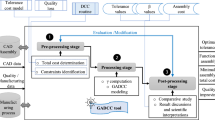
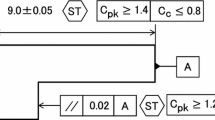
Abstract
The purpose of this research is to develop a computer aided method of tolerance synthesis. The assembly was represented by solid model, and dimensional and geometrical tolerances were formulated as a set of inequalities constraining substitute features. Differential coordinate transformation and linear programming were used to analyze the tolerance stack-up. The cost data base described the machining, inspectional and assembling costs for tolerances. Tolerance synthesis was represented as the combinatorial optimization problem under the stack-up conditions. Genetic Algorithm (GA) was applied to solve the problem. The coding method and genetic operators were discussed. The algorithm was evaluated through a gear box example.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boothroyd,G. and Dewhurst,P. (1986) Design for Assembly. Boothroyd Dewhurst Inc., Wakefield, RI.
Bjørke, Ø. (1978) Computer-aided Tolerancing. Tapir Publisher, Trondheim.
Chase, K.W. and Greenwood, W.H. (1988) Design issues in mechanical tolerance analysis. Manufacturing Review, 1(1), 50–59.
Chase, K.W., Greenwood, W.H., Loosli,B.G. and Hauglund,L.F. (1990) Least cost tolerance allocation for mechanical assemblies with automated process selection. Manufacturing Review, 3(1), 49–57.
ElMaraghy, H.A. and ElMaraghy,W.H. (1993) A system for modeling geometric tolerances for mechanical design. Proc. of 3rd CIRP Seminars on Computer Aided Tolerancing, 11–24.
Guilford,J. and Turner,J.U. (1993) Advanced tolerance analysis and synthesis for geometric tolerances. ASME Int. forum on dimensional tolerancing and metrology, CRTD 27, 187–198.
Inui,M. and Kimura,F. (1991) Algebraic reasoning of position uncertainties of parts in an assembly. Proc. of ACM Symp. on Solid Modeling Foundations and CAD/CAM Applicationsy 419–428.
Lee, J. and Johnson, G.E. (1993) Optimal tolerance allotment using a genetic algorithm and truncated monte carlo simulation. Computer-Aided Design, 25(9), 601–611.
Lee,W.J. and Woo, T.C. (1989) Optimum selection of discrete tolerances. Trans, of ASME Journal of Mechanisms, Transmiss.and Automation in Design, 111, 243–251.
Lee, W.J. and Woo, T.C. (1990) Tolerances: their analysis and synthesis. Trans, of ASME Journal of Engineering for Industry, 112, 113–121.
Lee, W.J., Woo, T.C. and Chou, S.Y. (1993) Tolerance synthesis for nonlinear systems based on nonlinear programming. IIE Trans., 25(1), 51–61.
Nassef, A.O. and ElMaraghy,H.A. (1993) Allocation of tolerance types and values using genetic algorithms. Proc. of 3rd CIRP Seminars on Computer Aided Tolerancing, 147–159.
Ostwald, P.F. and Huang, J. (1977) A method for optimal tolerance selection. Trans, of ASME Journal of Engineering for Industry, 99B(3), 558–565.
Paul, R.P. (1981) Robot Manipulators, MIT Press, Massachusetts, 85–118.
Spotts.,M.F. (1973) Allocation of tolerances to minimize cost of assembly. Trans, of ASME Journal of Engineering for Industry, 95, 762–764.
Turner,J.U. (1990) Relative positioning of parts in assemblies using mathematical programming. Computer Aided Design, 22(7), 394–400.
Wu,Z., ElMaraghy,W.H. and ElMaraghy,H.A. (1988) Evaluation of cost-tolerance algorithms for design tolerance analysis and synthesis. Manufacturing Review, 1(3), 168–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Chapman & Hall
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kanai, S., Onozuka, M., Takahashi, H. (1996). Optimal Tolerance Synthesis by Genetic Algorithm under the Machining and Assembling Constraints. In: Kimura, F. (eds) Computer-aided Tolerancing. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1529-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1529-9_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-7183-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-009-1529-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive