Abstract
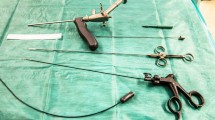
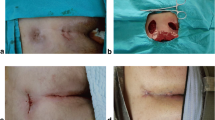
A vessel loop drainage after subcutaneous destruction of the sinus tract is a minimal invasive surgical treatment of pilonidal sinus disease (PSD). We started to use this technique in May 2015 and operated until now 38 patients with the simple forms of PSD on an outpatient basis. All patients have been investigated until 90 postoperative days but a 1-year follow-up time has been completed by less than 50% of patients. Three patients with persisting secretion from wound orifice over 6 weeks have been revised with a mosquito clamp under the local anaesthesia. Two patients developed recurrent PSD after completed wound healing in 6 and 10 months, respectively. These patients have been operated in the same technique under the local anaesthesia with a good postoperative result during the next 90 days. There are no adverse events like abscesses. The first results of these technique are promising; however the valid date are missing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanat BH, Sözen S (2015) Disease that should be remembered: sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease and short history. World J Clin Cases 3(10):876–879
Fahrni GT, Vuille-Dit-Bille RN, Leu S, Meuli M, Staerkle RF, Fink L, Dinçler S, Muff BS (2016) Five-year follow-up and recurrence rates following surgery for acute and chronic pilonidal disease: a survey of 421 cases. Wounds 28(1):20–26
Segre D, Pozzo M, Perinotti R, Roche B, Italian Society of Colorectal Surgery (2015) The treatment of pilonidal disease: guidelines of the Italian Society of Colorectal Surgery (SICCR). Tech Coloproctol 19(10):607–613
Iesalnieks I, Ommer A, Petersen S, Doll D, Herold A (2016) German national guideline on the management of pilonidal disease. Langenbecks Arch Surg 401(5):599–609
Kueper J, Evers T, Wietelmann K, Doll D, Roffeis J, Schwabe P, Märdian S, Wichlas F, Krapohl BD (2015) Sinus pilonidalis in patients of German military hospitals: a review. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW 4:Doc02
Lee PJ, Raniga S, Biyani DK, Watson AJ, Faragher IG, Frizelle FA (2008) Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. Colorectal Dis 10(7):639–650
Soll C, Dindo D, Steinemann D, Hauffe T, Clavien PA, Hahnloser D (2011) Sinusectomy for primary pilonidal sinus: less is more. Surgery 150(5):996–1001
Immerman SC (2014) Treatment of pilonidal disease using the Bascom ‘Cleft-Lift’ procedure. Am Surg 80(2):E49–E50
Sevinç B, Karahan Ö, Okuş A, Ay S, Aksoy N, Şimşek G (2016) Randomized prospective comparison of midline and off-midline closure techniques in pilonidal sinus surgery. Surgery 159(3):749–754
Shabbir J, Chaudhary BN, Britton DC (2011) Management of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease: a snapshot of current practice. Int J Colorectal Dis 26(12):1619–1620
McCallum IJ, King PM, Bruce J (2008) Healing by primary closure versus open healing after surgery for pilonidal sinus: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 336:868–871
Bascom J, Bascom T (2007) Utility of the cleft lift procedure in refractory pilonidal disease. Am J Surg 193(5):606–609
Karydakis GE (1973) New approach to the problem of pilonidal sinus. Lancet 2(7843):1414–1415
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendlandt TP, Ludwig K (2002) Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of the results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 45:1458–1467
Guner A, Ozkan OF, Kece C, Kesici S, Kucuktulu U (2013) Modification of the Bascom cleft lift procedure for chronic pilonidal sinus: results in 141 patients. Colorectal Dis 15(7):e402–e406
Keshvari A, Keramati MR, Fazeli MS, Kazemeini A, Nouritaromlou MK (2016) Risk factors for complications and recurrence after the Karydakis flap. J Surg Res 204(1):55–60
Lord PH, Millar DM (1965) Pilonidal sinus: a simple treatment. Br J Surg 52:298–300
Zinicola R, Cracco N, Serventi A, Martina S, Milone M, Sallustio P, Bondurri A, Giani I, Figus A, Zorcolo L (2014) Pilonidal sinus: are we missing something? Colorectal Dis 16(11):929–930
Guner A, Cekic AB, Boz A, Turkyilmaz S, Kucuktulu U (2016) A proposed staging system for chronic symptomatic pilonidal sinus disease and results in patients treated with stage-based approach. BMC Surg 16:18
Tezel EA (2007) New classification according to navicular area concept for sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. Colorectal Dis 9(6):575–576
Irkorucu O, Erdem H, Reyhan E (2012) The best therapy for pilonidal disease: which management for which type? World J Surg 36:691–692
Enriquez-Navascues JM, Emparanza JI, Alkorta M, Placer C (2014) Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing different techniques with primary closure for chronic pilonidal sinus. Tech Coloproctol 18(10):863–872
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Korenkov, M. (2017). Subcutaneous Destruction of Sinus Tract with Long-Term Vessel-Loop Drainage as Minimal Invasive Surgical Treatment for Primary Pilonidal Sinus. In: Shiffman, M., Low, M. (eds) Biofilm, Pilonidal Cysts and Sinuses. Recent Clinical Techniques, Results, and Research in Wounds, vol 1. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/15695_2017_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/15695_2017_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-03076-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-03077-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)