Abstract
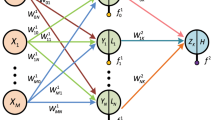
This paper used improved Levenberg-Marquart BP neural network technology to predict GPS tropospheric delay with the data of Beijing GPS data and meteorological data, which the input parameters are either space position (longitude, latitude, elevation) or space position, temperature, pressure. The testing results showed that the two predicted results are mostly closer; meanwhile the prediction results considering space position, temperature and pressure are slightly superior to the other method. The deviations between the predicted values of most GPS Stations and the actual atmospheric delay values are about 5mm. The accuracy of tropospheric delay predicted by BP neural network amounted to millimeters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, G.: Application examples of InSAR and its limitation analysis. Surveying and Mapping of Sichuan 28(3), 139–143 (2005)
Shan, X., Liu, H.: Detecting digital elevation model by InSAR technique. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources (2), 43–47 (2001)
You, X.: Synthetic aperature radar interferometry and its application. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics (3), 109–116 (2002)
Lu, X.: Experiment on land subsidence monitoring by INSAR. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics (4), 66–70 (2002)
You, X.: Quantitative estimation of effect of atmospheric refraction on InSAR. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics (2), 81–87 (2003)
Qiao, X.: Acquisition of DEM of Three Gorges area by INSAR. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics 23(2), 122–126 (2003)
Liang, W., Wang, Q.: Application of INSAR to monitoring and studying volcano. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics 23(4), 120–124 (2003)
Li, Z., Liu, J., Xu, C.: Error analysis in InSAR data processing. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 29(1), 72–76 (2004)
Xu, J.: Spatial interpolation methods for correcting atmospheric effects using interferometric SAR. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology (4), 911–915 (2008)
Wang, Y., Jiao, J., Zeng, Q.: Study on Zenith Tropospheric Delay Interpolation Methods for different terrain. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics 30(3), 132–136 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag GmbH Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Yang, J. (2012). Prediction of Zenith Tropospheric Delay Based on BP Neural Network. In: Xie, A., Huang, X. (eds) Advances in Computer Science and Education. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 140. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27945-4_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27945-4_73
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27944-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27945-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)