Abstract
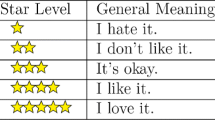
With the increase in the use of Web 2.0, there are lot of opinions on the web about any product. Most of the opinions contain opinion words which has same polarity in all contexts. But there are some opinion words called context dependent words which have different polarity in different context. So there is a need to determine the polarity of ambiguous words (context dependent words) efficiently and effectively. This task is also known as word polarity disambiguation (WPD). This literature survey is done to familiarize with general applications and approaches of opinion mining then it presents the context dependent word polarity problem in depth by explaining the existing literature of sentiment classification of context dependent words and finally, some open problems, conclusion, and future directions are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, B. (2010). Sentiment analysis and subjectivity. In N. Indurkhya & F. Damerau, (Eds.), Handbook of Natural Language Processing (2nd edn.).
Pang, B., & Lee, L. (2008). Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Foundations and Trends in Information Retrieval., 2(1/2), 1–135.
Kaur, A., & Duhan, N. (2015). A survey on sentiment analysis and opinion mining. International Journal of Innovations & Advancement in Computer Science, 107–116.
Feldman, R. (2013). Techniques and applications for sentiment analysis. Communications of the ACM, 56(4), 82–89.
Liu, B., & Zhang, L. (2012). A survey of opinion mining and sentiment analysis. In C. C. Aggarwal & C. X. Zhai (Eds.), Mining Text Data (pp. 415–163).New York: Springer.
Chandrakala, C. S., & Sindhu, C. (2012). Opinion mining and sentiment classification: A survey. ICTACT Journal on Soft Computing, 3(1), 420–425.
Rashid, A., et al. (2013). A survey paper: areas, techniques and challenges of opinion mining. International Journal of Computer Science (IJCSI), 10(6), 2.
Ding, X., Liu, B., & Yu, P. S. (2008). A holistic lexicon-based approach to opinion mining. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (pp 231–240).
Matineau, J., & Finin, T. (2009). Delta tfidf:an improved feature space for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Third International ICWSM Conference (pp. 258–261).
Yuming, L., Zhang, J., Wang, X., & Zhou, A. (2012). An information theoretic approach to sentiment polarity classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd Joint WICOW/AIRWeb Workshop on Web Quality (pp. 35–40). ACM.
Farag, S., & Mathiak, B. (2013). Revised mutual information approach for german text sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web Companion (pp. 579–586).
Kansal, H., & Toshniwal, D. (2014). Aspect based summarization of context dependent opinion words. 18th International Conference on Knowledge-Based and Intelligent Information & Engineering Systems—KES (pp. 166–177).
Rosario, B., Rajon, C., & Cheng, C. K. (2011). Word sense disambiguation of opinionated words using extended gloss overlap. In Proceedings of the 8th Natural Language Processing (pp 1–5).
Jalilvand, A., & Salim, N. (2012). Sentiment classification using graph based word sense disambiguation. AMLTA 2012, CCIS, 322, 351–358.
Xia, Y., Cambria, E., Hussain, A., & Zhao, H. (2014). Word polarity disambiguation using bayesian model and opinion-level features. Cognitive Computation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this paper
Cite this paper
Garg, S., Sharma, D.K. (2016). Sentiment Classification of Context Dependent Words. In: Satapathy, S., Joshi, A., Modi, N., Pathak, N. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on ICT for Sustainable Development. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 408. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0129-1_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0129-1_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-0127-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-0129-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)