Abstract
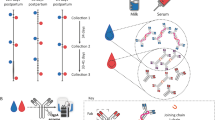
Different protocols are required for the collection and isolation of antibodies from various body sites. For the sample collection factors to be considered include anatomic or physiological particularities. Secretory fluids such as saliva, gastrointestinal fluid, or breast milk may contain degrading enzymes that potentially affect the integrity of isolated antibodies. While the isolation of IgG from plasma is a common and often-described procedure, here we focus on methodological approaches to isolate antibodies immunoglobulin A (IgA) or IgM from plasma or secretory fluids. These protocols shall facilitate research on natural and induced antibodies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mantis NJ, Rol N, Corthesy B (2011) Secretory IgA's complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol 4(6):603–611
von Gunten S, Schaub A, Vogel M, Stadler BM, Miescher S, Simon HU (2006) Immunological and functional evidence for anti-Siglec-9 autoantibodies in intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) preparations. Blood 108(13):4255–4259
Altznauer F, von Gunten S, Späth P, Simon H-U (2003) Concurrent presence of agonistic and antagonistic anti-CD95 autoantibodies in intravenous Ig preparations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112(6):1185–1190
Quast I, Keller CW, Maurer MA, Giddens JP, Tackenberg B, Wang L-X et al (2015) Sialylation of IgG Fc domain impairs complement-dependent cytotoxicity. J Clin Invest 125(11):4160–4170
Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Donkova-Petrini V, Carbonneil C, Misra N, Lepelletier Y et al (2004) Natural antibodies sustain differentiation and maturation of human dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(39):14210–14215
Kaveri SV (2012) Intravenous immunoglobulin: exploiting the potential of natural antibodies. Autoimmun Rev 11(11):792–794
Trinath J, Hegde P, Sharma M, Maddur MS, Rabin M, Vallat JM et al (2013) Intravenous immunoglobulin expands regulatory T cells via induction of cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 in human dendritic cells. Blood 122(8):1419–1427
Kaveri S, Vassilev T, Hurez V, Lengagne R, Lefranc C, Cot S et al (1996) Antibodies to a conserved region of HLA class I molecules, capable of modulating CD8 T cell-mediated function, are present in pooled normal immunoglobulin for therapeutic use. J Clin Invest 97(3):865–869
Svetlicky N, Ortega-Hernandez O-D, Mouthon L, Guillevin L, Thiesen H-J, Altman A et al (2013) The advantage of specific intravenous immunoglobulin (sIVIG) on regular IVIG: experience of the last decade. J Clin Immunol 33(1):27–32
Schaub A, von Gunten S, Vogel M, Wymann S, Ruegsegger M, Stadler BM et al (2011) Dimeric IVIG contains natural anti-Siglec-9 autoantibodies and their anti-idiotypes. Allergy 66(8):1030–1037
von Gunten S, Simon HU (2012) Granulocyte death regulation by naturally occurring autoantibodies. Adv Exp Med Biol 750:157–172
von Gunten S, Vogel M, Schaub A, Stadler BM, Miescher S, Crocker PR et al (2007) Intravenous immunoglobulin preparations contain anti-Siglec-8 autoantibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119(4):1005–1011
Gelfand EW (2012) Intravenous immune globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 367(21):2015–2025
Gilardin L, Bayry J, Kaveri SV (2014) Intravenous immunoglobulin as clinical immune-modulating therapy. CMAJ 187:257–264
von Gunten S, Simon HU (2008) Natural anti-Siglec autoantibodies mediate potential immunoregulatory mechanisms: implications for the clinical use of intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg). Autoimmun Rev 7(6):453–456
von Gunten S, Simon H-U (2010) Cell death modulation by intravenous immunoglobulin. J Clin Immunol 30(1):24–30
von Gunten S, Shoenfeld Y, Blank M, Branch DR, Vassilev T, Kasermann F et al (2014) IVIG pluripotency and the concept of Fc-sialylation: challenges to the scientist. Nat Rev Immunol 14(5):349
von Gunten S (2014) Protein-glycan interactions as targets of intravenous/subcutaneous immunoglobulin (IVIg/SCIg) preparations. Clin Exp Immunol 178:151–152
Schneider C, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Boligan KF, Hamilton RG, Bochner BS et al (2015) The human IgG anti-carbohydrate repertoire exhibits a universal architecture and contains specificity for microbial attachment sites. Sci Transl Med 7(269):269ra1
von Gunten S, Smith D, Cummings R, Riedel S, Miescher S, Schaub A et al (2009) Intravenous immunoglobulin contains a broad repertoire of anti-carbohydrate antibodies that is no restricted to the IgG2 subclass. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(6):1268–1276
Stowell SR, Arthur CM, McBride R, Berger O, Razi N, Heimburg-Molinaro J et al (2014) Microbial glycan microarrays define key features of host-microbial interactions. Nat Chem Biol 10(6):470–476
Grader-Beck T, Boin F, von Gunten S, Smith D, Rosen A, Bochner BS (2011) Antibodies recognising sulfated carbohydrates are prevalent in systemic sclerosis and associated with pulmonary vascular disease. Ann Rheum Dis 70(12):2218–2224
Antalis TM, Shea-Donohue T, Vogel SN, Sears C, Fasano A (2007) Mechanisms of disease: protease functions in intestinal mucosal pathobiology. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 4(7):393–402
Andreas NJ, Kampmann B, Mehring Le-Doare K (2015) Human breast milk: a review on its composition and bioactivity. Early Hum Dev 91(11):629–635
Marsh PD, Do T, Beighton D, Devine DA (2006) Influence of saliva on the oral microbiota. Periodontol 70(1):80–92
Gaspari MM, Brennan PT, Solomon SM, Elson CO (1988) A method of obtaining, processing, and analyzing human intestinal secretions for antibody content. J Immunol Methods 110(1):85–91
Wehrli M, Cortinas-Elizondo F, Hlushchuk R, Daudel F, Villiger PM, Miescher S et al (2014) Human IgA Fc receptor FcαRI (CD89) triggers different forms of neutrophil death depending on the inflammatory microenvironment. J Immunol 193(11):5649–5659
Rossato E, Ben Mkaddem S, Kanamaru Y, Hurtado-Nedelec M, Hayem G, Descatoire V et al (2015) Reversal of arthritis by human monomeric IgA through the receptor-mediated SH2 domain–containing phosphatase 1 inhibitory pathway. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(7):1766–1777
Acknowledgments
Research by the authors is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant No. 310030_162552/1) and the Bulgarian–Swiss Research Program (BSRP) No. IZEBZO_142967 to SVG. MW received support from the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant No. 323530-139174, MD-PhD Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Schneider, C., Illi, M., Lötscher, M., Wehrli, M., von Gunten, S. (2017). Isolation of Antibodies from Human Plasma, Saliva, Breast Milk, and Gastrointestinal Fluid. In: Kaveri, S., Bayry, J. (eds) Natural Antibodies. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1643. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7180-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7180-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7179-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7180-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols