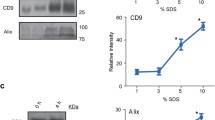
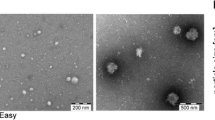
Abstract
Dengue is an infectious disease caused by Dengue Virus, mainly transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Severe dengue is a potentially fatal syndrome in consequence of overwhelmed inflammation, in which thrombocytopenia and increased vascular permeability are frequently observed. Several experimental evidences point to the participation of both microvesicles (MVs) and circulating lipoproteins in inflammatory amplification in dengue pathogenesis. On this regard, many protocols for isolating plasma MVs have shown lipoproteins as the main contaminant. This is a limitation to studies aiming at the functional characterization of MVs, since both MVs and lipoproteins can modulate inflammatory responses. Here, we describe a biphasic density-based gradient ultracentrifugation as a tool for concomitant isolation of MVs and lipoproteins without cross-contamination. Flow cytometry for MVs quantification and western blot for detection of apoB100 may be used to confirm the isolation and purity of the MVs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilder-Smith A, Ooi EE, Horstick O et al (2019) Dengue. Lancet 393(10169):350–363
de Almeida RR, Paim B, de Oliveira SA et al (2017) Dengue hemorrhagic fever: a state-of-the-art review focused in pulmonary involvement. Lung 195:389–395
Punyadee N, Mairiang D, Thiemmeca S et al (2015) Microparticles provide a novel biomarker to predict severe clinical outcomes of dengue virus infection. J Virol 89:1587–1607
Patil R, Bajpai S, Ghosh K et al (2018) Microparticles as prognostic biomarkers in dengue virus infection. Acta Trop 181:21–24
Hottz ED, Lopes JF, Freitas C et al (2013) Platelets mediate increased endothelium permeability in dengue through NLRP3-inflammasome activation. Blood 122:3405–3414
Burger D, Schock S, Thompson CS et al (2013) Microparticles: biomarkers and beyond. Clin Sci 124:423–441
Sódar BW, Kittel Á, Pálóczi K et al (2016) Low-density lipoprotein mimics blood plasma-derived exosomes and microvesicles during isolation and detection. Sci Rep 6:24316
Zhang P, Yeo JC, Lim CT (2019) Advances in technologies for purification and enrichment of extracellular vesicles. SLAS Technol 24:477–488
Shelness GS, Sellers JA (2001) Very-low-density lipoprotein assembly and secretion. Curr Opin Lipidol 12:151–157
Kurien BT, Scofield RH (2006) Western blotting. Methods 38:283–293
Lacroix R, Judicone C, Mooberry M et al (2013) Standardization of pre-analytical variables in plasma microparticle determination: results of the international society on thrombosis and Haemostasis SSC collaborative workshop. J Thromb Haemost 11:1190–1193
Lee RD, Barcel DA, Williams JC et al (2012) Pre-analytical and analytical variables affecting the measurement of plasma-derived microparticle tissue factor activity. Thromb Res 129:80–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Merij, L.B., Andrade, F.B., Silva, A.R., Hottz, E.D. (2022). Isolation of Microvesicles from Plasma Samples Avoiding Lipoprotein Contamination. In: Mohana-Borges, R. (eds) Dengue Virus. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2409. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1879-0_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1879-0_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1878-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1879-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols