Abstract
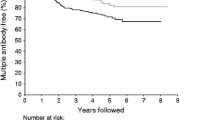
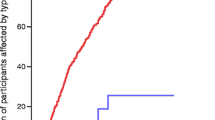
It is widely accepted that autoimmune mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of type I (insulin-dependent, IDDM) diabetes mellitus. (1)Islet cell antibodies (ICA) reacting with antigens in the cytoplasma, or on the surface of islet-cells (ICSA), or against a 64 kD human islet-cell protein, as well as insulin autoantibodies (lAA) are present years before the onset of clinical diabetes. They probably serve as serologic markers of ongoing beta-cell destruction in predisposed individuals. In monozygotic twins initially discordant for type I diabetes, loss of beta-cell function has been shown to be temporarily associated with the presence of ICA (2). Several studies in discordant monozygotic twins or first-degree relatives of type I diabetics revealed that ICA-positive relatives are more likely to develop overt diabetes than are the ICA-negative (3). Moreover, the presence of both ICA and lAA in these individuals confers an even higher risk of progression to IDDM (1)
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srikanta, S., Ricker, T., McCulloch, D.K., Soeldner, J.S., Eisenbarth, G.S., and Palmer, J.P., 1986, Diabetes 35: 139–142.
Srikanta, S., Ganda, O.P., Jackson, R.A., Gleason, R.E., Kaldany, A., Garovoy, M.R., Milford, E.L., Carpenter, C.B., Soeldner, J.S., and Eisenbarth, G.S., 1983, Type 1 diabetes mellitus in monozygotic twins: chronic progressive beta cell dysfunction. Ann Interr Med 99: 320–326.
Spencer, J.M., Tarn, A., Dean, B.M., Lister, J., and Bottazzo, F., 1984, Fluctuating islet-cell automimmunity in unaffected relatives of patients with insulin-dependent idabetes. Lancet, i: 764–766.
Spinas, G.A., Keller, U., Neri, T.M., Matter, L., Staffelbach, O., and Berger, W., 1985, HLA-Antigene and Inselzellantikorper bei Typ-l-Diabe- tikern verschiedener Altersgruppen und ihren Verwandten 1. Grades Schweiz Med Wschr 115: 48–54.
Wilkin, T.J., Hoskins, P.J., Armitage, M., Kodier, M., Casey, C., Diaz, J., Pyke, D.A., and Leslie, R.D.G., 1985, Value of insulin autoantibodies as serum markers for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet i: 480–482.
Srikanta, S., Ganda, O.P., Rabizadeh, A., Soeldner, J.S., and Eisenbarth, G.S., 1985, First-degree relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Islet-cell antibodies and abnormal insulin secretion. N Engl J Med 313: 461–464.
Marner, B., Agner, T., Binder, C., Lernmark, A., Nerup, J., Mandrup- Poulsen, T., and Waldorff, S., 1985, Increased reduction in fasting C-pep- tide is associated with islet-cell antibodies in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 28: 875–800.
Irvine, W.J., McCallum, C.J.M., Gray, R.S., Campbell, C.J., Ducan, L.J.P., Farquhar, J.W., Vaughan, H., and Morris, P.J., 1977, Pancreatic islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus correlated with the duration and type of diabetes, coexistent autoimmune disease, and HLA type. Diabetes 26: 138–147.
Gleichmann, H., Zoercher, B., Greulich, B., Gries, F.A., Henrichs, R., Bertrams, J., and Kolb, H., 1984, Correlation of islet-cell antibodies and HLA-DR phenotypes with diabetes mellitus in adults. Diabetologia 27: 90–92.
Sochett, C., McKey, M., Yoon, J.W., and Daneman, D., 1986, Insulin antibodies in IDDM children before insulin therapy: relationship to islet- cell antibodies, C-peptide and antibody response to human insulin. Diabetes 35: 93 A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1988 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Spinas, G.A., Matter, L., Wilkin, T., Staffelbach, O., Berger, W. (1988). Iselt-Cell and Insulin Autoantibodies in First-Degree Relatives of Type I Diabetics: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study in a Swiss Population. In: Camerini-Davalos, R.A., Cole, H.S. (eds) Prediabetes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 246. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5616-5_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5616-5_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5618-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5616-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive