Abstract
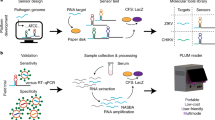
Norovirus infections are the leading cause of foodborne illness and human gastroenteritis, afflicting hundreds of millions of people each year. Molecular assays with the capacity to detect norovirus without expensive equipment and with high sensitivity and specificity represent useful tools to track and contain future outbreaks. Here we describe how norovirus can be detected in low-cost paper-based cell-free reactions. These assays combine freeze-dried, thermostable cell-free transcription-translation reactions with toehold switch riboregulators designed to target the norovirus genome, enabling convenient colorimetric assay readouts. Coupling cell-free reactions with synbody-based viral enrichment and isothermal amplification enables detection of norovirus from clinical samples down to concentrations as low as 270 zM. These diagnostic tests are promising assays for confronting norovirus outbreaks and can be adapted to a variety of other human pathogens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartsch SM, Lopman BA, Ozawa S et al (2016) Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS One 11:e0151219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151219
Siebenga JJ, Vennema H, Zheng DP et al (2009) Norovirus illness is a global problem: emergence and spread of norovirus gii.4 variants, 2001–2007. J Infect Dis 200:802–812. https://doi.org/10.1086/605127
Ambert-Balay K, Pothier P (2013) Evaluation of 4 immunochromatographic tests for rapid detection of norovirus in faecal samples. J Clin Virol 56:278–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2012.11.001
Vyas K, Atkinson C, Clark DA, Irish D (2015) Comparison of five commercially available immunochromatographic tests for the detection of norovirus in faecal specimens. J Hosp Infect 91:176–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2015.06.013
Henningsson AJ, Nilsson Bowers A, Nordgren J et al (2017) Rapid diagnosis of acute norovirus-associated gastroenteritis: evaluation of the Xpert Norovirus assay and its implementation as a 24/7 service in three hospitals in Jönköping County, Sweden. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36:1867–1871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3005-9
Green AA, Silver PA, Collins JJ, Yin P (2014) Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression. Cell 159:925–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.002
Ma D, Shen L, Wu K et al (2018) Low-cost detection of norovirus using paper-based cell-free systems and synbody-based viral enrichment. Synth Biol 3. https://doi.org/10.1093/SYNBIO/YSY018
Green AA, Kim J, Ma D et al (2017) Complex cellular logic computation using ribocomputing devices. Nature 548:117–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23271
Pardee K, Green AA, Ferrante T et al (2014) Paper-based synthetic gene networks. Cell 159:940–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.004
Pardee K, Green AA, Takahashi MK et al (2016) Rapid, low-cost detection of zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell 165:1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.059
Amalfitano E, Karlikow M, Norouzi M et al (2021) A glucose meter interface for point-of-care gene circuit-based diagnostics. Nat Commun 12:724
Kim J, Zhou Y, Carlson PD et al (2019) De novo-designed translation-repressing riboregulators for multi-input cellular logic. Nat Chem Biol 15:1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0388-1
Hong F, Ma D, Wu K et al (2020) Precise and programmable detection of mutations using ultraspecific riboregulators. Cell 180:1018–1032.e16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.011
Takahashi MK, Tan X, Dy AJ et al (2018) A low-cost paper-based synthetic biology platform for analyzing gut microbiota and host biomarkers. Nat Commun 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05864-4
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY et al (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1318
Gupta N, Lainson JC, Belcher PE et al (2017) Cross-reactive synbody affinity ligands for capturing diverse noroviruses. Anal Chem 89:7174–7181. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Wu, K., Green, A.A. (2022). Detection of Norovirus Using Paper-Based Cell-Free Systems. In: Karim, A.S., Jewett, M.C. (eds) Cell-Free Gene Expression. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2433. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1998-8_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1998-8_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1997-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1998-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols