Abstract
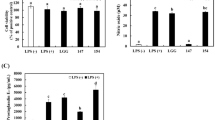
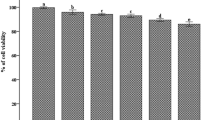
In this study, we synthesized Galactose-Taurine sodium salt (G-T) as a functional food ingredient to enhance biological activities of taurine. Also, anti-inflammatory effects of G-T were investigated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. G-T found to reduce the generations of the LPS-stimulated nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) via down-regulating the expression levels of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Also, G-T reduced the secretion of inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells. Finally, we identified that G-T inhibits the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the phosphorylation of inhibitor κB (IκB)-α. From these results, this study first suggests that G-T could be considered as an effective anti-inflammatory agent.
$N. Kang and K.J. Chang are equally contributed to this study.
§S.H. Cheong and G. Ahn are equally contributed to this study.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- Gal-Tau:
-
Galactose-Taurine sodium salt
- IκB-α:
-
Inhibitor κB-α
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- iNOS:
-
Inducible NO synthase
- PGE2 :
-
Prostaglandin E2
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Ajizian SJ, English BK, Meals EA (1999) Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. J Infect Dis 179:939–944. doi:10.1086/314659
Bae IK, Min HY, Han AR, Seo EK, Lee SK (2005) Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by brazilin in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Eur J Pharmacol 513:237–242. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.03.011
Caramori G, Adcock IM, Ito K (2004) Anti-inflammatory inhibitors of IkappaB kinase in asthma and COPD. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 5:1141–1147
Cho HJ, You JS, Chang KJ, Kim KS, Kim SH (2014) Anti-adipogenic effect of taurine-carbohydrate derivatives. Bull Korean Chem Soc 35:1863–1866
Fang FC (2004) Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: concepts and controversies. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:820–832. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1004
Higashimoto T, Panopoulos A, Hsieh CL, Zandi E (2006) TNFalpha induces chromosomal abnormalities independent of ROS through IKK, JNK, p38 and caspase pathways. Cytokine 34:39–50. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2006.03.015
Jones E, Adcock IM, Ahmed BY, Punchard NA (2007) Modulation of LPS stimulated NFκB mediated nitric oxide production by PKCε and JAK2 in RAW macrophages. J Inflamm 4:23. doi:10.1186/1476-9255-4-23
Kharitinov SA, Barnes JP (2004) Effects of corticosteroids on noninvasive biomarkers of inflammation in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 1:191–199
Kim HK, Cheon BS, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim HP (1999) Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol 58:759–765. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(99)00160-4
Kim SY, Lee YJ, You JS, Kim SH, Chang KJ (2015) N-(D-Ribopyranosyl) taurine sodium salt has anti-obesity effect in diet-induced obesity and taurine deficiency rat model. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:897–905. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-15126-7_73
Lee WW, Ahn G, Wijesinghe WAJP, Kim YM, Kim SK, Lee BJ, Jeon YJ (2011) A polysaccharide isolated from Ecklonia cava fermented by Lactobacillus brevis inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of nuclear factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Med Food 14(12):1546–1553
Marcinkiewicz J, Kurnyta M, Biedroń R, Bobek M, Kontny E, Maśliński W (2006) Antiinflammatory effects of taurine derivatives (taurine chloramine, taurine bromamine, and taurolidine) are mediated by different mechanisms. Adv Exp Med Biol 583:481–492
Miao J, Fa Y, Gu B, Zhu W, Zou S (2012) Taurine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced disfunction in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Cytokine 59:35–40. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.04.009
Miggin SM, O’Neill LA (2006) New insights into the regulation of TLR signalling. J Leukoc Biol 80:220–226. doi:10.1189/jlb.1105672
Nakagawa T, Yokozawa T (2002) Direct scavenging of nitric oxide and superoxide by green tea. Food Chem Toxicol 40:1745–1750. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(02)00169-2
Pasantes-Morales H, Wright CE, Gaull GE (1985) Taurine protection of lymphoblastoid cells from iron-ascorbate induced damage. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2205–2207. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90419-8
Posadas I, Terencio MC, Guillén I, Ferrándiz ML, Coloma J, Payá M, Alcaraz MJ (2000) Co-regulation between cyclo-oxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the time-course of murine inflammation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:98–106
Stapleton PP, Bloomfield FJ (1993) Effect of zwitterions on the respiratory burst. J Biomed Sci 3:79–84
Sturman JA (1993) Taurine in development. Physiol Rev 73:119–148
Takahashi K, Harada H, Schaffer SW (1992) Effect of taurine on intracellular calcium dynamics of cultured myocardial cells during the calcium paradox. In: Lombardini JB (ed) Taurine nutritional value and mechanisms of action. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3768–3774
Uto T, Fujii M, Hou DX (2005) 6-(Methylsulfinyl) hexyl isothiocyanate suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase expression through the inhibition of Janus kinase 2-mediated JNK pathway in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 70:1211–1221. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.07.011
Ward RJ, Lallemand F, de Witte P, Crichton RR, Piette J, Tipton K, Hemmings K, Pitard A, Page M, Della Corte L, Taylor D, Dexter D (2011) Anti-inflammatory actions of a taurine analogue, ethane β-sultam, in phagocytic cells, in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 81:743–751. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.12.030
Yasuda T, Kakinuma T, Julovi SM, Hiramatsu T, Akiyoshi M, Nakamura T (2004) COOH- terminal heparin-binding fibronectin fragment induces nitric oxide production in rheumatoid cartilage through CD44. Rheumatology 43:1116–1120. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh274
Yoon WJ, Moon JY, Kang JY, Kim GO, Lee NH, Hyun CG (2010) Neolitsea sericea essential oil attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPK activation. Nat Prod Commun 5:1311–1316
You JS, Lee YJ, Kim SY, Chang KJ, Cho HJ, Kim SH (2015) N-(β-D-Xylopyranosyl) taurine sodium salt supplementation has beneficial effect on the hepatic antioxidant system of rats fed a high-fat diet and β-alanine. Adv Exp Med Biol 803:869–877. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-15126-7_70
Zhang F, Mao Y, Qiao H, Jiang H, Zhao H, Chen X, Tong L, Sun X (2010) Protective effects of taurine against endotoxin-induced acute liver injury after hepatic ischemia reperfusion. Amino Acids 38:237–245. doi:10.1007/s00726-009-0233-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kang, N. et al. (2017). Anti-inflammatory Effects of Galactose-Taurine Sodium Salt in LPS-Activated RAW 264.7 Cells. In: Lee, DH., Schaffer, S.W., Park, E., Kim, H.W. (eds) Taurine 10. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 975. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_75
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_75
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-024-1077-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-024-1079-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)