Abstract
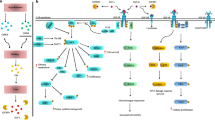
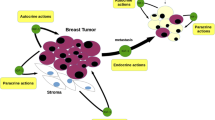
Major molecular abnormalities in breast cancer include the deregulation of several components of the IGF system. It is well recognized that the epithelial breast cancer cells commonly overexpress the IGF-I receptor while IGF-II is expressed by the tumor stroma. In view to the fact that the IGF-IR has mitogenic, pro-invasive and anti-apoptotic effects and mediates resistance to a variety of anti-cancer therapies, breast cancer is expected to be a candidate to therapeutic approaches aimed to inhibit the IGF-IR. However, there is increasing awareness that IGF system in cancer undergoes signal diversification by various mechanisms. One of these mechanisms is the aberrant expression of insulin receptor (IR) isoform A (IR-A), which is a high affinity receptor for both insulin and IGF-II, in breast cancer cells. Moreover, overexpression of both IGF-IR and IR-A in breast cancer cells, leads to overexpression of hybrid IR/IGF-IR receptors (HRs) as well. Upon binding to IGF-II, both IR-A and HRs may activate unique signaling patterns, which predominantly mediate proliferative effects. A better understanding of IGF system signal diversification in breast cancer has important implications for cancer prevention measures, which should include control of insulin resistance and associated hyperinsulinemia. Moreover, in addition to the IGF-IR, both IR-A and HRs should be also considered as molecular targets for anti-cancer therapies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Akt:
-
Thymoma viral proto-oncogene 1
- APS:
-
Associate protein substrate
- ATM:
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- BAD:
-
Bcl-2-associated death promoter
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- Bcl-XL :
-
Basal cell lymphoma-extra large
- Brca1:
-
Breast and ovarian cancer gene 1, early onset
- Cbl:
-
Cas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence
- CDK4:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4
- DMBA:
-
7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)antracene
- 4E-BP1:
-
4E-binding protein 1
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- HER-2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- Erk1/2:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinases
- ES:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- Fak:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- FKHR:
-
Forkhead in human rabdomyosarcoma
- GAB-1:
-
GRB2-associated binding protein 1
- GDP:
-
Guanosine diphosphate
- GH:
-
Growth hormone
- GLUT 4:
-
Glucose transporter protein 4
- GTP:
-
Guanosine-5′-triphosphate
- HIF1:
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1
- HR-A:
-
IR/IGF-IR hybrid A
- HR-B:
-
IR/IGF-IR hybrid B
- HRs:
-
IR/IGF-IR hybrid receptors
- IGFBP3:
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3
- IGF-IR:
-
IGF-I receptor
- IGF-I:
-
Insulin-like growth factor I
- IGF-II:
-
Insulin-like growth factor II
- IGFs:
-
Insulin-like growth factors
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- IR-A:
-
Insulin receptor isoform A
- IR-B:
-
Insulin receptor isoform B
- IRR:
-
Insulin receptor-related receptor
- JNK:
-
Jun N terminal kinase
- LOI:
-
Loss of genomic imprinting
- MAD2:
-
Mitotic arrest deficient 2
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloprotease
- MMTV:
-
Mouse mammary tumor virus
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase
- M6P:
-
Mannose-6-phosphate
- M6P/IGF-IIR:
-
Mannose-6-phosphate/IGF-II receptor
- mSOS:
-
Son of sevenless protein homolog
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PH:
-
Pleckstrin homology
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PKD-1:
-
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1
- PIP3:
-
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
- Ras:
-
Harvey rat sarcoma virus oncogene 1
- RFS:
-
Relapse free survival
- S6K1:
-
Ribosomal S6 kinase 1
- Src:
-
Rous sarcoma oncogene
- SH2:
-
Src-homology 2 domain
- Shc:
-
Src/collagen homology proteins
- TrkC:
-
Tyrosine kinase C receptor
References
Stewart CE, Rotwein P. Growth, differentiation, and survival: multiple physiological functions for insulin-like growth factors. Physiol Rev. 1996;76(4):1005–26.
Bartke A. Minireview: role of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor system in mammalian aging. Endocrinology. 2005;146(9):3718–23. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0411.
Morgan DO, Edman JC, Standring DN, Fried VA, Smith MC, Roth RA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987;329(6137):301–7. doi:10.1038/329301a0.
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(7):505–18. doi:10.1038/nrc1387.
LeRoith D, Roberts CT Jr. The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003;195(2):127–37.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, et al. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet. 1998;351(9113):1393–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10384-1.
Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, Chan JM, Tao Y, Hennekens CH, et al. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91(7):620–5. doi:10.1093/jnci/91.7.620.
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science. 1998;279(5350):563–6. doi:10.1126/science.279.5350.563.
Yu H, Spitz MR, Mistry J, Gu J, Hong WK, Wu X. Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and lung cancer risk: a case–control analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91(2):151–6. doi:10.1093/jnci/91.2.151.
Carboni JM, Lee AV, Hadsell DL, Rowley BR, Lee FY, Bol DK, et al. Tumor development by transgenic expression of a constitutively active insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65(9):3781–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4602.
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Gunther EJ, Chodosh LA, Petrik JJ, Khokha R, et al. Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene. 2007;26(11):1636–44. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209955.
DiGiovanni J, Kiguchi K, Frijhoff A, Wilker E, Bol DK, Beltran L, et al. Deregulated expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 in prostate epithelium leads to neoplasia in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(7):3455–60. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3455.
Hadsell DL, Murphy KL, Bonnette SG, Reece N, Laucirica R, Rosen JM. Cooperative interaction between mutant p53 and des(1–3)IGF-I accelerates mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2000;19(7):889–98. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203386.
Bates P, Fisher R, Ward A, Richardson L, Hill DJ, Graham CF. Mammary cancer in transgenic mice expressing insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II). Br J Cancer. 1995;72(5):1189–93.
Moorehead RA, Fata JE, Johnson MB, Khokha R. Inhibition of mammary epithelial apoptosis and sustained phosphorylation of Akt/PKB in MMTV-IGF-II transgenic mice. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8(1):16–29. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400762.
Byrd JC, Devi GR, de Souza AT, Jirtle RL, MacDonald RG. Disruption of ligand binding to the insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor by cancer-associated missense mutations. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(34):24408–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.34.24408.
Belfiore A. The role of insulin receptor isoforms and hybrid insulin/IGF-I receptors in human cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(7):671–86. doi:10.2174/138161207780249173.
Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Frittitta L, Vigneri R. Obesity and cancer. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2005.10.013.
Strickler HD, Wylie-Rosett J, Rohan T, Hoover DR, Smoller S, Burk RD, et al. The relation of type 2 diabetes and cancer. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2001;3(2):263–74. doi:10.1089/152091501300209633.
Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ. Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159(12):1160–7. doi:10.1093/aje/kwh161.
Kaaks R, Lukanova A. Effects of weight control and physical activity in cancer prevention: role of endogenous hormone metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;963:268–81.
Vainio H, Kaaks R, Bianchini F. Weight control and physical activity in cancer prevention: international evaluation of the evidence. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2002;11(Suppl 2):S94–100.
Fair AM, Dai Q, Shu XO, Matthews CE, Yu H, Jin F, et al. Energy balance, insulin resistance biomarkers, and breast cancer risk. Cancer Detect Prev. 2007;31(3):214–9. doi:10.1016/j.cdp.2007.04.003.
Pisani P. Hyper-insulinaemia and cancer, meta-analyses of epidemiological studies. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008;114(1):63–70. doi:10.1080/13813450801954451.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Pezzino V, Squatrito S, Belfiore A, et al. The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008;114(1):23–37. doi:10.1080/13813450801969715.
Mosthaf L, Grako K, Dull TJ, Coussens L, Ullrich A, McClain DA. Functionally distinct insulin receptors generated by tissue-specific alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1990;9(8):2409–13.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L, Mineo R, Costantino A, et al. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(5):3278–88.
Shier P, Watt VM. Primary structure of a putative receptor for a ligand of the insulin family. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(25):14605–8.
Andersen AS, Wiberg FC, Kjeldsen T. Localization of specific amino acids contributing to insulin specificity of the insulin receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;766:466–8. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb26696.x.
Mynarcik DC, Williams PF, Schaffer L, Yu GQ, Whittaker J. Identification of common ligand binding determinants of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors. Insights into mechanisms of ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(30):18650–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.30.18650.
Yip CC, Hsu H, Patel RG, Hawley DM, Maddux BA, Goldfine ID. Localization of the insulin-binding site to the cysteine-rich region of the insulin receptor alpha-subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;157(1):321–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(88)80050-0.
Whittaker J, Groth AV, Mynarcik DC, Pluzek L, Gadsboll VL, Whittaker LJ. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor ligand binding site. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(47):43980–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102863200.
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986;5(10):2503–12.
Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Ikeya T, Rintelen F, Fernandez R, Hafen E. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr Biol. 2001;11(4):213–21. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00068-9.
Drakas R, Tu X, Baserga R. Control of cell size through phosphorylation of upstream binding factor 1 by nuclear phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(25):9272–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403328101.
Hubbard SR, Wei L, Ellis L, Hendrickson WA. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor. Nature. 1994;372(6508):746–54. doi:10.1038/372746a0.
Pawson T. Signal transduction. Look at a tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1994;372(6508):726–7. doi:10.1038/372726a0.
Lee J, O’Hare T, Pilch PF, Shoelson SE. Insulin receptor autophosphorylation occurs asymmetrically. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(6):4092–8.
White MF, Shoelson SE, Keutmann H, Kahn CR. A cascade of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the beta-subunit activates the phosphotransferase of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(6):2969–80.
Ellis L, Clauser E, Morgan DO, Edery M, Roth RA, Rutter WJ. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986;45(5):721–32. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5.
Wilden PA, Kahn CR, Siddle K, White MF. Insulin receptor kinase domain autophosphorylation regulates receptor enzymatic function. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(23):16660–8.
Chiang SH, Baumann CA, Kanzaki M, Thurmond DC, Watson RT, Neudauer CL, et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature. 2001;410(6831):944–8. doi:10.1038/35073608.
White MF. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin action. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182(1–2):3–11. doi:10.1023/A:1006806722619.
Backer JM, Myers MG Jr, Shoelson SE, Chin DJ, Sun XJ, Miralpeix M, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992;11(9):3469–79.
Skolnik EY, Lee CH, Batzer A, Vicentini LM, Zhou M, Daly R, et al. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993;12(5):1929–36.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, et al. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91(2):231–41. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80405-5.
Barthel A, Schmoll D, Unterman TG. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005;16(4):183–9. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2005.03.010.
Nakae J, Park BC, Accili D. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR on serine 253 through a Wortmannin-sensitive pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(23):15982–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.23.15982.
Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(11):847–59. doi:10.1038/nrc2223.
Zou Y, Tsai WB, Cheng CJ, Hsu C, Chung YM, Li PC, et al. Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a suppresses estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(1):R21. doi:10.1186/bcr1872.
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17(6):596–603. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2005.09.009.
Hay N, Sonenberg N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004;18(16):1926–45. doi:10.1101/gad.1212704.
Wang X, Proud CG. The mTOR pathway in the control of protein synthesis. Physiology (Bethesda). 2006;21:362–9. doi:10.1152/physiol.00024.2006.
Levine AJ, Feng Z, Mak TW, You H, Jin S. Coordination and communication between the p53 and IGF-1–AKT–TOR signal transduction pathways. Genes Dev. 2006;20(3):267–75. doi:10.1101/gad.1363206.
Ceresa BP, Pessin JE. Insulin regulation of the Ras activation/inactivation cycle. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182(1–2):23–9. doi:10.1023/A:1006819008507.
Sasaoka T, Kobayashi M. The functional significance of Shc in insulin signaling as a substrate of the insulin receptor. Endocr J. 2000;47(4):373–81. doi:10.1507/endocrj.47.373.
Kondoh K, Torii S, Nishida E. Control of MAP kinase signaling to the nucleus. Chromosoma. 2005;114(2):86–91. doi:10.1007/s00412-005-0341-9.
Roux PP, Blenis J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004;68(2):320–44. doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.2.320-344.2004.
Brunet A, Roux D, Lenormand P, Dowd S, Keyse S, Pouyssegur J. Nuclear translocation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for growth factor-induced gene expression and cell cycle entry. EMBO J. 1999;18(3):664–74. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.3.664.
Monno S, Newman MV, Cook M, Lowe WL Jr. Insulin-like growth factor I activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2000;141(2):544–50. doi:10.1210/en.141.2.544.
Mamay CL, Mingo-Sion AM, Wolf DM, Molina MD, Van Den Berg CL. An inhibitory function for JNK in the regulation of IGF-I signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22(4):602–14. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206186.
Heron-Milhavet L, Karas M, Goldsmith CM, Baum BJ, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor activation rescues UV-damaged cells through a p38 signaling pathway. Potential role of the IGF-I receptor in DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(21):18185–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011490200.
Bartucci M, Morelli C, Mauro L, Ando S, Surmacz E. Differential insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and function in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61(18):6747–54.
Xu B, Bird VG, Miller WT. Substrate specificities of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase catalytic domains. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(50):29825–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.50.29825.
Zapf A, Hsu D, Olefsky JM. Comparison of the intracellular itineraries of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin and their receptors in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1994;134(6):2445–52. doi:10.1210/en.134.6.2445.
Mastick CC, Brady MJ, Printen JA, Ribon V, Saltiel AR. Spatial determinants of specificity in insulin action. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182(1–2):65–71. doi:10.1023/A:1006835430797.
Najjar SM, Blakesley VA, Li Calzi S, Kato H, LeRoith D, Choice CV. Differential phosphorylation of pp120 by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors: role for the C-terminal domain of the beta-subunit. Biochemistry. 1997;36(22):6827–34. doi:10.1021/bi962634h.
O’Neill TJ, Zhu Y, Gustafson TA. Interaction of MAD2 with the carboxyl terminus of the insulin receptor but not with the IGFIR. Evidence for release from the insulin receptor after activation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(15):10035–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.15.10035.
Baumann CA, Ribon V, Kanzaki M, Thurmond DC, Mora S, Shigematsu S, et al. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature. 2000;407(6801):202–7. doi:10.1038/35025089.
Hu J, Liu J, Ghirlando R, Saltiel AR, Hubbard SR. Structural basis for recruitment of the adaptor protein APS to the activated insulin receptor. Mol Cell. 2003;12(6):1379–89. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00487-8.
Liu J, Kimura A, Baumann CA, Saltiel AR. APS facilitates c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in response to insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(11):3599–609. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.11.3599-3609.2002.
Kanzaki M. Insulin receptor signals regulating GLUT4 translocation and actin dynamics. Endocr J. 2006;53(3):267–93. doi:10.1507/endocrj.KR-65.
Butler AA, Blakesley VA, Koval A, deJong R, Groffen J, LeRoith D. In vivo regulation of CrkII and CrkL proto-oncogenes in the uterus by insulin-like growth factor-I. Differential effects on tyrosine phosphorylation and association with paxillin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(44):27660–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.44.27660.
Koval AP, Blakesley VA, Roberts CT Jr, Zick Y, Leroith D. Interaction in vitro of the product of the c-Crk-II proto-oncogene with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Biochem J. 1998;330(Pt 2):923–32.
Klammt J, Barnikol-Oettler A, Kiess W. Mutational analysis of the interaction between insulin receptor and IGF-I receptor with c-Crk and Crk-L in a yeast two-hybrid system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;325(1):183–90. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.10.018.
Furlanetto RW, Dey BR, Lopaczynski W, Nissley SP. 14-3-3 proteins interact with the insulin-like growth factor receptor but not the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1997;327(Pt 3):765–71.
Dupont J, Khan J, Qu BH, Metzler P, Helman L, LeRoith D. Insulin and IGF-1 induce different patterns of gene expression in mouse fibroblast NIH-3T3 cells: identification by cDNA microarray analysis. Endocrinology. 2001;142(11):4969–75. doi:10.1210/en.142.11.4969.
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD. Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(1):56–68. doi:10.1038/nrm1549.
Pillay TS, Sasaoka T, Olefsky JM. Insulin stimulates the tyrosine dephosphorylation of pp125 focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(3):991–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.3.991.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Malaguarnera R, Mandarino A, Messina RL, Sciacca L, et al. Role of c-Abl in directing metabolic versus mitogenic effects in insulin receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(36):26077–88. doi:10.1074/jbc.M705008200.
Urso B, Cope DL, Kalloo-Hosein HE, Hayward AC, Whitehead JP, O’Rahilly S, et al. Differences in signaling properties of the cytoplasmic domains of the insulin receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(43):30864–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.43.30864.
Siddle K, Urso B, Niesler CA, Cope DL, Molina L, Surinya KH, et al. Specificity in ligand binding and intracellular signalling by insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29(Pt 4):513–25. doi:10.1042/BST0290513.
Kornfeld S. Structure and function of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulinlike growth factor II receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:307–30. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001515.
Oka Y, Rozek LM, Czech MP. Direct demonstration of rapid insulin-like growth factor II. Receptor internalization and recycling in rat adipocytes. Insulin stimulates 125I-insulin-like growth factor II degradation by modulating the IGF-II receptor recycling process. J Biol Chem. 1985;260(16):9435–42.
Wang ZQ, Fung MR, Barlow DP, Wagner EF. Regulation of embryonic growth and lysosomal targeting by the imprinted Igf2/Mpr gene. Nature. 1994;372(6505):464–7. doi:10.1038/372464a0.
Lau MM, Stewart CE, Liu Z, Bhatt H, Rotwein P, Stewart CL. Loss of the imprinted IGF2/cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor results in fetal overgrowth and perinatal lethality. Genes Dev. 1994;8(24):2953–63. doi:10.1101/gad.8.24.2953.
Zaina S, Squire S. The soluble type 2 insulin-like growth factor (IGF-II) receptor reduces organ size by IGF-II-mediated and IGF-II-independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(44):28610–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.44.28610.
Wutz A, Theussl HC, Dausman J, Jaenisch R, Barlow DP, Wagner EF. Non-imprinted Igf2r expression decreases growth and rescues the Tme mutation in mice. Development. 2001;128(10):1881–7.
Christoforidis A, Maniadaki I, Stanhope R. Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis during puberty. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2005;3(1):5–10.
Ruan W, Newman CB, Kleinberg DL. Intact and amino-terminally shortened forms of insulin-like growth factor I induce mammary gland differentiation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(22):10872–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.22.10872.
Ruan W, Powell-Braxton L, Kopchick JJ, Kleinberg DL. Evidence that insulin-like growth factor I and growth hormone are required for prostate gland development. Endocrinology. 1999;140(5):1984–9. doi:10.1210/en.140.5.1984.
Probst-Hensch NM, Yuan JM, Stanczyk FZ, Gao YT, Ross RK, Yu MC. IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 in prediagnostic serum: association with colorectal cancer in a cohort of Chinese men in Shanghai. Br J Cancer. 2001;85(11):1695–9. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2001.2172.
Zhao H, Grossman HB, Spitz MR, Lerner SP, Zhang K, Wu X. Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and binding protein-3, and their association with bladder cancer risk. J Urol. 2003;169(2):714–7. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)63999-7.
Moon JW, Chang YS, Ahn CW, Yoo KN, Shin JH, Kong JH, et al. Promoter −202 A/C polymorphism of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene and non-small cell lung cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(2):353–6. doi:10.1002/ijc.21339.
Zecevic M, Amos CI, Gu X, Campos IM, Jones JS, Lynch PM, et al. IGF1 gene polymorphism and risk for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(2):139–43.
Wagner K, Hemminki K, Israelsson E, Grzybowska E, Soderberg M, Pamula J, et al. Polymorphisms in the IGF-1 and IGFBP 3 promoter and the risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;92(2):133–40. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-2417-x.
Yu H, Li BD, Smith M, Shi R, Berkel HJ, Kato I. Polymorphic CA repeats in the IGF-I gene and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2001;70(2):117–22. doi:10.1023/A:1012947027213.
Habuchi T. Common genetic polymorphisms and prognosis of sporadic cancers: prostate cancer as a model. Future Oncol. 2006;2(2):233–45. doi:10.2217/14796694.2.2.233.
Cui H, Cruz-Correa M, Giardiello FM, Hutcheon DF, Kafonek DR, Brandenburg S, et al. Loss of IGF2 imprinting: a potential marker of colorectal cancer risk. Science. 2003;299(5613):1753–5. doi:10.1126/science.1080902.
Feinberg AP. Genomic imprinting and gene activation in cancer. Nat Genet. 1993;4(2):110–3. doi:10.1038/ng0693-110.
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D, Brodt P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 2007;28(1):20–47. doi:10.1210/er.2006-0001.
Hakam A, Yeatman TJ, Lu L, Mora L, Marcet G, Nicosia SV, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol. 1999;30(10):1128–33. doi:10.1016/S0046-8177(99)90027-8.
Gicquel C, Bertagna X, Gaston V, Coste J, Louvel A, Baudin E, et al. Molecular markers and long-term recurrences in a large cohort of patients with sporadic adrenocortical tumors. Cancer Res. 2001;61(18):6762–7.
Liu JL, Yakar S, LeRoith D. Conditional knockout of mouse insulin-like growth factor-1 gene using the Cre/loxP system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000;223(4):344–51. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1373.2000.22349.x.
Wu Y, Yakar S, Zhao L, Hennighausen L, LeRoith D. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I levels regulate colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2002;62(4):1030–5.
Wu Y, Cui K, Miyoshi K, Hennighausen L, Green JE, Setser J, et al. Reduced circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels delay the onset of chemically and genetically induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2003;63(15):4384–8.
Moore T, Carbajal S, Beltran L, Perkins SN, Yakar S, Leroith D, et al. Reduced susceptibility to two-stage skin carcinogenesis in mice with low circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels. Cancer Res. 2008;68(10):3680–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6271.
Dunn SE, Kari FW, French J, Leininger JR, Travlos G, Wilson R, et al. Dietary restriction reduces insulin-like growth factor I levels, which modulates apoptosis, cell proliferation, and tumor progression in p53-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 1997;57(21):4667–72.
Zhang D, Bar-Eli M, Meloche S, Brodt P. Dual regulation of MMP-2 expression by the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor: the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and Raf/ERK pathways transmit opposing signals. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(19):19683–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313145200.
Dupont J, Pierre A, Froment P, Moreau C. The insulin-like growth factor axis in cell cycle progression. Horm Metab Res. 2003;35(11–12):740–50.
Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science. 1996;272(5263):877–80. doi:10.1126/science.272.5263.877.
O’Connor R, Fennelly C, Krause D. Regulation of survival signals from the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(2):47–51.
Stawowy P, Kallisch H, Kilimnik A, Margeta C, Seidah NG, Chretien M, et al. Proprotein convertases regulate insulin-like growth factor 1-induced membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in VSMCs via endoproteolytic activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;321(3):531–8. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.001.
Catrina SB, Botusan IR, Rantanen A, Catrina AI, Pyakurel P, Savu O, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha are expressed in kaposi sarcoma and modulated by insulin-like growth factor-I. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4506–14. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2473.
Cosaceanu D, Budiu RA, Carapancea M, Castro J, Lewensohn R, Dricu A. Ionizing radiation activates IGF-1R triggering a cytoprotective signaling by interfering with Ku-DNA binding and by modulating Ku86 expression via a p38 kinase-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 2007;26(17):2423–34. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210037.
Gooch JL, Van Den Berg CL, Yee D. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I rescues breast cancer cells from chemotherapy-induced cell death-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999;56(1):1–10. doi:10.1023/A:1006208721167.
Ouban A, Muraca P, Yeatman T, Coppola D. Expression and distribution of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2003;34(8):803–8. doi:10.1016/S0046-8177(03)00291-0.
Baserga R, Peruzzi F, Reiss K. The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int J Cancer. 2003;107(6):873–7. doi:10.1002/ijc.11487.
Tao Y, Pinzi V, Bourhis J, Deutsch E. Mechanisms of disease: signaling of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathway—therapeutic perspectives in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2007;4(10):591–602. doi:10.1038/ncponc0934.
Kaleko M, Rutter WJ, Miller AD. Overexpression of the human insulinlike growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10(2):464–73.
Sell C, Dumenil G, Deveaud C, Miura M, Coppola D, DeAngelis T, et al. Effect of a null mutation of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene on growth and transformation of mouse embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14(6):3604–12.
Miura M, Surmacz E, Burgaud JL, Baserga R. Different effects on mitogenesis and transformation of a mutation at tyrosine 1251 of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(38):22639–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.38.22639.
Liu JL, Blakesley VA, Gutkind JS, LeRoith D. The constitutively active mutant Galpha13 transforms mouse fibroblast cells deficient in insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(47):29438–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.47.29438.
Sutherland BW, Knoblaugh SE, Kaplan-Lefko PJ, Wang F, Holzenberger M, Greenberg NM. Conditional deletion of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in prostate epithelium. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3495–504. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6531.
Osborne CK, Monaco ME, Lippman ME, Kahn CR. Correlation among insulin binding, degradation, and biological activity in human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1978;38(1):94–102.
Pillemer G, Lugasi-Evgi H, Scharovsky G, Naor D. Insulin dependence of murine lymphoid T-cell leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1992;50(1):80–5. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910500117.
Nandi S, Guzman RC, Yang J. Hormones and mammary carcinogenesis in mice, rats, and humans: a unifying hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(9):3650–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.9.3650.
Heuson JC, Legros N, Heimann R. Influence of insulin administration on growth of the 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary carcinoma in intact, oophorectomized, and hypophysectomized rats. Cancer Res. 1972;32(2):233–8.
Sharon R, Pillemer G, Ish-Shalom D, Kalman R, Ziv E, Berry EM, et al. Insulin dependence of murine T-cell lymphoma. II. Insulin-deficient diabetic mice and mice fed low-energy diet develop resistance to lymphoma growth. Int J Cancer. 1993;53(5):843–9. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910530523.
Milazzo G, Giorgino F, Damante G, Sung C, Stampfer MR, Vigneri R, et al. Insulin receptor expression and function in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992;52(14):3924–30.
Giorgino F, Belfiore A, Milazzo G, Costantino A, Maddux B, Whittaker J, et al. Overexpression of insulin receptors in fibroblast and ovary cells induces a ligand-mediated transformed phenotype. Mol Endocrinol. 1991;5(3):452–9.
Mastick CC, Kato H, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D, Saltiel AR. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptors similarly stimulate deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis despite differences in cellular protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Endocrinology. 1994;135(1):214–22. doi:10.1210/en.135.1.214.
Sciacca L, Mineo R, Pandini G, Murabito A, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. In IGF-I receptor-deficient leiomyosarcoma cells autocrine IGF-II induces cell invasion and protection from apoptosis via the insulin receptor isoform A. Oncogene. 2002;21(54):8240–50. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206058.
Benoliel AM, Kahn-Perles B, Imbert J, Verrando P. Insulin stimulates haptotactic migration of human epidermal keratinocytes through activation of NF-kappa B transcription factor. J Cell Sci. 1997;110(Pt 17):2089–97.
Ish-Shalom D, Christoffersen CT, Vorwerk P, Sacerdoti-Sierra N, Shymko RM, Naor D, et al. Mitogenic properties of insulin and insulin analogues mediated by the insulin receptor. Diabetologia. 1997;40(Suppl 2):S25–31. doi:10.1007/s001250051393.
De Meyts P, Shymko RM. Timing-dependent modulation of insulin mitogenic versus metabolic signalling. Novartis Found Symp. 2000;227:46–57. doi:10.1002/0470870796.ch4 discussion 57–60.
Drejer K. The bioactivity of insulin analogues from in vitro receptor binding to in vivo glucose uptake. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992;8(3):259–85.
Milazzo G, Sciacca L, Papa V, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R. ASPB10 insulin induction of increased mitogenic responses and phenotypic changes in human breast epithelial cells: evidence for enhanced interactions with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Mol Carcinog. 1997;18(1):19–25. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2744(199701)18:1<19::AID-MC3>3.0.CO;2-M.
Hankins GR, De Souza AT, Bentley RC, Patel MR, Marks JR, Iglehart JD, et al. M6P/IGF2 receptor: a candidate breast tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene. 1996;12(9):2003–9.
Yamada T, De Souza AT, Finkelstein S, Jirtle RL. Loss of the gene encoding mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor is an early event in liver carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(19):10351–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.19.10351.
Oates AJ, Schumaker LM, Jenkins SB, Pearce AA, DaCosta SA, Arun B, et al. The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R), a putative breast tumor suppressor gene. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;47(3):269–81. doi:10.1023/A:1005959218524.
Massague J. TGFbeta signaling: receptors, transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell. 1996;85(7):947–50. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81296-9.
Wang S, Souza RF, Kong D, Yin J, Smolinski KN, Zou TT, et al. Deficient transforming growth factor-beta1 activation and excessive insulin-like growth factor II (IGFII) expression in IGFII receptor-mutant tumors. Cancer Res. 1997;57(13):2543–6.
Vignon F, Rochefort H. Interactions of pro-cathepsin D and IGF-II on the mannose-6-phosphate/IGF-II receptor. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22(1):47–57. doi:10.1007/BF01833333.
Mathieu M, Vignon F, Capony F, Rochefort H. Estradiol down-regulates the mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor gene and induces cathepsin-D in breast cancer cells: a receptor saturation mechanism to increase the secretion of lysosomal proenzymes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991;5(6):815–22.
Seino S, Seino M, Nishi S, Bell GI. Structure of the human insulin receptor gene and characterization of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(1):114–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.1.114.
Yamaguchi Y, Flier JS, Benecke H, Ransil BJ, Moller DE. Ligand-binding properties of the two isoforms of the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology. 1993;132(3):1132–8. doi:10.1210/en.132.3.1132.
Denley A, Bonython ER, Booker GW, Cosgrove LJ, Forbes BE, Ward CW, et al. Structural determinants for high-affinity binding of insulin-like growth factor II to insulin receptor (IR)-A, the exon 11 minus isoform of the IR. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18(10):2502–12. doi:10.1210/me.2004-0183.
Mosthaf L, Vogt B, Haring HU, Ullrich A. Altered expression of insulin receptor types A and B in the skeletal muscle of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(11):4728–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.11.4728.
Louvi A, Accili D, Efstratiadis A. Growth-promoting interaction of IGF-II with the insulin receptor during mouse embryonic development. Dev Biol. 1997;189(1):33–48. doi:10.1006/dbio.1997.8666.
Vogt B, Carrascosa JM, Ermel B, Ullrich A, Haring HU. The two isotypes of the human insulin receptor (HIR-A and HIR-B) follow different internalization kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;177(3):1013–8. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)90639-O.
Kosaki A, Pillay TS, Xu L, Webster NJ. The B isoform of the insulin receptor signals more efficiently than the A isoform in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(35):20816–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.35.20816.
Leibiger B, Leibiger IB, Moede T, Kemper S, Kulkarni RN, Kahn CR, et al. Selective insulin signaling through A and B insulin receptors regulates transcription of insulin and glucokinase genes in pancreatic beta cells. Mol Cell. 2001;7(3):559–70. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00203-9.
Uhles S, Moede T, Leibiger B, Berggren PO, Leibiger IB. Isoform-specific insulin receptor signaling involves different plasma membrane domains. J Cell Biol. 2003;163(6):1327–37. doi:10.1083/jcb.200306093.
Kosaki A, Webster NJ. Effect of dexamethasone on the alternative splicing of the insulin receptor mRNA and insulin action in HepG2 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(29):21990–6.
Entingh AJ, Taniguchi CM, Kahn CR. Bi-directional regulation of brown fat adipogenesis by the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(35):33377–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303056200.
Sciacca L, Prisco M, Wu A, Belfiore A, Vigneri R, Baserga R. Signaling differences from the A and B isoforms of the insulin receptor (IR) in 32D cells in the presence or absence of IR substrate-1. Endocrinology. 2003;144(6):2650–8. doi:10.1210/en.2002-0136.
Morrione A, Valentinis B, Xu SQ, Yumet G, Louvi A, Efstratiadis A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor II stimulates cell proliferation through the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(8):3777–82. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.8.3777.
Scalia P, Heart E, Comai L, Vigneri R, Sung CK. Regulation of the Akt/Glycogen synthase kinase-3 axis by insulin-like growth factor-II via activation of the human insulin receptor isoform-A. J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(4):610–8. doi:10.1002/jcb.1196.
Pandini G, Medico E, Conte E, Sciacca L, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Differential gene expression induced by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-II through the insulin receptor isoform A. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(43):42178–89. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304980200.
Ullrich A, Bell JR, Chen EY, Herrera R, Petruzzelli LM, Dull TJ, et al. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature. 1985;313(6005):756–61. doi:10.1038/313756a0.
Blanquart C, Achi J, Issad T. Characterization of IRA/IRB hybrid insulin receptors using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76(7):873–83. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.027.
Soos MA, Whittaker J, Lammers R, Ullrich A, Siddle K. Receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I can form hybrid dimmers. Characterisation of hybrid receptors in transfected cells. Biochem J. 1990;270(2):383–90.
Moxham CP, Jacobs S. Insulin/IGF-I receptor hybrids: a mechanism for increasing receptor diversity. J Cell Biochem. 1992;48(2):136–40. doi:10.1002/jcb.240480205.
