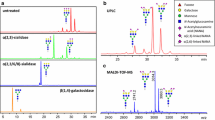
Abstract
More than half of human proteins are glycosylated by a bewildering array of complex and heterogeneous N- and O-linked glycans. They function in myriad biological processes, including cell adhesion and signalling and influence the physical characteristics, stability, function, activity and immunogenicity of soluble glycoproteins. A single protein may be glycosylated differently to yield heterogenous glycoforms. Glycosylation analysis is of increasing interest in biomedical and biological research, the pharmaceutical and healthcare industry and biotechnology. This is because it is increasingly apparent that glycosylation changes in diseases, such as cancer, making it a promising target for development of clinically useful biomarkers and therapeutics. Furthermore, as the non-human cells employed in expression systems glycosylate their proteins very differently to human cells, and as glycosylation changes unpredictably under changing environmental conditions, glycans analysis for quality control, optimum efficacy and safety of recombinant glycoproteins destined for human therapeutic use is paramount. The complexities of carbohydrate chemistry make analysis challenging and while there are a variety of robust methodologies available for glycan analysis, there is currently a pressing need for the development of new, streamlined, high throughput approaches accessible to non-specialist laboratories.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudd, P. M. (1993). Oligosaccharides in human biology. Glyco News, 3, 1–8.
Apweiler, R., Hermjakob, H., & Sharon, N. (1999). On the frequency of protein glycosylation as deduced from analysis of the SWISS-PROT database. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1473, 4–8.
Hagglund, P., Bunkenborg, J., Elortza, F., Jensen, O. N., & Roepstorff, P. (2004). A new strategy for identification of I-glycosylated proteins and unambiguous assignment of their glycosylation sites using HILIC enrichment and partial deglycosylation. Journal of Proteome Research, 3, 556–566.
Kameyama, A., Nakaya, S., Ito, H., Kikuchi, N., Angata, T., Nakamura, M., et al. (2006). Strategy for simulation of CID spectra of N-linked oligosaccharides towards glycomics. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 808–814.
Dwek, R. A. (1996). Glycobiology: Toward the understanding of the function of sugars. Chemical Reviews, 96, 683–720.
Delves, P. J. (1998). The role of glycosylation in autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity, 27, 239–253.
Roseman, S. (2001). Reflections on glycobiology. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 41527–44152.
Haltiwanger, R. S., & Lowe, J. B. (2004). Role of glycosylation in development. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 73, 491–537.
Rudd, P. M., Wormald, M. R., & Dwek, R. A. (2004). Sugar-mediated interactions in the immune system. Trends in Biotechnology, 22, 524–530.
Ohtsubo, K., & Marth, J. D. (2006). Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell, 126, 855–867.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). Disease processes in which carbohydrates are involved, Chapter 16. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 287–312). Oxford: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Taylor, M. E., & Drickamer, K. (2006). Glycosylation and disease, Chapter 12. In Introduction to glycobiology (2nd ed., pp. 218–235). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Dennis, J. W. (1992). Oligosaccharides in carcinogenesis and metastasis. Glyco News, 2, 1–4.
Dall’Olio, F. (1996). Protein glycosylation in cancer biology: An overview. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 49, M126–M135.
Fukuda, M. (1996). Possible roles of tumour associated carbohydrate antigens. Cancer Research, 56, 2237–2244.
Ho, S. B., & Kim, Y. S. (1997). Glycoproteins and glycosylation changes in cancer in Encyclopaedia of Cancer (Vol. II, pp. 744–759). London: Academic Press.
Kannagi, R. (1997). Carbohydrate-mediated cell adhesion involved in hematogenous metastasis of cancer. Glycoconjugate Journal, 14, 577–584.
Kim, Y. J., & Varki, A. (1997). Perspectives on the significance of altered glycosylation of glycoproteins in cancer. Glycoconjugate Journal, 14, 569–576.
Price, J. T., Bonovich, M. T., & Kohn, E. C. (1997). The biochemistry of cancer dissemination. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 32, 175–253.
Brooks, S. A. (2000). The involvement of Helix pomatia lectin (HPA) binding N-acetylgalactosamine glycans in cancer progression. Histology and Histopathology, 15, 143–158.
Dube, D. H., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2005). Glycans in cancer and inflammation–potential for therapeutics and diagnostics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 4, 477–488.
Rademacher, T. W., Parekh, R. B., & Dwek, R. A. (1998). Glycobiology. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 57, 785–838.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). Carbohydrate biotechnology, Chapter 18. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 329–345). Oxford: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Brooks, S. A. (2004). Appropriate glycosylation of recombinant proteins for human use: Implications of choice of expression system. Molecular Biotechnology, 28, 241–256.
Brooks, S. A. (2006). Protein glycosylation in diverse cell systems—implications for modification and analysis of recombinant proteins. Expert Review in Proteomics, 3, 345–359.
Varki, A., Cummings, R. D., Esko, J. D., Freeze, H. H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, P. R., et al. (1999). Saccharide structure and nomenclature, Chapter 2. In Essentials of glycobiology (pp. 17–30). New York: Cold Harbor Laboratory Press.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). An introduction to carbohydrate chemistry, Chapter 1. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 1–30). Oxford: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Van den Eijnden, D. H., & Joziasse, D. H. (1993). Enzymes associated with glycosylation. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 3, 711–721.
Varki, A., Cummings, R. D., Esko, J. D., Freeze, H. H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, P. R., et al. (1999). N-glycans, Chapter 7. In Essentials of glycobiology (pp. 85–100). New York: Cold Harbor Laboratory Press.
Varki, A., Cummings, R. D., Esko, J. D., Freeze, H. H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, P. R., et al. (1999). O-glycans, Chapter 8. In Essentials of glycobiology (pp. 101–114). New York: Cold Harbor Laboratory Press.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). N-linked glycoproteins, Chapter 4. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 73–88). Oxford: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). O-linked (mucin-type) glycoproteins, Chapter 5. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 89–115). Oxford: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Brooks, S. A., Carter, T. M., Royle, L., Harvey, D. J., Fry, S. A., Kinch, C., et al. (2008). Altered glycosylation of proteins in cancer: What is the potential for new anti-tumour strategies? Anticancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 8, 2–21.
Harris, R. J., Leonard, C. K., Guzzetta, A. W., & Spellman, M. W. (1991). Tissue plasminogen activator has an O-linked fucose attached to threonine-61 in the epidermal growth factor domain. Biochemistry, 30, 2311–2314.
Nishimura, H., Takao, T., Hase, S., Shimonishi, Y., & Iwanaga, S. (1992). Human factor IX has a tetrasaccharide O-glycosidically linked to Serine 61 through the fucose residue. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 17520–17525.
Kieliszewski, M. J., O’Neill, M., Leykam, J., & Orlando, R. (1995). Tandem mass spectrometry and structural elucidation of glycopeptides from a hydroxyproline-rich plant cell wall glycoprotein indicate that contiguous hydroxyproline residues are the major sites of hydoxyproline O-arabinosylation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270, 2541–2549.
Duman, J. G., Miele, R. G., Liang, H., Grella, D. K., Sim, K. L., Castellino, F. J., et al. (1998). O-mannosylation of Pichia pastoris cellular and recombinant proteins. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 28, 39–45.
Hanisch, F. -G. (2001). O-glycosylation of the mucin type. Biological Chemistry, 382, 143–149.
Haltiwanger, R. S., Kelly, W. G., Roquemore, E. P., Blomberg, M. A., Dong, L. Y. D., Kreppel, L., et al. (1992). Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins is ubiquitous and dynamic. Biochemical Society Transactions, 20, 264–269.
Hart, G. W. (1997). Dynamic O-linked glycosylation of nuclear and cytoskeletal proteins. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 66, 315–335.
