Abstract
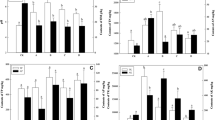
The present experiment was conducted to study the effects of vinasse application on physico-chemical properties of soil. Different treatments, viz., (i) spraying water at 105.0 t/ha (CK), (ii) conventional fertilization + spraying water at 105.0 t/ha (CF) and (iii) soil application of vinasse at 75.0 t/ha + spraying water at 30.0 t/ha, have been applied in two sugarcane fields in Fusui County, Guangxi, during 2005–2006 and 2006–2007, respectively. The results showed that, after 2–3 years of continuous vinasse application to sugarcane fields, the soil bulk density declined, while the total porosity and capillary porosity increased in the plow layer of soil. The soil water stable aggregate content enhanced, but the soil clay content decreased. Soil K content increased, and soil did not showed the phenomenon of acidification. The vinasse application in sugarcane fields resulted in improved physico-chemical properties of soil, and soil hardening and soil acidification were not detected in the field. The present study not only provides the basis of using vinasse as a liquid fertilizer in agriculture fields but also help in reducing the environmental pollution imposed due to disposal of non-treated sugar industry effluents.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao, J.H., H.H. Deng, Q.W. Li, Z.R. Huang, and Y. Jiang. 2009. Effects of vinasse on the properties of soil. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences 7: 177–180.
Anonymous, 1986. Efeitos da aplicacao da vinhaca como fertilizante em cana de acúcar. Boletín Técnico Copersucar 7: 9–14.
Anonymous, 1980. Aplicacao de vinhaca a soqueira da cana de acúcar en tres anos consecutivos. Boletín Técnico Copersucar 12: 2–5.
Cambardella, C.A., and E.T. Elliott. 1992. Particulate soil organic matter across a grassland cultivation sequence. Soil Science Society of America Journal 56: 776–783.
Elliott, E.T. 1986. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 50: 627–633.
Gloria, N. 1985. Environmental aspects in ethanol production related to vinasse disposal and groundwater, 31. Piracicaba: ESALQ.
García, A. 1994. Efecto de la concentración de electrolitos en el agua de riego, sobre la recuperación de suelos sódicos. Uso de vinazas. Suelos Ecuatoriales 24: 80–83.
Hidalgo, K. 2009. Vinasse in feed: Good for animal and environment. Feed Technology 13(5): 18–20.
Li, X.G., Z.J. Cui, L.Y. Wang, and H.J. Hu. 2002. Effects of salinization and organic matter on soil structural stability and atterberg limits. Acta Pedologica Sinica 39(4): 550–559.
Li, Y.R., Q.Z. Zhu, and W.Z. Wang. 2008. Multiple location experiment of technique system for direct rational application of vinasse from cane mill in sugarcane fields. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 21(3): 749–756.
Lu, R.K. 2000. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis, 150–416. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
Meng, Y.C., Q.Z. Tang, Z. Liu, G.F. Chen, and Y. Wang. 2009. Impact of several organic materials of sugar industry on soil microbe population in sugarcane field. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 22(2): 389–392.
Mo, Y.C., Y.P. Ye, Q. Liang, and Y.R. Li. 2009. Effects of vinasse on the quality of sugarcane and key enzymes in sucrose synthesis. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 22(1): 55–59.
Orlando, F. 1984. Simposio sobre Fertilizantes na Agricultura Brasileira, 451–475. Brasília, DF, Anais.
Ou, S.B., H. Yang, H.Q. Liang, H.Z. Zhou, and Z.M. Fang. 2002. Review and prospect of vinasse management technology of China. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry 4: 10–21.
Pereira, S.Y. 2008. Environmental aspects in ethanol production related to vinasse disposal and groundwater. In: 33rd International geological congress, OSLO, August 6–14.
Puget, P., D.A. Angers, and C. Chenu. 1999. Nature of carbohydrates associated with water-stable aggregates of two cultivated soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 31(1): 55–63.
Su, T.M., Y.R. Li, G.P. Wei, and Z.P. Jiang. 2009. Effect of sugarcane vinasse on soil physicochemical properties and oxidoreductase enzymes. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture 6: 1106–1110.
Sun, B., T.L. Zhang, and Q.G. Zhao. 1999. Fertility evolution of red soil derived from quaternary red clay in low-hilly region middle subtropics: I. Evolution of soil physical fertility. Acta Pedologica Sinica 36(2): 203–217.
Wu, S.J., F.S. Lan, J. Luo, N.Z. Huang, F. Li, C.Q. Xu, and T. Huang. 1998. Study on the nutrition situation of soil and sugarcane in the main sugarcane productive areas of Guangxi. Guihaia 18(3): 291–297.
Yao, X.L., and D.F. Yu. 1966. Effect of different structures of red soil on some water physical properties in the hilly region of Jiangxi. Acta Pedologica Sinica 14(1): 65–72.
You, Q., T.M. Su, and Y. Zhong. 2009. Effects of vinasse on sugarcane field. Guangxi Agricultural Sciences 40(6): 677–680.
Zhou, M.Q., Y.H. Luo, Z.B. Zhou, D.Y. Gong, and X. Zhou. 2008. The effect of alcohol waste liquid (as a top dressing) on growth and yield of sugarcane. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences 36(6): 102–103.
Zhou, Z.B., Y.H. Luo, M.Q. Zhou, D.Y. Gong, and X. Zhou. 2009. Effects of alcohol wastewater (as basal manure or dressing) from the sugar refinery on growth and economic benefit of sugarcane. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences 37(6): 66–68.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by National Technology Support Project (2007BAD30B03), Guangxi Environmental Protection Special Fund (No. 81 GHJ2005), Guangxi Science and Technology Key Project (0782004-3) and Guangxi Science and Technology Project (GKN05112001-5B2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, ZP., Li, YR., Wei, GP. et al. Effect of Long-Term Vinasse Application on Physico-chemical Properties of Sugarcane Field Soils. Sugar Tech 14, 412–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0174-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0174-9