Abstract
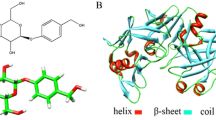
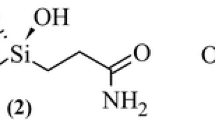
In this study we report the X-ray analysis of a complex between the aspartic protease endothiapepsin (EC 3.4.23.6) and an inhibitor bound as a carbonyl hydrate (gem-diol) to the catalytic aspartates of this enzyme, in a manner closely resembling the putative tetrahedral intermediate in proteolytic cleavage of the peptide bond.1 This study was undertaken in order to obtain a closer model of the interactions stabilizing this intermediate than those used in previous analyses, which were based on X-ray crystallographic data obtained from inhibitors lacking one or both of the hydroxyl residues of this species.2,3
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Full experimental details will be reported elsewhere. The coordinates of the complex will be deposited in the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank.
M. N. G. James and A. R. Sielecki, Stereochemical analysis of peptide bond hydrolysis catalyzed by the aspartic proteinase penicillopepsin, Biochemistry 24: 3701 (1985).
K. Suguna, E. A. Padlan, C. W. Smith, W. D. Carlson, and D. R. Davies, Binding of a reduced peptide inhibitor to the aspartic proteinase from rhizopus chinensis: implications for a mechanism of action, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 84: 7009 (1987).
A. Sali, B. Veerapandian, J. B. Cooper, S. I. Foundling, D. J. Hoover, and T. L. Blundell, High-resolution X-ray diffraction study of the complex between endothiapepsin and an oligopeptide inhibitor: the analysis of the inhibitor binding and description of the rigid body shift in the enzyme, Embo J. 8: 2179 (1989), and refs. therein.
M. H. Gelb, J. P. Svaren, and R. H. Abeles, Fluoro-ketone inhibitors of hydrolytic enzymes, Biochemistry 24: 1813 (1985).
S. Thaisrivongs, D. T. Pals, W. M. Kati, S. R. Turner, L. M. Thomasco, and W. Watt, Design and synthesis of potent and specific renin inhibitors containing difluorostatine, difluorostatone, and related analogs, J. Med. Chem. 29: 2080 (1986), and references therein.
D. B. Damon and D. J. Hoover, Synthesis of the ketodifluoromethylene dipeptide isostere, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112: 6439 (1990).
T. Ishihara, T. Yamanaka, and T. Ando, New low-valent titanium catalyzed reaction of chlorodifluoromethyl ketones leading to difluorinated ß-hydroxy ketones, Chem. Lett. 1165 (1984).
A. Goldblum, Theoretical calculations on the acidity of the active site in aspartic proteinases, Biochemistry 27: 1653 (1988).
P. Deslongchamps, Stereoelectronic control in the cleavage of tetrahedral intermediates in the hydrolysis of esters and amides, Tetrahedron 31: 2463 (1975).
R. A. Eades, D. A. Well, D. A. Dixon, and C. H. Douglass, Jr., Inversion barriers in methyl-substituted amines, J. Phys. Chem. 85: 976 (1981).
L. Polgar, The mechanism of action of aspartic proteases involves ‘push-pull’ catalysis, FEBS Lett. 219: 1 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hoover, D.J. et al. (1991). X-Ray Analysis of a Difluorostatone Renin Inhibitor Bound as the Tetrahedral Hydrate to the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin. In: Dunn, B.M. (eds) Structure and Function of the Aspartic Proteinases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 306. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-6012-4_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-6012-4_32
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-6014-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-6012-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive