Abstract
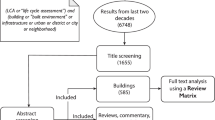
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a methodology to systematically investigating impacts from interactions between environment and human activities. However, the number of parameters and uncertainty factors that characterize built impacts over their full-lifecycle, preclude a broader LCA adoption. This enable faster progress towards reducing building impacts by combining established environmental impact assessment methods with artificial intelligence approaches, such as machine learning (ML) and neural networks. This article will present previous research on ML for LCA of buildings. To achieve this goal, we perform a Systematic Literature Review (SLR). SLR was governed by the question “What are scientific research developed for Architecture, Engineering and Construction (AEC) industry in LCA and ML context?”. This SLR was performed in three databases: Scopus, Engineering Village and Web of Science, using keywords: Life Cycle Assessment, Machine Learning, Learning, Building and Neural Network. From SLR, we identified best practices, acquired and developed by other studies, clarifying how to interpret large data sets monitored through advanced analysis to improve LCA. The results showed: (i) number of articles increase in recent years; (ii) the most searched environmental indicators are energy consumption and Global Warming Potential (GWP); (iii) machine learning is mainly used for prediction impacts and; (iv) the most used ML method is Artificial Neural Networks. Advances in LCA and ML field can contribute to calculation and analysis of buildings environmental indicators, as well as can develop and improve LCA methods. The combination of reliable data and ML will produce an unprecedented change in speed and accuracy of LCA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Amico, B., Myers, R.J., Sykes, J., Voss, E., Cousins-Jenvey, B., Fawcett, W., Richardson, S., Kermani, A., Pomponi, F.: Machine learning for sustainable structures: a call for data. Structures 19, 1–4 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2018.11.013
D’Amico, A., Ciulla, G., Traverso, M., Lo Brano, V., Palumbo, E.: Artificial Neural Networks to assess energy and environmental performance of buildings: an Italian case study. J. Clean. Prod. 239, 117993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.117993
Li, Y., Zhang, H., Roy, U., Lee, Y.T.: A data-driven approach for improving sustainability assessment in advanced manufacturing. In: Nie, J.Y., Obradovic, Z., Suzumura, T., Ghosh, R., Nambiar, R., Wang, C., Zang, H., BaezaYates, R., Hu, X., Kepner, J., Cuzzocrea, A., Tang, J., Toyoda, M. (eds.) IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). IEEE, Boston (2017)
Kitchenham, B., Charters, S.: Guidelines for performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering, UK (2007)
Dresch, A., Lacerda, D.P., Antunes Junior, J.A.V.: Design Science Research: A Method for Science and Technology Advancement. Springer, Cham (2015)
Manfren, M., Caputo, P., Costa, G.: Paradigm shift in urban energy systems through distributed generation: methods and models. Appl. Energy 88, 1032–1048 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.10.018
Sharif, S.A., Hammad, A.: Developing surrogate ANN for selecting near-optimal building energy renovation methods considering energy consumption, LCC and LCA. J. Build. Eng. 25, 100790 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOBE.2019.100790
Azari, R., Garshasbi, S., Amini, P., Rashed-Ali, H., Mohammadi, Y.: Multi-objective optimization of building envelope design for life cycle environmental performance. Energy Build. 126, 524–534 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.05.054
Perrotta, F., Parry, T., Neves, L.C., Mesgarpour, M.: A machine learning approach for the estimation of fuel consumption related to road pavement rolling resistance for large fleets of trucks. In: The Sixth International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering (IALCCE 2018), Belgium (2018)
Ma, J., Kim, H.M.: Predictive usage mining for life cycle assessment. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 38, 125–143 (2015)
Duprez, S., Fouquet, M., Herreros, Q., Jusselme, T.: Improving life cycle-based exploration methods by coupling sensitivity analysis and metamodels. Sustain. Cities Soc. 44, 70–84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.09.032
Wang, E., Shen, Z.: Lifecycle energy consumption prediction of residential buildings by incorporating longitudinal uncertainties. J. Civ. Eng. Manage. 19, S161–S171 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3846/13923730.2013.802744
Ziyadi, M., Al-Qadi, I.L.: Model uncertainty analysis using data analytics for life-cycle assessment (LCA) applications. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 24, 945–959 (2018)
Shi, Q., Xu, Y.: The selection of green building materials using GA-BP hybrid algorithm. In: 2009 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, pp. 40–45 (2009)
Marvuglia, A., Kanevski, M., Benetto, E.: Machine learning for toxicity characterization of organic chemical emissions using USEtox database: learning the structure of the input space. Environ. Int. 83, 72–85 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.05.011
Schwartz, Y., Raslan, R., Mumovic, D.: Implementing multi objective genetic algorithm for life cycle carbon footprint and life cycle cost minimisation: a building refurbishment case study. Energy 97, 58–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.11.056
Xia, L., Liu, J.: Research on green building assessment system based on bp neural network and life cycle assessment (LCA). Appl. Mech. Mater. 357–360, 508–514 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.357-360.508
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Barros, N.N., Ruschel, R.C. (2021). Machine Learning for Whole-Building Life Cycle Assessment: A Systematic Literature Review. In: Toledo Santos, E., Scheer, S. (eds) Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering. ICCCBE 2020. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 98. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51295-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51295-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51294-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51295-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)