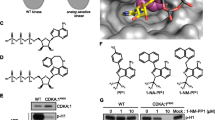
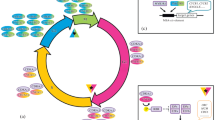
The production of new cells by division and their subsequent elongation are key cellular events in the plant life cycle. The orderly progression of cells through the various phases of the cell cycle and their appropriate responses to nutritional, hormonal, developmental and environmental signals are governed by multiple regulatory mechanisms, including reversible protein phosphorylation, inter- actions of proteins, and specific protein degradation. Since protein phosphorylation is widely recognized to be the major mechanism controlling cell cycle progression, the roles of different kinases, and particularly the family of cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), are critical for cell division control. After discovery of plant homolo gues of cdc2/CDC28 kinases by complementation of the yeast temp erature sensitive mutants, the functional characterization of the plant CDK genes and protein complexes was largely based on the use of tissue culture systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayaydin F, Vissi E, Mészáros T, Miskolczi P, Kovács I, Fehér A, Dombrádi V, Erdődi F, Gergely P, Dudits D (2000) Inhibition of serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatases causes premature activation of cdc2MsF kinase at G2/M transition and early mitotic microtubule organization in alfalfa. Plant J 23: 85-96.
Fehér A, Pasternak T, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an em-bryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74(3): 201-228.
Ötvös K, Paternak T, Miskolczi P, Domoki M, Djorgotov D, Szűcs A, Bottka S, Dudits D, Fehér A. (2005) Nitric oxide is required for, and promotes auxin-mediated activation of, cell division and embryogenic cell formation but does not influence cell cycle progression in alfalfa cell cultures. Plant J 43: 849-860.
Magyar Z, Mészáros T, Miskolczi P, Deák M, Fehér A, Brown, S, Kondorosi É, Athanasiadis A, Pongor S, Bilgin M, Bakó L, Koncz CS, Dudits D (1997) Cell cycle phase specificity of putative cyclin-dependent kinase variants in synchronized alfalfa cells. The Plant Cell 9: 223-235.
Zhiponova MK, Pettkó-Szandtner A, Stelkovics É, Neer Zs, Bottka S, Krenács T, Dudits D, Fehér A, Szilák L (2006) Mitosis-specific promoter of the alfalfa cyclin-dependent Kinase Gene (Medsa;CDKB2;1) is activated by wounding and ethylene in a non-cell division-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 140: 693-703.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dudits, D., Cserháti, M., Miskolczi, P., Fehér, A., Ayaydin, F., Horváth, G.V. (2007). Use of Alfalfa In Vitro Cultures in Studies on Regulation of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) Functions. In: Xu, Z., Li, J., Xue, Y., Yang, W. (eds) Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture 2006 and Beyond. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6635-1_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6635-1_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-6634-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-6635-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)