Brockhausen, I. (1995). Biosynthesis of O-glycans of the N-acetylgalactosamine-α-Ser/Thr linkage type, Chapter 5. In J. Montreuil, H. Schacter, & J. F. G. Vliegenthart (Eds.), Glycoproteins (pp. 201–259). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science BV.
Dekker, J., Rossen, J. W. A., Buller, H. A., & Einerhand, A. W. C. (2002). Review: The MUC family—an obituary. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 27, 126–131.
Springer, G. F. (1997). Immunoreactive T and Tn epitopes in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and immunotherapy. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 75, 594–602.
Brooks, S. A., Dwek, M. V., & Schumacher, U. (2002). Glycan chain extension and some common and important glycan structures, Chapter 10. In Functional and molecular glycobiology (pp. 187–202). Oxford, UK: Bios Scientific Publishers, Ltd.
Dwek, R. A., Edge, C. J., Harvey, D. J., Wormald, M. R., & Parekh, R. B. (1993). Analysis of glycoprotein-associated oligosaccharides. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 62, 65–100.
Rudd, P. M., Guile, G. R., Kuster, B., Harvey, D. J., Opdenakker, G., & Dwek, R. A. (1997). Oligosaccharide sequencing technology. Nature, 388, 205–207.
Rudd, P. M., & Dwek, R. A. (1997). Rapid, sensitive sequencing of oligosaccharides from glycoproteins. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 8, 488–497.
Anumula, K. R. (2000). High-sensitivity and high-resolution methods for glycoprotein analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 283, 17–26.
Wuhrer, M., Deelder, A. M., & Hokke, C. H. (2005). Protein glycosylation analysis by liquid chromatography—mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 825, 124–133.
Geyer, H., & Geyer, R. (2006). Strategies for analysis of glycosylation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta—Proteins and Proteomics., 1764, 1853–1869.
Mechref, Y., & Novotny, M. V. (2006). Miniturized separation techniques in glycomic investigations. Journal of Chromatography B, 841, 65–78.
Pilobello, K. T., & Mahal, L. K. (2007). Deciphering the glycocode: The complexity and analytical challenge of glycomics. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 11, 300–305.
Mamitsuka, H. (2007). Informatic innovations in glycobiology: Relevance to drug discovery. Drug Discovery Today, 13, 118–123.
Raman, R., Raguram, S., Venkataraman, G., Paulson, J. C., & Sasisekharan, R. (2005). Glycomics: An integrated systems approach to structure-function relationships of glycans. Nature Methods, 2, 817–824.
Rudiger, H., & Gabius, H. J. (2001). Plant lectins: Occurrence, biochemistry, functions and applications. Glycoconjugate Journal, 18, 589–613.
Sharon, N., & Lis, H. (2004). History of lectins: From hemagglutinins to biological recognition molecules. Glycobiology, 14, 53–62.
Schumacher, U., Brooks, S. A., & Leathem, A. J. (1991). Lectins as tools in histochemical techniques: A review of methodological aspects. In D. C. Kilpatrick, E. Van Driessche, & T. C. Bog-Hansen (Eds.), Lectin reviews (Vol. 1, pp. 195–201). St Louis, MO, USA: Sigma Chemical Company.
Brooks, S. A., Leathem, A. J. C., & Schumacher, U. (1997). Lectin histochemistry—a concise practical handbook. Oxford, UK: Bios Scientific Publishers.
Brooks, S. A., & Hall, D. M. S. (2001). Lectin histochemistry to detect altered glycosylation in cells and tissues. In S. A. Brooks & U. Schumacher (Eds.), Metastasis research protocols, vol I: Analysis of cells and tissues (pp. 49–66). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
Carter, T. M., & Brooks, S. A. (2006). Detection of aberrant glycosylation in breast cancer using lectin histochemistry. In S. A. Brooks & A. Harris (Eds.), Breast Cancer Research Protocols (pp. 201–216). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
Khan, S., Brooks, S. A., & Leathem, A. J. C. (1994). GalNAc-type glycoproteins in breast cancer—a 26 lectin study. Journal of Pathology, 172(Suppl), 134A.
