Abstract
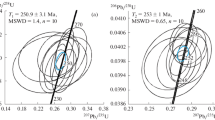
The chapter presents data on Rb–Sr and Sm–Nd TIMS analysis of pyroxenes, plagioclases, gross samples of igneous rocks and sulphide ores. In most Sm–Nd analyses of minerals, the isotope system (pyroxene–plagioclase) does not reflect the age of intrusions and shows a rejuvenated or aged isochronous age. Only for the Kharaelakh intrusion, one 241 ± 32 Ma isochron was obtained, close to the U–Pb age of zircons. The primary isotope ratio 87Sr/88Sr and the εNd parameter of samples are calculated for the age of 250 Ma based on the average U–Pb age of zircons. The primary ratio of plagioclases strontium from magmatic rocks of intrusions (0.7032–0.7090) is lower than that of ore sulphides (0.7081–0.7116). The heterogeneity of Sr and Nd isotope composition of minerals and rocks within a single intrusion is caused by different degrees of impact of ore and host-rock contamination. In the gross samples of igneous rocks from the studied massifs, the primary ratio of strontium varies from 0.7049 to 0.7128, and εNd varies from −7.7 to +7.0. These data indicate a significant effect of the crustal component in the formation of igneous rocks during the injection of mantle material with the parameters 87Sr/88Sr = 0.7037 and εNd = +9.5. Based on Nd and Sr isotopic data, it is impossible to clearly distinguish groups of intrusions with different ore content.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arndt NT, Czamanske GK, Walker RJ et al (2003) Geochemistry and origin of the intrusion hosts of the Noril’sk-Talnakh Cu–Ni–PGE sulphide deposits. Econ Geology 98:495–515
Faure G (1989) Fundamentals of isotope geology. M.: Mir, 590 p
Liew TC, Hofmann AW (1988) Precambrian crustal components, plutonic associations, plate environment of the Hercynian Fold Belt of central Europe: Indications from a Nd and Sr isotopic study. Contrib Mineral Petrol 98:129–138
Goldstein SJ, Jacobsen SB (1988) Nd and Sr isotopic systematics of river water suspended material: implications for crustal evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 87:249–265
De Paolo DJ, Wasserburg GJ (1976) Nd Isotopic variations and petrogenetic models. Geophys Rev Lett 3:249–252
Ludwig KR (1999) User’s manual for Isoplot/Ex. Vers. 2.05. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley, Special Publication N 1a. 48 p
Jacobsen SB, Wasserburg GJ (1980) Sm-Nd isotopic evolution of chondrites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 50:139–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bogomolov, Y., Belyatsky, B., Krymsky, R., Pushkarev, Y. (2019). Strontium and Neodymium Isotopes. In: Petrov, O. (eds) Isotope Geology of the Norilsk Deposits. Springer Geology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05216-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05216-4_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-05215-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-05216-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)