Bailyes EM, Nave BT, Soos MA, Orr SR, Hayward AC, Siddle K. Insulin receptor/IGF-I receptor hybrids are widely distributed in mammalian tissues: quantification of individual receptor species by selective immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Biochem J. 1997;327(Pt 1):209–15.
Pandini G, Frasca F, Mineo R, Sciacca L, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors have different biological characteristics depending on the insulin receptor isoform involved. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(42):39684–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202766200.
Soos MA, Field CE, Siddle K. Purified hybrid insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I receptors bind insulin-like growth factor-I, but not insulin, with high affinity. Biochem J. 1993;290(Pt 2):419–26.
Frattali AL, Treadway JL, Pessin JE. Insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptors: implications for the dominant-negative phenotype in syndromes of insulin resistance. J Cell Biochem. 1992;48(1):43–50. doi:10.1002/jcb.240480108.
Langlois WJ, Sasaoka T, Yip CC, Olefsky JM. Functional characterization of hybrid receptors composed of a truncated insulin receptor and wild type insulin-like growth factor 1 or insulin receptors. Endocrinology. 1995;136(5):1978–86. doi:10.1210/en.136.5.1978.
Benyoucef S, Surinya KH, Hadaschik D, Siddle K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem J. 2007;403(3):603–13. doi:10.1042/BJ20061709.
Slaaby R, Schaffer L, Lautrup-Larsen I, Andersen AS, Shaw AC, Mathiasen IS, et al. Hybrid receptors formed by insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) have low insulin and high IGF-1 affinity irrespective of the IR splice variant. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(36):25869–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605189200.
Garcia-de Lacoba M, Alarcon C, de la Rosa EJ, de Pablo F. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I hybrid receptors with high affinity for insulin are developmentally regulated during neurogenesis. Endocrinology. 1999;140(1):233–43. doi:10.1210/en.140.1.233.
Tollefsen SE, Thompson K, Petersen DJ. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(34):16461–9.
Jonas HA, Cox AJ. Insulin receptor sub-types in a human lymphoid-derived cell line (IM-9): differential regulation by insulin, dexamethasone and monensin. J Recept Res. 1991;11(5):813–29.
Jonas HA, Eckardt GS, Clark S. Expression of atypical and classical insulin receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with cloned cDNA for the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology. 1990;127(3):1301–9.
Alexandrides TK, Smith RJ. A novel fetal insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I receptor. Mechanism for increased IGF I- and insulin-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity in fetal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(22):12922–30.
Navarro M, Joulia D, Fedon Y, Levin J, Barenton B, Bernardi H. The atypical alpha2beta2 IGF receptor expressed in inducible c2.7 myoblasts is derived from post-translational modifications of the mouse IGF-I receptor. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008;18(5):412–23. doi:10.1016/j.ghir.2008.03.001.
Milazzo G, Yip CC, Maddux BA, Vigneri R, Goldfine ID. High-affinity insulin binding to an atypical insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in human breast cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 1992;89(3):899–908. doi:10.1172/JCI115670.
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J, Beuscart R, Djiane J, Demaille A. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer and their relation to estradiol and progesterone receptors. Cancer Res. 1988;48(22):6429–33.
Cullen KJ, Yee D, Sly WS, Perdue J, Hampton B, Lippman ME, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and function in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50(1):48–53.
Papa V, Gliozzo B, Clark GM, McGuire WL, Moore D, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53(16):3736–40.
Resnik JL, Reichart DB, Huey K, Webster NJ, Seely BL. Elevated insulin-like growth factor I receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58(6):1159–64.
Koda M, Sulkowski S, Garofalo C, Kanczuga-Koda L, Sulkowska M, Surmacz E. Expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases: correlations with estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Horm Metab Res. 2003;35(11–12):794–801.
Soos MA, Nave BT, Siddle K. Immunological studies of type I IGF receptors and insulin receptors: characterisation of hybrid and atypical receptor subtypes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;343:145–57.
Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP, Beuscart R, Demaille A. Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50(21):6931–5.
Foekens JA, Portengen H, van Putten WL, Trapman AM, Reubi JC, Alexieva-Figusch J, et al. Prognostic value of receptors for insulin-like growth factor 1, somatostatin, and epidermal growth factor in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1989;49(24 Pt 1):7002–9.
Berns EM, Klijn JG, van Staveren IL, Portengen H, Foekens JA. Sporadic amplification of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor gene in human breast tumors. Cancer Res. 1992;52(4):1036–9.
Railo MJ, von Smitten K, Pekonen F. The prognostic value of insulin-like growth factor-I in breast cancer patients. Results of a follow-up study on 126 patients. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(3):307–11. doi:10.1016/0959-8049(94)90247-X.
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L, Yuan J, Havre PA, Gumbs AA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res. 1997;57(15):3079–83.
Yu D, Watanabe H, Shibuya H, Miura M. Redundancy of radioresistant signaling pathways originating from insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(9):6702–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209809200.
Novosyadlyy R, Kurshan N, Lann D, Vijayakumar A, Yakar S, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor-I protects cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis via enhancement of the adaptive capacity of endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(8):1304–17. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.52.
Zhang X, Lin M, van Golen KL, Yoshioka K, Itoh K, Yee D. Multiple signaling pathways are activated during insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulated breast cancer cell migration. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;93(2):159–68. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-4626-8.
Lynch L, Vodyanik PI, Boettiger D, Guvakova MA. Insulin-like growth factor I controls adhesion strength mediated by alpha5beta1 integrins in motile carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(1):51–63. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0399.
Akekawatchai C, Holland JD, Kochetkova M, Wallace JC, McColl SR. Transactivation of CXCR4 by the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(48):39701–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509829200.
Maor S, Yosepovich A, Papa MZ, Yarden RI, Mayer D, Friedman E, et al. Elevated insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) levels in primary breast tumors associated with BRCA1 mutations. Cancer Lett. 2007;257(2):236–43. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.07.019.
Hudelist G, Wagner T, Rosner M, Fink-Retter A, Gschwantler-Kaulich D, Czerwenka K, et al. Intratumoral IGF-I protein expression is selectively upregulated in breast cancer patients with BRCA1/2 mutations. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14(4):1053–62. doi:10.1677/ERC-06-0075.
Ohlsson C, Kley N, Werner H, LeRoith D. p53 regulates insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor expression and IGF-I-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in an osteosarcoma cell line: interaction between p53 and Sp1. Endocrinology. 1998;139(3):1101–7. doi:10.1210/en.139.3.1101.
Papa V, Pezzino V, Costantino A, Belfiore A, Giuffrida D, Frittitta L, et al. Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 1990;86(5):1503–10. doi:10.1172/JCI114868.
Sciacca L, Costantino A, Pandini G, Mineo R, Frasca F, Scalia P, et al. Insulin receptor activation by IGF-II in breast cancers: evidence for a new autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Oncogene. 1999;18(15):2471–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202600.
Pandini G, Vigneri R, Costantino A, Frasca F, Ippolito A, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor overexpression in breast cancers leads to insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptor overexpression: evidence for a second mechanism of IGF-I signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5(7):1935–44.
Cohen ND, Hilf R. Influence of insulin on growth and metabolism of 7,12-dimethylbenz(alpha)anthracene-induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 1974;34(12):3245–52.
Papa V, Belfiore A. Insulin receptors in breast cancer: biological and clinical role. J Endocrinol Invest. 1996;19(5):324–33.
Papa V, Milazzo G, Goldfine ID, Waldman FM, Vigneri R. Sporadic amplification of the insulin receptor gene in human breast cancer. J Endocrinol Invest. 1997;20(9):531–6.
Frittitta L, Cerrato A, Sacco MG, Weidner N, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R. The insulin receptor content is increased in breast cancers initiated by three different oncogenes in transgenic mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1997;45(2):141–7. doi:10.1023/A:1005801713713.
Webster NJ, Resnik JL, Reichart DB, Strauss B, Haas M, Seely BL. Repression of the insulin receptor promoter by the tumor suppressor gene product p53: a possible mechanism for receptor overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996;56(12):2781–8.
Paonessa F, Foti D, Costa V, Chiefari E, Brunetti G, Leone F, et al. Activator protein-2 overexpression accounts for increased insulin receptor expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(10):5085–93. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3678.
Mathieu MC, Clark GM, Allred DC, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor expression and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1997;109(6):565–71.
Mulligan AM, O’Malley FP, Ennis M, Fantus IG, Goodwin PJ. Insulin receptor is an independent predictor of a favorable outcome in early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106(1):39–47. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9471-x.
Pandini G, Wurch T, Akla B, Corvaia N, Belfiore A, Goetsch L. Functional responses and in vivo anti-tumour activity of h7C10: a humanised monoclonal antibody with neutralising activity against the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor and insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptors. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43(8):1318–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.03.009.
Cullen KJ, Allison A, Martire I, Ellis M, Singer C. Insulin-like growth factor expression in breast cancer epithelium and stroma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22(1):21–9. doi:10.1007/BF01833330.
Arteaga CL, Osborne CK. Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res. 1989;49(22):6237–41.
Sara VR, Hall K. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 1990;70(3):591–614.
Rasmussen AA, Cullen KJ. Paracrine/autocrine regulation of breast cancer by the insulin-like growth factors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;47(3):219–33. doi:10.1023/A:1005903000777.
Mathews LS, Hammer RE, Behringer RR, D’Ercole AJ, Bell GI, Brinster RL, et al. Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1988;123(6):2827–33.
Hadsell DL, Greenberg NM, Fligger JM, Baumrucker CR, Rosen JM. Targeted expression of des(1–3) human insulin-like growth factor I in transgenic mice influences mammary gland development and IGF-binding protein expression. Endocrinology. 1996;137(1):321–30. doi:10.1210/en.137.1.321.
Neuenschwander S, Schwartz A, Wood TL, Roberts CT Jr, Hennighausen L, LeRoith D. Involution of the lactating mammary gland is inhibited by the IGF system in a transgenic mouse model. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(10):2225–32. doi:10.1172/JCI118663.
Pollak M, Blouin MJ, Zhang JC, Kopchick JJ. Reduced mammary gland carcinogenesis in transgenic mice expressing a growth hormone antagonist. Br J Cancer. 2001;85(3):428–30. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2001.1895.
Sussenbach JS, Rodenburg RJ, Scheper W, Holthuizen P. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the human IGF-II gene expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;343:63–71.
Zhang L, Kashanchi F, Zhan Q, Zhan S, Brady JN, Fornace AJ, et al. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor II P3 promoter by p53: a potential mechanism for tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1996;56(6):1367–73.
Cullen KJ, Smith HS, Hill S, Rosen N, Lippman ME. Growth factor messenger RNA expression by human breast fibroblasts from benign and malignant lesions. Cancer Res. 1991;51(18):4978–85.
Ellis MJ, Jenkins S, Hanfelt J, Redington ME, Taylor M, Leek R, et al. Insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;52(1–3):175–84. doi:10.1023/A:1006127621512.
Ellis MJ, Singer C, Hornby A, Rasmussen A, Cullen KJ. Insulin-like growth factor mediated stromal–epithelial interactions in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;31(2–3):249–61. doi:10.1007/BF00666158.
Manni A, Badger B, Wei L, Zaenglein A, Grove R, Khin S, et al. Hormonal regulation of insulin-like growth factor II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein expression by breast cancer cells in vivo: evidence for stromal epithelial interactions. Cancer Res. 1994;54(11):2934–42.
Yee D, Lee AV. Crosstalk between the insulin-like growth factors and estrogens in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000;5(1):107–15. doi:10.1023/A:1009575518338.
Qiu Q, Basak A, Mbikay M, Tsang BK, Gruslin A. Role of pro-IGF-II processing by proprotein convertase 4 in human placental development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(31):11047–52. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502357102.
Korn E, Van Hoff J, Buckley P, Daughaday WH, Carpenter TO. Secretion of a large molecular-weight form of insulin-like growth factor by a primary renal tumor. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1995;24(6):392–6. doi:10.1002/mpo.2950240610.
Singh SK, Moretta D, Almaguel F, De Leon M, De Leon DD. Precursor IGF-II (proIGF-II) and mature IGF-II (mIGF-II) induce Bcl-2 And Bcl-X L expression through different signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. Growth Factors. 2008;26(2):92–103. doi:10.1080/08977190802057258.
Wu HK, Squire JA, Catzavelos CG, Weksberg R. Relaxation of imprinting of human insulin-like growth factor II gene, IGF2, in sporadic breast carcinomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;235(1):123–9. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6744.
van Roozendaal CE, Gillis AJ, Klijn JG, van Ooijen B, Claassen CJ, Eggermont AM, et al. Loss of imprinting of IGF2 and not H19 in breast cancer, adjacent normal tissue and derived fibroblast cultures. FEBS Lett. 1998;437(1–2):107–11. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01211-3.
Yballe CM, Vu TH, Hoffman AR. Imprinting and expression of insulin-like growth factor-II and H19 in normal breast tissue and breast tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(4):1607–12. doi:10.1210/jc.81.4.1607.
Ito Y, Koessler T, Ibrahim AE, Rai S, Vowler SL, Abu-Amero S, et al. Somatically acquired hypomethylation of IGF2 in breast and colorectal cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17(17):2633–43. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn163.
Pacher M, Seewald MJ, Mikula M, Oehler S, Mogg M, Vinatzer U, et al. Impact of constitutive IGF1/IGF2 stimulation on the transcriptional program of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28(1):49–59. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl091.
Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T, et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature. 2007;448(7157):1015–21. doi:10.1038/nature06027.
Wicha MS, Liu S, Dontu G. Cancer stem cells: an old idea—a paradigm shift. Cancer Res. 2006;66(4):1883–90. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3153 discussion 1895–6.
Berthe ML, Esslimani Sahla M, Roger P, Gleizes M, Lemamy GJ, Brouillet JP, et al. Mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor expression levels during the progression from normal human mammary tissue to invasive breast carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39(5):635–42. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(02)00627-5.
Chen Z, Ge Y, Landman N, Kang JX. Decreased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor promotes growth of human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2002;2:18. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-2-18.
Lee JS, Weiss J, Martin JL, Scott CD. Increased expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor in breast cancer cells alters tumorigenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2003;107(4):564–70. doi:10.1002/ijc.11453.
Wise TL, Pravtcheva DD. Delayed onset of Igf2-induced mammary tumors in Igf2r transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2006;66(3):1327–36. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3107.
Xie S, Kang JX. Differential expression of the mannose 6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor-II receptor in human breast cancer cell lines of different invasive potential. Med Sci Monit. 2002;8(8):BR293–300.
Casa AJ, Dearth RK, Litzenburger BC, Lee AV, Cui X. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway: a key player in cancer therapeutic resistance. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3273–87. doi:10.2741/2925.
Gupta AK, Bakanauskas VJ, Cerniglia GJ, Cheng Y, Bernhard EJ, Muschel RJ, et al. The Ras radiation resistance pathway. Cancer Res. 2001;61(10):4278–82.
Shahrabani-Gargir L, Pandita TK, Werner H. Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene controls insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene expression in a deoxyribonucleic acid damage response pathway via mechanisms involving zinc-finger transcription factors Sp1 and WT1. Endocrinology. 2004;145(12):5679–87. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0613.
Peretz S, Jensen R, Baserga R, Glazer PM. ATM-dependent expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in a pathway regulating radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(4):1676–81. doi:10.1073/pnas.041416598.
Beech DJ, Parekh N, Pang Y. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor antagonism results in increased cytotoxicity of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin and taxol. Oncol Rep. 2001;8(2):325–9.
Dunn SE, Hardman RA, Kari FW, Barrett JC. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1997;57(13):2687–93.
Parisot JP, Hu XF, DeLuise M, Zalcberg JR. Altered expression of the IGF-1 receptor in a tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer cell line. Br J Cancer. 1999;79(5–6):693–700. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690112.
Nicholson RI, Gee JM. Oestrogen and growth factor cross-talk and endocrine insensitivity and acquired resistance in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2000;82(3):501–13. doi:10.1054/bjoc.1999.0954.
Nicholson RI, Staka C, Boyns F, Hutcheson IR, Gee JM. Growth factor-driven mechanisms associated with resistance to estrogen deprivation in breast cancer: new opportunities for therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004;11(4):623–41. doi:10.1677/erc.1.00778.
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Barrow D, Gee JM, Nicholson RI. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Endocrinology. 2005;146(11):4609–18. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0247.
Sisci D, Surmacz E. Crosstalk between IGF signaling and steroid hormone receptors in breast cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(7):705–17. doi:10.2174/138161207780249182.
Maor S, Mayer D, Yarden RI, Lee AV, Sarfstein R, Werner H, et al. Estrogen receptor regulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in breast tumor cells: involvement of transcription factor Sp1. J Endocrinol. 2006;191(3):605–12. doi:10.1677/joe.1.07016.
Pandini G, Genua M, Frasca F, Squatrito S, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. 17beta-estradiol up-regulates the insulin-like growth factor receptor through a nongenotropic pathway in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(18):8932–41. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4814.
Carter P, Presta L, Gorman CM, Ridgway JB, Henner D, Wong WL, et al. Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(10):4285–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4285.
Lu Y, Zi X, Zhao Y, Mascarenhas D, Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(24):1852–7. doi:10.1093/jnci/93.24.1852.
Nahta R, Yuan LX, Zhang B, Kobayashi R, Esteva FJ. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(23):11118–28. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3841.
Jones HE, Gee JM, Barrow D, Tonge D, Holloway B, Nicholson RI. Inhibition of insulin receptor isoform-A signalling restores sensitivity to gefitinib in previously de novo resistant colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2006;95(2):172–80. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603237.
Baserga R, Sell C, Porcu P, Rubini M. The role of the IGF-I receptor in the growth and transformation of mammalian cells. Cell Prolif. 1994;27(2):63–71. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.1994.tb01406.x.
Hofmann F, Garcia-Echeverria C. Blocking the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a strategy for targeting cancer. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10(15):1041–7. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03512-9.
Mur C, Valverde AM, Kahn CR, Benito M. Increased insulin sensitivity in IGF-I receptor-deficient brown adipocytes. Diabetes. 2002;51(3):743–54. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.3.743.
Zhang H, Pelzer AM, Kiang DT, Yee D. Down-regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to insulin. Cancer Res. 2007;67(1):391–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1712.
Fulzele K, DiGirolamo DJ, Liu Z, Xu J, Messina JL, Clemens TL. Disruption of the insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor in osteoblasts enhances insulin signaling and action. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(35):25649–58. doi:10.1074/jbc.M700651200.
Sachdev D, Singh R, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Yee D. Down-regulation of insulin receptor by antibodies against the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor: implications for anti-insulin-like growth factor therapy in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(4):2391–402. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3126.
Miyamoto S, Nakamura M, Shitara K, Nakamura K, Ohki Y, Ishii G, et al. Blockade of paracrine supply of insulin-like growth factors using neutralizing antibodies suppresses the liver metastasis of human colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(9):3494–502. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1701.
Goya M, Miyamoto S, Nagai K, Ohki Y, Nakamura K, Shitara K, et al. Growth inhibition of human prostate cancer cells in human adult bone implanted into nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice by a ligand-specific antibody to human insulin-like growth factors. Cancer Res. 2004;64(17):6252–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0919.
Feng Y, Zhu Z, Xiao X, Choudhry V, Barrett JC, Dimitrov DS. Novel human monoclonal antibodies to insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II that potently inhibit the IGF receptor type I signal transduction function. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(1):114–20. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0252.
Haluska P, Carboni JM, Loegering DA, Lee FY, Wittman M, Saulnier MG, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer Res. 2006;66(1):362–71. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1107.
Girnita A, Girnita L, del Prete F, Bartolazzi A, Larsson O, Axelson M. Cyclolignans as inhibitors of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and malignant cell growth. Cancer Res. 2004;64(1):236–42. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2522.
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Riccardo Vigneri (University of Catania, Italy) for his constant support and advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grant support: This work was partially supported by grants from the AIRC (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro) and PRIN-MIUR 2005 (Ministero Italiano Università e Ricerca) to A.B.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belfiore, A., Frasca, F. IGF and Insulin Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13, 381–406 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9099-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9099-z