Abstract
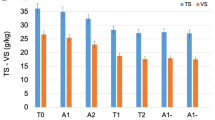
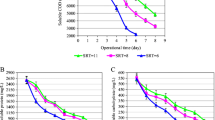
Thermophilic conditions for waste sludge fermentation have been reported to produce more SCFAs than mesophilic conditions. In this study, A series of SCFAs production experiments were carried out under different sludge sources and conditions to calibrate and validate the proposed model. A kinetic model had been developed to understand the production of SCFAs from waste sludge via thermophilic fermentation. Good agreement was obtained between the measured SCFAs, soluble chemical oxygen demand and volatile suspended solids data and the model output results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Jiang S, Yuan H, Zhou Q, Gu G (2007) Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res 41:683–689
De La Rubia MA, Raposo F, Borja R (2009) Evaluation of the hydrolytic-acidogenic step of a two-stage mesophilic anaerobic digestion process of sunflower oil cake. Bioresour Technol 100:4133–4138
Mengmeng C, Hong C, Qingliang Z, Shirley SN, Jie R (2009) Optimal production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in activated sludge fed by volatile fatty acids (VFAs) generated from alkaline excess sludge fermentation. Bioresour Technol 100:1399–1405
Sahm H (1984) Anaerobic wastewater treatment. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 29:83–115
Siegert I, Banks C (2005) The effect of volatile fatty acid additions on the anaerobic digestion of cellulose and glucose in batch reactors. Process Biochem 40:3412–3418
Zhang P, Chen Y, Zhou Q, Zheng X, Zhu X, Zhao Y (2010) Understanding short-chain fatty acids accumulation enhanced in waste activated sludge alkaline fermentation: kinetics and microbiology. Environ Sci Technol 44:9343–9348
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks to the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (No. 2014ZX07305001) and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (No. 2014z21028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zuo, Z.Q., Zheng, M., Xiong, H.L., Liu, Y.C., Shi, H.C. (2017). Thermophilic Hydrolysis and Fermentation to Produce Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Waste Sludge. In: Mannina, G. (eds) Frontiers in Wastewater Treatment and Modelling. FICWTM 2017. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering , vol 4. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58421-8_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58421-8_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-58420-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-58421-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)