Brooks, S. A., Khan, S., & Leathem, A. J. C. (1994). Lectins—exquisitely selective probes for complex sugars. Histochemical Journal, 26, 602.
Brooks, S. A., & Leathem, A. J. C. (1991). Prediction of lymph node involvement in breast cancer by detection of altered glycosylation in the primary tumour. The Lancet, 338, 71–74.
Hirabayshi, J. (2004). Lectin-based structural glycomics: Glycoproteomics and glycan profiling. Glycoconjugate Journal, 21, 35–40.
Hsu, K. L., & Mahal, L. K. (2006). A lectin microarray approach for the rapid analysis of bacterial glycans. Nature Protocols, 1, 543–549.
Hsu, K. L., Pilobello, K. T., & Mahal, L. K. (2006). Analyzing the dynamic bacterial glycome with a lectin microarray approach. Nature Chemical Biology, 2, 153–157.
Pilobello, K. T., Slawek, D. E., & Mahal, L. K. (2007). A ratiometric lectin microarray approach to analysis of the dynamic mammalian glycome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 11534–11539.
Manimala, J. C., Li, Z. T., Jain, A., VedBrat, S., & Gildersleeve, J. C. (2005). Carbohydrate array analysis of anti-Tn antibodies and lectins reveals unexpected specificities: Implications for diagnostic and vaccine development. ChemBioChem, 6, 2229–2241.
Vocadio, D. J., Hang, H. C., Kim, E. J., Hanover, J. A., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2004). A chemical approach for identifying O-GlcNAc modified proteins in cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 9116–9121.
Saxon, E., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2000). Cell surface engineering by a modified Staudinger reaction. Science, 287, 2007–2010.
Hang, H. C., Yu, C., Kato, D. L., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2003). A metabolic labelling approach toward proteomic analysis of mucin type O-linked glycosylation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 14846–14851.
Prescher, J. A., Dube, D. H., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2004). Chemical remodelling of cell surfaces in living animals. Nature, 430, 873–877.
Dube, D. H., Prescher, J. A., Quang, C. N., & Bertozzi, C. R. (2006). Probing mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in living animals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 4819–4824.
Brooks, S. A., Hall, D. M. S., & Buley, I. (2001). GalNAc glycoprotein expression by breast cell lines, primary breast cancer and normal breast epithelial membrane. British Journal of Cancer, 85, 1014–1022.
Patton W. F. (2002). Fluorescence detection of glycoproteins in gels and on electroblots. In Current protocols in cell biology, Chapter 6, Unit 6.8.
Osborne, C., & Brooks, S. A. (2006). SDS-PAGE and western blotting to detect proteins and glycoproteins of interest in breast cancer research. In S. A. Brooks & A. Harris (Eds.), Breast Cancer Research Protocols (pp. 217–230). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
Wilson, N. L., Schulz, B. L., Karlsson, N. G., & Packer, N. H. (2002). Sequential analysis of N- and O-linked glycosylation of 2D-PAGE separated glycoproteins. Journal of Proteome Research, 1, 521–529.
Dwek, M. V., & Rawlings, S. L. (2002). Current perspectives in cancer proteomics. Molecular Biotechnology, 22, 139–152.
Dwek, M. V., & Rawlings, S. L. (2006). Breast cancer proteomics using two-dimensional electrophoresis: Studying the breast cancer proteome. In S. A. Brooks & A. Harris (Eds.), Breast Cancer Research Protocols (pp. 231–244). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
Dwek, M. V., & Alaiya, A. A. (2003). Proteome analysis enables separate clustering of normal breast, benign breast and breast cancer tissues. Breast Journal of Cancer, 89, 305–307.
Block, T. M., Comunale, M. A., Lowman, M., Steel, L. F., Romano, P. R., Fimmel, C., et al. (2005). Use of targeted glycoproteomics to identify serum glycoproteins that correlate with liver cancer in woodchucks and humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 779–784.
Rudd, P. M., Colominas, C., Royle, L., Murphy, N., Hart, E., Merry, A. H., et al. (2001). A high-performance liquid chromatography based strategy for rapid, sensitive sequencing of N-linked oligosaccharide modifications to proteins in sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel bands. Proteomics, 1, 285–294.
Manzi A. E. (2001). Total compositional analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography or gas-liquid chromatography. In Current protocols in molecular biology, Chapter 17, Unit17, 19A.
Patel, T. P., & Parekh, R. B. (1994). Release of oligosaccharides from glycoproteins by hydrazinolysis. Methods in Enzymology, 230, 57–66.
Morelle, W., & Strecker, G. (1998). Structural analysis of a new series of oligosaccharide-alditols released by reductive beta-elimination from oviducal mucins of Rana utricularia. Biochemical Journal, 330, 469–478.
Huang, Y., Mechref, Y., & Novotny, M. V. (2001). Microscale non-reductive release of O-linked glycans for subsequent analysis through MALDI mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 6063–6069.
Hong, J. C., & Kim, Y. S. (2000). Alkali-catalyzed beta-elimination of periodate-oxidised glycans: A novel method of chemical deglycosylation of mucin gene products in paraffin embedded sections. Glycoconjugate Journal, 17, 691–703.
Hanisch, F. G., Teitz, S., Schwientek, T., & Mueller, S. (2009). Chemical de-O-glycosylation of glycoproteins for application in LC-based proteomics. Proteomics, 9, 710–719.
Kuster, B., Hunter, A. P., Wheeler, S. F., Dwek, R. A., & Harvey, D. J. (1998). Structural determination of N-linked carbohydrates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry following enzymatic release within sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels: Application to species-specific glycosylation of alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Electrophoresis, 19, 1950–1959.
Freeze, H. H., & Varki, A. (1986). Endo-glycosidase F and peptide N-glycosidase F release the great majority of total cellular N-linked oligosaccharides: Use in demonstrating that sulfated N-linked oligosaccharides are frequently found in cultured cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 140, 967–973.
Cataldi, T. R., Campa, C., & De Benedetto, G. E. (2000). Carbohydrate analysis by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection: The potential is still growing. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 368, 739–758.
Rohrer, J. S. (2000). Analyzing sialic acids using high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection. Analytical Biochemistry, 283, 3–9.
Bigge, J. C., Patel, T. P., Bruce, J. A., Goulding, P. N., Charles, S. M., & Parekh, R. B. (1995). Nonselective and efficient fluorescent labeling of glycans using 2-amino benzamide and anthranilic acid. Analytical Biochemistry, 230, 229–238.
Zhuang, Z., Starkey, J. A., Mechref, Y., Novotny, M. V., & Jacobson, S. C. (2007). Electrophoretic analysis of N-glycans on microfluidic devices. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 7170–7175.
Anumula, K. R. (2008). Unique anthranilic acid chemistry facilitates profiling and characterization of Ser/Thr-linked sugar chains following hydrazinolysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 373, 104–111.
Xia, B., Kawar, Z. S., Ju, T. Z., Alvarez, R. A., Sachdev, G. P., & Cummings, R. D. (2005). Versatile fluorescent derivatization of glycans for glycomic analysis. Nature Methods, 2, 845–850.
Royle, L., Campbell, M. P., Radcliffe, C. M., White, D. M., Harvey, D. J., Abrahams, J. L., et al. (2008). HPLC-based analysis of serum N-glycans on a 96-well plate platform with dedicated database software. Analytical Biochemistry, 376, 1–12.
Guile, G. R., Wong, S. Y. C., & Dwek, R. A. (1994). Analytical and preparative separation of anionic oligosaccharides by weak anion exchange high performance liquid chromatography on an inert polymer column. Analytical Biochemistry, 222, 231–235.
Lee, Y. C. (1996). Review: Carbohydrate analyses with high performance anion-exchange chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 720, 137–149.
Nakano, M., Kakehi, K., & Lee, Y. C. (2003). Sample clean-up method for analysis of complex N-glycans released from glycopeptides. Journal of Chromatography A, 1005, 13–21.
Jackson, P. (1991). Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of reducing saccharides labelled with the fluorophore 2-aminoacridone: Subpicomolar detection using an imaging system based on a cooled charge-coupled device. Analytical Biochemistry, 196, 238–244.
Nakajima, K., Oda, Y., Kinoshita, M., & Kakehi, K. (2003). Capillary affinity electrophoresis for the screening of post-translational modification of protein with carbohydrates. Journal of Proteome Research, 2, 81–88.
Park, Y., & Lebrilla, C. B. (2005). Application of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry to oligosaccharides. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 24, 232–264.
Lohmann, K. K., & von der Leith, C. W. (2004). GlycoFragment and GlycoSearchMS: Web tools to support the interpretation of mass spectra of complex carbohydrates. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, W261–W266.
Goldberg, D., Bern, M., Li, B. S., & Lebrilla, C. B. (2005). Automatic determination of O-glycan structure from fragmentation spectra. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 1429–1434.
von der Leith, C. W., Lutteke, T., & Frank, M. (2006). The role of informatics in glycobiology research with special emphasis on automatic interpretation of MS spectra. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1760, 568–577.
Budnik, B. A., Lee, R. S., & Steen, J. A. J. (2006). Global methods for protein glycosylation analysis by mass spectrometry. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta—Proteins and Proteomics, 1764, 1870–1880.
Jang-Jee, J., North, S. J., Sutton-Smith, M., Goldberg, D., Panico, M., Morris, H., et al. (2006). Glycomic profiling of cells and tissues by mass spectrometry: Fingerprinting and sequencing methodologies. Methods in Enzymology, 415, 59–86.
Morelle, W., & Michalski, J. C. (2005). Glycomics and mass spectrometry. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 11, 2615–2645.
Morelle, W., & Michalski, J. C. (2007). Analysis of protein glycosylation by mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 2, 1585–1602.
Lohse, A., Martins, R., Jorgensen, M. R., & Hindgaul, O. (2006). Solid phase oligosaccharide tagging (SPOT): Validation on glycolipid-derived structures. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 45, 4167–4172.
Shimaoka, H., Kuramoto, H., Furukawa, J., Miura, Y., Kurogochi, M., Kita, Y., et al. (2007). One-pot solid-phase glycoblotting and probing by transoximization for high-throughput glycomics and glycoproteomics. Chemistry, 13, 1664–1673.
Uematsu, R., Furukawa, J., Nakagawa, H., Shinohara, Y., Deguchi, K., Monde, K., et al. (2005). High throughput quantitative glycomics and glycoform-focused proteomics of murine dermis and epidermis. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 4, 1977–1989.
Karas, M., & Hillenkamp, F. (1988). Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Analytical Chemistry, 60, 2299–2301.
Wada, Y., Gu, J. G., Okamoto, N., & Inui, K. (1994). Diagnosis of carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome by matrix-assisted laser desorption time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biological Mass Spectrometry, 23, 108–109.
Fenn, J. B., Mann, M., Meng, C. K., & Whitehouse, C. M. (1989). Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science, 246, 64–71.
Harvey, D. J. (1999). Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of carbohydrates. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 18, 349–450.
Dell, A., & Morris, H. R. (2001). Glycoprotein structure determination by mass spectrometry. Science, 291, 2351–2356.
Harvey, D. J., Royle, L., Radcliffe, C. M., Rudd, P. M., & Dwek, R. A. (2008). Structural and quantitative analysis of N-linked glycans by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and negative ion nanospray mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry, 376, 44–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brooks, S.A. Strategies for Analysis of the Glycosylation of Proteins: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Mol Biotechnol 43, 76–88 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9184-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9184-6