Abstract
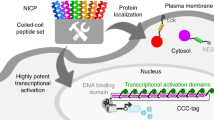
Protein interactions play a crucial role in a variety of biological processes. Therefore, regulation of these interactions has received considerable attention in terms of synthetic biology tool development. Of those, a toolbox of small peptides known as coiled coils (CCs) represents a unique effective tool for mediating protein–protein interactions because their binding specificity and affinity can be designed and controlled. CC peptides have been used as a building module for designing synthetic regulatory circuits in mammalian cells, construction of fast response to a signal, amplification of the response, and localization and regulation of function of diverse proteins. In this chapter, we describe a designed set of CCs used for mammalian cell engineering and provide a protocol for the construction of CC-mediated logic circuits in mammalian cells. Ultimately, these tools could be used for diverse biotechnological and therapeutic applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burkhard P, Stetefeld J, Strelkov SV (2001) Coiled coils: a highly versatile protein folding motif. Trends Cell Biol 11:82–88
Woolfson DN (2005) The design of coiled-coil structures and assemblies. Adv Protein Chem 70:79–112
Ljubetič A, Lapenta F, Gradišar H et al (2017) Design of coiled-coil protein-origami cages that self-assemble in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 35:1094–1101
Beesley JL, Woolfson DN (2019) The de novo design of α-helical peptides for supramolecular self-assembly. Curr Opin Biotechnol 58:175–182
Božič Abram S, Gradišar H, Aupič J et al (2021) Triangular in vivo self-assembling coiled-coil protein origami. ACS Chem Biol 16:310–315
Gradišar H, Božič S, Doles T et al (2013) Design of a single-chain polypeptide tetrahedron assembled from coiled-coil segments. Nat Chem Biol 9:362–366
Fink T, Lonzarić J, Praznik A et al (2019) Design of fast proteolysis-based signaling and logic circuits in mammalian cells. Nat Chem Biol 15:115–122
Lebar T, Lainšček D, Merljak E et al (2020) A tunable orthogonal coiled-coil interaction toolbox for engineering mammalian cells. Nat Chem Biol 16:513–519
Plaper T, Aupič J, Dekleva P et al (2021) Coiled-coil heterodimers with increased stability for cellular regulation and sensing SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cell fusion. Sci Rep 111(11):1–16
Praznik A, Fink T, Franko N et al (2022) Regulation of protein secretion through chemical regulation of endoplasmic reticulum retention signal cleavage. Nat Commun 13:1–14
Lainšček D, Forstnerič V, Mikolič V et al (2022) Coiled-coil heterodimer-based recruitment of an exonuclease to CRISPR/Cas for enhanced gene editing. Nat Commun 131(13):1–12
Cho JH, Collins JJ, Wong WW (2018) Universal chimeric antigen receptors for multiplexed and logical control of T cell responses. Cell 173:1426–1438
Chao G, Wannier TM, Gutierrez C et al (2022) helixCAM: a platform for programmable cellular assembly in bacteria and human cells. Cell 185:3551–3567
Plaper T, Merljak E, Fink T et al (2022) Designed allosteric protein logic. bioRxiv 2022.06.03.494683. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.03.494683
Woodall NB, Weinberg Z, Park J et al (2021) De novo design of tyrosine and serine kinase-driven protein switches. Nat Struct Mol Biol 28:762–770
Aupič J, Lapenta F, Strmšek Ž et al (2022) Metal ion–regulated assembly of designed modular protein cages. Sci Adv 8:8243
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang R-Y et al (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the Slovenian Research Agency grant number P4-0176, Z4-2657, N4-0080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Rihtar, E., Fink, T., Jerala, R. (2024). Coiled-Coil Interaction Toolbox for Engineering Mammalian Cells. In: Ceroni, F., Polizzi, K. (eds) Mammalian Synthetic Systems. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2774. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3718-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3718-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3717-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3718-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols