Abstract
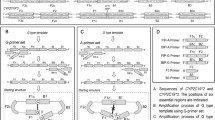
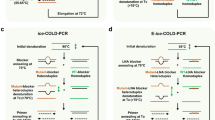
Single-nucleotide variations have been associated to various genetic diseases, variations on drug efficiency, and differences in cancer prognostics. The detection of these changes in nucleic acid sequences from patient samples is particularly useful for accurate diagnosis, therapeutics, and disease management. A reliable allele-specific amplification is still an important challenge for molecular-based diagnostic technologies. In the last years, allele-specific primers have been designed for promoting the enrichment of certain variants, based on a higher stability of primer/template duplexes. Also, several methods are based on the addition of a blocking oligonucleotide that prevent the amplification of a specific variant, enabling that other DNA variants can be observed. In this context, genotyping methods based on isothermal amplification techniques are increasing, especially those assays aimed to be deployed at point-of-care applications. The correct selection of target sequences is crucial for reaching the required analytical performances, in terms of reaction time, amplification yield, and selectivity. The present chapter describes the design criteria for the selection of primers and blockers for relevant PCR approaches and novel isothermal strategies. Several successful examples are provided in order to highlight the main design restrictions and the potential to be extended to other applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karki R, Pandya D, Elston RC, Ferlini C (2015) Defining “mutation” and “polymorphism” in the era of personal genomics. BMC Med Genet 8(1):37
Růžička M, Kulhánek P, Radová L, Čechová A, Špačková N, Fajkusová L, Réblová K (2017) DNA mutation motifs in the genes associated with inherited diseases. PLoS One 12(8):e0182377
Wu LR, Chen SX, Wu Y, Patel AA, Zhang DY (2017) Multiplexed enrichment of rare DNA variants via sequence-selective and temperature-robust amplification. Nat Biomed Eng 1(9):714–723
Rodríguez A, Rodríguez M, Córdoba JJ, Andrade MJ (2015) Design of primers and probes for quantitative real-time PCR methods. In: PCR primer design. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 31–56
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL (2012) Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics 13(1):134
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40(15):e115
Raymaekers M, Smets R, Maes B, Cartuyvels R (2009) Checklist for optimization and validation of real-time PCR assays. J Clin Lab Anal 23(3):145–151
Bustin S, Huggett J (2017) qPCR primer design revisited. Biomol Detect Quant 14:19–28
Neff MM, Turk E, Kalishman M (2002) Web-based primer design for single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Trends Genet 18(12):613–615
Tortajada-Genaro LA, Puchades R, Maquieira Á (2017) Primer design for SNP genotyping based on allele-specific amplification—application to organ transplantation pharmacogenomics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 136:14–21
Wangkumhang P, Chaichoompu K, Ngamphiw C, Ruangrit U, Chanprasert J, Assawamakin A, Tongsima S (2007) WASP: a web-based allele-specific PCR assay designing tool for detecting SNPs and mutations. BMC Genomics 8(1):1–9
You FM, Huo N, Gu YQ, Luo MC, Ma Y, Hane D, Lazo GR, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (2008) BatchPrimer3: a high-throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1):253
Day JP, Barany F, Bergstrom D, Hammer RP (1999) Nucleotide analogs facilitate base conversion with 3′ mismatch primers. Nucleic Acids Res 27(8):1810–1818
Newton CR, Heptinstall LE, Summers C, Super M, Schwarz M, Anwar R, Graham A, Smith JC, Markham AF (1989) Amplification refractory mutation system for prenatal diagnosis and carrier assessment in cystic fibrosis. Lancet 334(8678–8679):1481–1483
Little S (1995) Amplification-refractory mutation system (ARMS) analysis of point mutations. Curr Protoc Hum Genet 7(1):9–8
Luo JD, Chan EC, Shih CL, Chen TL, Liang Y, Hwang TL, Chiou CC (2006) Detection of rare mutant K-ras DNA in a single-tube reaction using peptide nucleic acid as both PCR clamp and sensor probe. Nucleic Acids Res 34(2):e12
Hao W, Fan L, Chen Q, Chen X, Zhang S, Lan K, Lu J, Zhang C (2015) Modified proofreading PCR for detection of point mutations, insertions and deletions using a ddNTP-blocked primer. PLoS One 10(4):e0123468
Dominguez PL, Kolodney MS (2005) Wild-type blocking polymerase chain reaction for detection of single-nucleotide minority mutations from clinical specimens. Oncogene 24(45):6830–6834
Choi JJ, Jang M, Kim J, Park H (2010) Highly sensitive PNA array platform technology for single-nucleotide mismatch discrimination. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(2):287–293
Zhang S, Chen Z, Huang C, Ding C, Li C, Chen J, Zhao J, Miao L (2019) Ultrasensitive and quantitative detection of EGFR mutations in plasma samples from patients with non-small-cell lung cancer using a dual PNA clamping-mediated LNA-PNA PCR clamp. Analyst 144(5):1718–1724
Latorra D, Campbell K, Wolter A, Hurley JM (2003) Enhanced allele-specific PCR discrimination in SNP genotyping using 3′ locked nucleic acid (LNA) primers. Hum Mutat 22(1):79–85
Craw P, Balachandran W (2012) Isothermal nucleic acid amplification technologies for point-of-care diagnostics: a critical review. Lab Chip 12(14):2469–2486
Tortajada-Genaro LA, Santiago-Felipe S, Maquieira A (2017) Isothermal nucleic acid amplification for food toxicity analyses. In: Analysis of food toxins and toxicants, vol 2. Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, p 103
Mayboroda O, Katakis I, O’Sullivan CK (2018) Multiplexed isothermal nucleic acid amplification. Anal Biochem 545:20–30
Piepenburg O, Williams CH, Stemple DL, Armes NA (2006) DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol 4(7):e204
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28(12):e63–e63
Fire A, Xu SQ (1995) Rolling replication of short DNA circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(10):4641–4645
Higgins M, Ravenhall M, Ward D, Phelan J, Ibrahim A, Forrest MS, Clark TG, Campino S (2019) PrimedRPA: primer design for recombinase polymerase amplification assays. Bioinformatics 35(4):682–684
Torres C, Vitalis EA, Baker BR, Gardner SN, Torres MW, Dzenitis JM (2011) LAVA: an open-source approach to designing LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) DNA signatures. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1):240
Wang C, Chen X, Wu Y, Li H, Wang Y, Pan X, Tang T, Liu Z, Li X (2016) Lateral flow strip for visual detection of K-ras mutations based on allele-specific PCR. Biotechnol Lett 38(10):1709–1714
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M (2014) Single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breed 33(1):1–14
Tortajada-Genaro LA, Mena S, Niñoles R, Puigmule M, Viladevall L, Maquieira Á (2016) Genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(9):2339–2345
Yamanaka ES, Tortajada-Genaro LA, Maquieira Á (2017) Low-cost genotyping method based on allele-specific recombinase polymerase amplification and colorimetric microarray detection. Microchim Acta 184(5):1453–1462
Martorell S, Palanca S, Maquieira Á, Tortajada-Genaro LA (2018) Blocked recombinase polymerase amplification for mutation analysis of PIK3CA gene. Anal Biochem 544:49–56
Martorell S, Tortajada-Genaro LA, Maquieira Á (2019) Magnetic concentration of allele-specific products from recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal Chim Acta 1092:49–56
Zhang L, Zhang Y, Wang C, Feng Q, Fan F, Zhang G, Kang X, Qin X, Sun J, Li Y, Jiang X (2014) Integrated microcapillary for sample-to-answer nucleic acid pretreatment, amplification, and detection. Anal Chem 86(20):10461–10466
Yongkiettrakul S, Kampeera J, Chareanchim W, Rattanajak R, Pornthanakasem W, Kiatpathomchai W, Kongkasuriyachai D (2017) Simple detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism in Plasmodium falciparum by SNP-LAMP assay combined with lateral flow dipstick. Parasitol Int 66(1):964–971
Yamanaka ES, Tortajada-Genaro LA, Pastor N, Maquieira Á (2018) Polymorphism genotyping based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification and smartphone detection. Biosens Bioelectron 109:177–183
Ren Y, Li Y, Duan X, Wang H, Wang H, Li Z (2019) One-step quantitative single- nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) diagnosis by modified loop-mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP). ChemistrySelect 4(4):1423–1427
Su Q, Xing D, Zhou X (2010) Magnetic beads based rolling circle amplification–electrochemiluminescence assay for highly sensitive detection of point mutation. Biosens Bioelectron 25(7):1615–1621
Itonaga M, Matsuzaki I, Warigaya K, Tamura T, Shimizu Y, Fujimoto M, Kojima F, Ichinose M, Murata SI (2016) Novel methodology for rapid detection of KRAS mutation using PNA-LNA-mediated loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS One 11(3):e0151654
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Tortajada-Genaro, L.A. (2022). Design of Oligonucleotides for Allele-Specific Amplification Based on PCR and Isothermal Techniques. In: Basu, C. (eds) PCR Primer Design. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2392. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1799-1_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1799-1_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1798-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1799-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols