Abstract
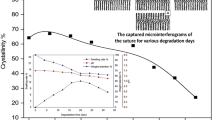
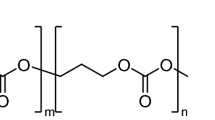
A Novel monofilament bioabsorbable sutures was made from a copolymer of e-caprolactone and L-lactide (Poly(CL-LA)). The Composition weight ratio of L-lactide: e-caprolactone was 85: 15. Initial tensile strength of the 5-0 suture was 838 ±72 gf (knot-pull 600 ±60 gf). An in vivo degradation test using rabbits showed: a poly(CL-LA) suture retains its strength for longer periods than other synthetic monofilament absorbable sutures such as MAXON®and PDS®. %Retention of tensile strength at 4 week was Poly(CL-LA) 83 ±13%, MAXON®36 ±9% PDS®50 ± 15%. At 8 weeks the Poly(CL-LA) was 38.2%, though the MAXON®and PDS®were 0%. The tissue reaction of this suture was not remarkable at any interval. At one year, the Poly(CL-LA) fiber was replaced with Collagen deposition.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Driscoll GL, Baird PJ, Merkelbach PJ, Smith DH (1982) Synthetic absor bable and nonabsorbable microsutures: a histological comparison, Clinical Reproduction and Fertility, 1: 151–156
Katz AR, Mukherjee DP, Kaganov AL and Gordon S (1985) A new syn thetic momofilament absorbable suture made from polytrimethylene carbonate, Surg. Gynecol. & Obstet., 161:213–222
Ray JA, Doddi N, Regula D, Williams JA and Melveger A (1981) Polydioxanone(PDS), A novel monofilament synthetic absorbable suture, Surg. Gynecol. & Obstet., 153:497–507
Nakamura T, Hitomi S, Shimamoto T, Hyon S. -H, Watanabe S, Shimizu Y (1987) Surgical Application of Biodegradable Films prepared from Lactide- ε -Caprolactone Copolymers in: Pizzoferrato A, Machetti PG, Ravaglioli A and Lee AJC (eds) Biomaterials and clinical Applications, 759–764, Elsevier Science Publ., Amsterdam
Naoe A, (1989) The role of suture material on healing of vascular anas tomosis, J. Jpn. Thorac. Surg., 90: 941–948
Steen S, Anderson L, Lowenhielm P, Stridbeck H, Walther B, Holmin T (1984) Comparison between absorbable and non absorbable, monofilament sutures for and-to-end arterial anastomoses in growing pigs, Surgery 95: 202–208
Tons CH, Armbrecht J, Bircks W (1986) The Use of Synthetic Absor bable Suture Materials (Polyglycolid Acid and Polydioxannone) in the Low Presure Circulatory System of Growing Organism, Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surgeon 34:128–131
Aarnio P, Harjula A, Lehtola A, Sariola H, Mattila S (1988) Polydioxanone and polypropylene suture material in free internal mamary artery graft anastomoses, J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 96:741–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nakamura, T., Shimizu, Y., Matsui, T., Okumura, N., Hyon, S.H., Nishiya, K. (1992). A Novel Bioabsorbable Monofilament Surgical Suture Made From (ε -Caprolactone, L-Lactide) Copolymer. In: Planck, H., Dauner, M., Renardy, M. (eds) Degradation Phenomena on Polymeric Biomaterials. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-77563-5_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-77563-5_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-77565-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-77563-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive