Abstract
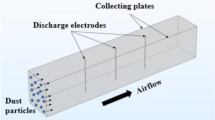
The specific gas flow influenced by the electrical field in the electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is called electrohydrodynamic (EHD) flow. The hybrid particulate collector (HPC) is a hybrid of the ESP and the baghouse in a unique approach combining the best features of both. The bags are placed between two perforated collection plates. The HPC is a very compact and high efficiency system. In this paper, numerical modeling of the three-dimensional EHD flow in a hybrid particulate collector (HPC) is presented. An unstructured finite volume method (FVM) was developed to solve the Poisson’s electrical equation and the current continuity equation within the collector. The Fluent code was used to solve the fluid N-S equations and the RNG k-∈ turbulent model equations with considering the electrical body force. The numerical results show that the EHD flow can produce strong recirculation in the hybrid collector. Different from the ESP, the electric field has still strong influence on the gas flow when the EHD number below one.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.J. White. Industrial Electrostatic Precipitation. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, Inc., 1963, 99–100.
Robinson M. Effects of the corona discharge on electric wind convection and eddy diffusion in an electrostatic precipitator. Ph. D. Thesis, The Coopr Union University, 1976.
Yabe A, Mori Y and Hijikata K. EHD study of the corona wind between wire and plate electrodes. AIAA J., 1978, 15: 340–345.
Yamamoto T and Velkoff H R. Electrohydrodynamics in an electrostatic precipitator, J. Fluid Mech., 1981, 108: 1–18.
Leonard G L, Mitchner M and Self S A., An experimental study of the electrohydrodynamic flow in electrostatic precipitators. J. Fluid Mech., 1983, 127: 123–140.
Larsen PS, Sorensen SK. Effect of secondary flows and turbulence on electrostatic precipitator efficiency. Atmos. Environ., 18: 1963–1967, 1984.
Yamamoto T. Effects of turbulence and electrohydrodynamics on the performance of electrostatic precipitators. J. Electrostatics, 1989, 22(1): 11–22.
Kallio G.A. and Stock, D.E., Interaction of electrostatic and fluid dynamic fields in wire-plate electrostatic precipitators. J. Fluid. Mech. 1992, 240: 133–166.
Liang W.J., Lin T. H. The characteristics of ionic wind, and its effect on electrostatic precipitators. Aerosol Sci. Technol., 1994, 20(4): 330–344.
Schemid, H.J., Stolz, S. and Buggisch, H., On the modeling of the electro-hydrodynamic flow field in electrostatic precipitators flow, Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2002, 68: 63–89.
Chun, Y. N. Berezin, A. A. Brocilo, D. Mizeraczyk, J. Chang, J.-S. Numerical Modelling of near corona wire electrohydrodynamic flow in a wire-plate electrostatic precípitator, IEEE. Trans. Die. Elec., 2007, 14(1): 119–124.
Hong Lei, Lian Ze and Wu Zinu. EHD turbulent flow and Monte-Carlo simulation for particle charging and tracing in a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator, J. Electrostat., 2008, 66: 130–141.
Zhuang, Y, Stanley. J. Miller. 2001. Advance Hybrid Particulate Collector final topic report for phase III.
J. R. McDonald, W. B. Smith, H. W. Spencer III, L. E. Sparks, A mathematical model for calculating electrical conditions in wire duct electrostatic precipitation devices, J. Appl. Phys, 1977, 48: 2231–2243.
B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding, The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Computer Method in Applied Mech. and Eng., 1974, 3: 269–289.
Fluent Inc. Fluent 6.3 User’s Guide, 2008.
IEEE-DEIS-EHD Technical Committee. Recommended International Standard for Dimensionless Parameters Used in Electrohydrodynamics, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., (10) 3–10, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou and Springer-Verlag GmbH Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhengwei, L., Qiang, Y., Qiang, S., Shuiqing, L. (2009). Numerical Modeling of the Electrohydrodynamics in a Hybrid Particulate Collector. In: Yan, K. (eds) Electrostatic Precipitation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-89251-9_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-89251-9_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-89250-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-89251-9
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)