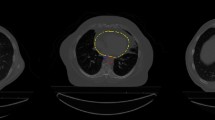
Abstract
The use of functional imaging such as PET in radiotherapy (RT) is rapidly expanding with new cancer treatment techniques. A fundamental step in RT planning is the accurate segmentation of tumours based on clinical diagnosis. Furthermore, recent tumour control techniques such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) dose painting requires the accurate calculation of multiple nested contours of intensity values to optimise dose distribution across the tumour. Recently, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved tremendous success in image segmentation tasks, most of which present the output map at a pixel-wise level. However, its ability to accurately recognize precise object boundaries is limited by the loss of information in the successive downsampling layers. In addition, for the dose painting strategy, there is a need to develop image segmentation approaches that reproducibly and accurately identify the high recurrent-risk contours. To address these issues, we propose a novel hybrid-CNN that integrates a kernel smoothing-based probability contour approach (KsPC) to produce contour-based segmentation maps, which mimic expert behaviours and provide accurate probability contours designed to optimise dose painting/IMRT strategies. Instead of user-supplied tuning parameters, our final model, named KsPC-Net, applies a CNN backbone to automatically learn the parameters and leverages the advantage of KsPC to simultaneously identify object boundaries and provide probability contour accordingly. The proposed model demonstrated promising performance in comparison to state-of-the-art models on the MICCAI 2021 challenge dataset (HECKTOR).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrearczyk, V., Oreiller, V., Hatt, M., Depeursinge, A.: Head and Neck Tumor Segmentation and Outcome Prediction. LNCS, vol. 13209. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98253-9
Bai, B., Bading, J., Conti, P.S.: Tumor quantification in clinical positron emission tomography. Theranostics 3(10), 787 (2013)
Bowman, A., Foster, P.: Density based exploration of bivariate data. Stat. Comput. 3, 171–177 (1993)
Bowman, A.W.: An alternative method of cross-validation for the smoothing of density estimates. Biometrika 71(2), 353–360 (1984)
Chacón, J.E., Duong, T.: Multivariate Kernel Smoothing and Its Applications. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton (2018)
Chen, X., Williams, B.M., Vallabhaneni, S.R., Czanner, G., Williams, R., Zheng, Y.: Learning active contour models for medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11632–11640 (2019)
Cho, M., Choi, Y., Hwang, D., Yie, S.Y., Kim, H., Lee, J.S.: Multimodal spatial attention network for automatic head and neck tumor segmentation in FDG-PET and CT images. In: Andrearczyk, V., Oreiller, V., Hatt, M., Depeursinge, A. (eds.) HECKTOR 2021. LNCS, vol. 13209, pp. 75–82. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98253-9_6
Gudi, S., et al.: Interobserver variability in the delineation of gross tumour volume and specified organs-at-risk during IMRT for head and neck cancers and the impact of FDG-PET/CT on such variability at the primary site. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 48(2), 184–192 (2017)
Hatamizadeh, A., et al.: Deep active lesion segmentation. In: Suk, H.-I., Liu, M., Yan, P., Lian, C. (eds.) MLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11861, pp. 98–105. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_12
Hatt, M., et al.: The first MICCAI challenge on pet tumor segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 44, 177–195 (2018)
Hyndman, R.J.: Computing and graphing highest density regions. Am. Stat. 50(2), 120–126 (1996)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Li, J., Ray, S., Lindsay, B.G.: A nonparametric statistical approach to clustering via mode identification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 8(8) (2007)
Ling, C.C., et al.: Towards multidimensional radiotherapy (MD-CRT): biological imaging and biological conformality. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 47(3), 551–560 (2000)
Parzen, E.: On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 33(3), 1065–1076 (1962)
Ray, S., Lindsay, B.G.: The topography of multivariate normal mixtures. Ann. Stat. 33(5) (2005). https://doi.org/10.1214/009053605000000417
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Shi, X., Meng, X., Sun, X., Xing, L., Yu, J.: PET/CT imaging-guided dose painting in radiation therapy. Cancer Lett. 355(2), 169–175 (2014)
Vallieres, M., et al.: Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 10117 (2017)
Visser, E.P., Boerman, O.C., Oyen, W.J.: SUV: from silly useless value to smart uptake value. J. Nucl. Med. 51(2), 173–175 (2010)
Wang, J., Peng, Y., Guo, Y., Li, D., Sun, J.: CCUT-net: pixel-wise global context channel attention UT-net for head and neck tumor segmentation. In: Andrearczyk, V., Oreiller, V., Hatt, M., Depeursinge, A. (eds.) HECKTOR 2021. LNCS, vol. 13209, pp. 38–49. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98253-9_2
Zhang, W., Ray, S.: Kernel smoothing-based probability contours for tumour segmentation. In: 26th UK Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. Springer, Cham (2022)
Zhang, Y., Chung, A.C.S.: Deep supervision with additional labels for retinal vessel segmentation task. In: Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11071, pp. 83–91. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_10
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Carnegie Trust of Scotland PhD Scholarships Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, W., Ray, S. (2023). Deep Probability Contour Framework for Tumour Segmentation and Dose Painting in PET Images. In: Greenspan, H., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023. MICCAI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14223. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43901-8_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43901-8_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43900-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43901-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)