li L, Feng J, Tong L, Wang Q, Tang B (2014) Versatile triggered release of multiple molecules from cyclodextrin modified gold-gated mesoporous silica nanocontainers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:9932–9936
Yekkala I, Dixit S (2018) Prediction of heart disease using random forest and rough set-based feature selection. Int J Big Data and Anal Healthcare, pp 1–12
Dixit S, Mahalakshmi J, Mahesh R (2022) Emerging pandemic COVID 19 vs. SARS-COV-1. Int J Appl Res Public Health Managem (IJARPHM) 1–10
Yekkala I, Dixit S (2020) A novel approach for heart disease prediction using genetic algorithm and ensemble classification. Int J Appl Res Public Health Managem (IJARPHM), Proceedings of SAI intelligent systems conference, pp 468–489
Peter K, MD, Steinberg IM (2018) Wireless chemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Sens Actuators B: Chem 266:228–245
Liu L, Ji D, Li S, Chen C, Lu Y, Wu J et al (2017) Smartphone-based cyclic voltammetry system with graphene modified screen printed electrodes for glucose detection. Biosens, Bioelectron 98:449–456
Huang X, Xu D, Chen J, Liu J, Li Y, Song J et al (2018) Smartphone-based analytical biosensors. Analyst 143:5339–5351
Lee SA, Yang C (2014) A Smartphone-based chip-scale microscope using ambient illumination. Lab Chip 14:3056–3063
Tseng D, Mudanyali O, Oztoprak C, Isikman SO, Sencan I, Yaglidere O et al (2010) Lensfree microscopy on a cellphone. Lab Chip 11:1787–1792
Tian L, Liu L, Li Y, Feng X, Wei Q, Cao W (2016) A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. Anal Methods 8:7380–7386
Li X, Li J, Liu Y, Zhang X, Chen J (2017) A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for prion detection based on poly β-cyclodextrin/gold nanoparticles/glassy carbon electrode. Sens Actuators B 250:1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Halakate, T., Dixit, S. (2023). Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Using NFC-Enabled Smartphone-Based Portable Amperometric Immunosensor. In: Tuba, M., Akashe, S., Joshi, A. (eds) ICT Infrastructure and Computing. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 520. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5330-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5331-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)