Abstract
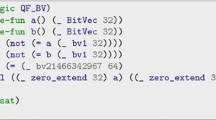
Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) is a well-established methodology that generalises propositional satisfiability (SAT) by adding support for a variety of theories such as integer arithmetic and bit-vector operations. SMT solvers have made rapid progress in recent years. In part, the efficiency of modern SMT solvers derives from the use of specialised decision procedures for each theory. In this paper we explore how the Essence Prime constraint modelling language can be translated to the standard SMT-LIB language. We target four theories: bit-vectors (QF_BV), linear integer arithmetic (QF_LIA), non-linear integer arithmetic (QF_NIA), and integer difference logic (QF_IDL). The encodings are implemented in the constraint modelling tool Savile Row. In an extensive set of experiments, we compare our encodings for the four theories, showing some notable differences and complementary strengths. We also compare our new encodings to the existing work targeting SMT and SAT, and to a well-established learning CP solver. Our two proposed encodings targeting the theory of bit-vectors (QF_BV) both substantially outperform earlier work on encoding to QF_BV on a large and diverse set of problem classes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Experiment scripts, model and parameter files and raw results can be found at: https://github.com/stacs-cp/CP2020-SRSMT [10].
References
Akgün, Ö., Gent, I.P., Jefferson, C., Miguel, I., Nightingale, P.: Exploiting short supports for improved encoding of arbitrary constraints into SAT. In: Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming - 22nd International Conference, CP, Toulouse, France, pp. 3–12 (2016)
Amadini, R., Gabbrielli, M., Mauro, J.: SUNNY-CP and the MiniZinc challenge. Theory Pract. Log. Programm. 18(1), 81–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1471068417000205
Bacchus, F.: GAC via unit propagation. In: Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming, 13th International Conference, CP Providence, RI, USA, pp. 133–147 (2007)
Barrett, C., Fontaine, P., Tinelli, C.: The SMT-LIB standard: version 2.6. Technical report, Department of Computer Science, The University of Iowa (2017). www.SMT-LIB.org
Belov, G., Stuckey, P.J., Tack, G., Wallace, M.: Improved linearization of constraint programming models. In: Rueher, M. (ed.) CP 2016. LNCS, vol. 9892, pp. 49–65. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44953-1_4
Bofill, M., Palahı, M., Suy, J., Villaret, M.: SIMPLY: a compiler from a CSP modeling language to the SMT-LIB format. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Constraint Modelling and Reformulation, pp. 30–44 (2009)
Bofill, M., Palahí, M., Suy, J., Villaret, M.: Solving constraint satisfaction problems with SAT modulo theories. Constraints 17(3), 273–303 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10601-012-9123-1
Bofill, M., Palahí, M., Suy, J., Villaret, M.: Solving intensional weighted CSPs by incremental optimization with BDDs. In: O’Sullivan, B. (ed.) CP 2014. LNCS, vol. 8656, pp. 207–223. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10428-7_17
Contaldo, F., Trentin, P., Sebastiani, R.: From minizinc to optimization modulo theories, and back (extended version). CoRR abs/1912.01476 (2019). http://arxiv.org/abs/1912.01476
Davidson, E., Akgün, Ö., Espasa, J., Nightingale, P.: Experiments for CP2020 SR-SMT paper (2020). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3953600
Dutertre, B.: Yices 2.2. In: Computer Aided Verification - 26th International Conference, CAV Vienna, Austria, pp. 737–744 (2014)
Dutertre, B., de Moura, L.M.: A fast linear-arithmetic solver for DPLL(T). In: Computer Aided Verification, 18th International Conference, CAV Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 81–94 (2006)
Hadarean, L., Bansal, K., Jovanovic, D., Barrett, C.W., Tinelli, C.: A tale of two solvers: eager and lazy approaches to bit-vectors. In: Computer Aided Verification - 26th International Conference, CAV Vienna, Austria, pp. 680–695 (2014)
Huang, J.: Universal booleanization of constraint models. In: Stuckey, P.J. (ed.) CP 2008. LNCS, vol. 5202, pp. 144–158. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85958-1_10
Kroening, D., Strichman, O.: Decision Procedures - An Algorithmic Point of View. Texts in Theoretical Computer Science. An EATCS Series, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-50497-0
de Moura, L.M., Bjørner, N.: Z3: an efficient SMT solver. In: Tools and Algorithms for the Construction and Analysis of Systems, 14th International Conference, TACAS, Budapest, Hungary, pp. 337–340 (2008)
Nethercote, N., Stuckey, P.J., Becket, R., Brand, S., Duck, G.J., Tack, G.: MiniZinc: towards a standard CP modelling language. In: Bessiere, C. (ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming - CP 2007, 13th International Conference, Providence, RI, USA, vol. 4741, pp. 529–543 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74970-7_38
Niebert, P., Mahfoudh, M., Asarin, E., Bozga, M., Maler, O., Jain, N.: Verification of timed automata via satisfiability checking. In: Formal Techniques in Real-Time and Fault-Tolerant Systems, 7th International Symposium, FTRTFT Oldenburg, Germany, pp. 225–244 (2002)
Niemetz, A., Preiner, M., Wolf, C., Biere, A.: Btor2, BtorMC and Boolector 3.0. In: Computer Aided Verification - 30th International Conference, CAV Oxford, UK, pp. 587–595 (2018)
Nieuwenhuis, R., Oliveras, A., Tinelli, C.: Solving SAT and SAT modulo theories: from an abstract Davis-Putnam-Logemann-Loveland procedure to DPLL(T). J. ACM 53(6), 937–977 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1217856.1217859
Nightingale, P., Akgün, Ö., Gent, I.P., Jefferson, C., Miguel, I., Spracklen, P.: Automatically improving constraint models in Savile Row. Artif. Intell. 251, 35–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2017.07.001
Nightingale, P., Rendl, A.: Essence’ description. Computing Research Repository (CoRR) abs/1601.02865 (2016), http://arxiv.org/abs/1601.02865
Nightingale, P., Spracklen, P., Miguel, I.: Automatically improving SAT encoding of constraint problems through common subexpression elimination in Savile row. In: Pesant, G. (ed.) CP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9255, pp. 330–340. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23219-5_23
Sebastiani, R., Trentin, P.: OptiMathSAT: a tool for optimization modulo theories. In: Computer Aided Verification - 27th International Conference, CAV, San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 447–454 (2015)
Van Hentenryck, P.: The OPL Optimization Programming Language. MIT Press (1999)
Acknowledgements
We thank Marc Roig Vilamala who worked on an early version of the SMT backend of Savile Row. This work is supported by EPSRC grant EP/P015638/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Davidson, E., Akgün, Ö., Espasa, J., Nightingale, P. (2020). Effective Encodings of Constraint Programming Models to SMT. In: Simonis, H. (eds) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming. CP 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12333. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58475-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58475-7_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58474-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58475-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)