Abstract
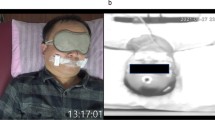
Sleep apnea (SA) is a very common disease with serious health consequences, yet is very under-diagnosed, partially because of the high cost and limited accessibility of in-laboratory polysomnography (PSG). The purpose of this work is to introduce a newly developed portable system for the diagnosis of SA at home that is both reliable and easy to use. The system includes personal devices for recording breath sounds and airflow during sleep and diagnostic algorithms to process the recorded data. The data capturing device consists of a wearable face frame with an embedded electronic module featuring a unidirectional microphone, a differential microphone preamplifier, a microcontroller with an onboard differential analogue to digital converter, and a microSD memory card. The device provides continuous data capturing for 8 h. Upon completion of the recording session, the memory card is returned to a location for acoustic analysis. We recruited 49 subjects who used the device independently at home, after which each subject answered a usability questionnaire. Random data samples were selected to measure the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as a gauge of hardware functionality. A subset of 11 subjects used the device on 2 different nights and their results were compared to examine diagnostic reproducibility. Independent of those, system’s performance was evaluated against PSG in the lab environment in 32 subject. The overall success rate of applying the device in un-attended settings was 94 % and the overall rating for ease-of-use was ‘excellent’. Signal examination showed excellent capturing of breath sounds with an average SNR of 31.7 dB. Nine of the 11 (82 %) subjects had equivalent results on both nights, which is consistent with reported inter-night variability. The system showed 96 % correlation with simultaneously performed in-lab PSG. Conclusion: Our results suggest excellent usability and performance of this system and provide a strong rationale to further improve it and test its robustness in a larger study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung RS, Bradley TD. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:2147–65.
Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, Shahar E, Samet JM, Redline S, D’Agostino RB, Newman AB, Lebowitz MD, Pickering TG. Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep heart health study. Jama. 2000;283:1829–36.
Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, Lee ET, Newman AB, Javier Nieto F, O’Connor GT, Boland LL, Schwartz JE, Samet JM. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the sleep heart health study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:19–25.
Bradley TD, Floras JS. Sleep apnea and heart failure: part I: obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation. 2003;107:1671–8.
Arzt M, Young T, Finn L, Skatrud JB, Bradley TD. Association of sleep-disordered breathing and the occurrence of stroke. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:1447–51.
Sassani A, Findley LJ, Kryger M, Goldlust E, George C, Davidson TM. Reducing motor-vehicle collisions, costs, and fatalities by treating obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep. 2004;27:453–8.
Otake K, Delaive K, Walld R, Manfreda J, Kryger MH. Cardiovascular medication use in patients with undiagnosed obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 2002;57:417–22.
Kaneko Y, Floras JS, Usui K, Plante J, Tkacova R, Kubo T, Ando S, Bradley TD. Cardiovascular effects of continuous positive airway pressure in patients with heart failure and obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1233–41.
Usui K, Bradley TD, Spaak J, Ryan CM, Kubo T, Kaneko Y, Floras JS. Inhibition of awake sympathetic nerve activity of heart failure patients with obstructive sleep apnea by nocturnal continuous positive airway pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:2008–11.
Ryan CM, Usui K, Floras JS, Bradley TD. Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on ventricular ectopy in heart failure patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax. 2005;60:781–5.
Ryan CM, Bayley M, Green R, Murray BJ, Bradley TD. Influence of continuous positive airway pressure on outcomes of rehabilitation in stroke patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Stroke. 2011;42:1062–7.
Leung RS, Bradley TD. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:2147–65.
Chung F, Yegneswaran B, Liao P, Chung SA, Vairavanathan S, Islam S, Khajehdehi A, Shapiro CM. STOP questionnaire: a tool to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:812–821.
Gupta RM, Parvizi J, Hanssen AD, Gay PC (2001) Postoperative complications in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome undergoing hip or knee replacement: a case–control study. Mayo Clin Proc. 76:897–905
Gentil B, de Larminat JM, Boucherez C, Lienhart A. Difficult intubation and obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 1994;72:368.
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–5.
Young T, Evans L, Finn L, Palta M. Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep 1997;20:705–6.
Hult P, Fjallbrant T, Wranne B, Engdahl O, Ask P. An improved bioacoustic method for monitoring of respiration. Technol Health Care. 2004;12:323–32.
Ferber R, Millman R, Coppola M, Fleetham J, Murray CF, Iber C, McCall V, Nino-Murcia G, Pressman M, Sanders M, et al. Portable recording in the assessment of obstructive sleep apnea. ASDA standards of practice. Sleep. 1994;17:378–92.
Golpe R, Jimenez A, Carpizo R. Home sleep studies in the assessment of sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Chest. 2002;122:1156–61.
Liesching TN, Carlisle C, Marte A, Bonitati A, Millman RP. Evaluation of the accuracy of SNAP technology sleep sonography in detecting obstructive sleep apnea in adults compared to standard polysomnography. Chest. 2004;125:886–91.
Flemons WW, Littner MR, Rowley JA, Gay P, Anderson WM, Hudgel DW, McEvoy RD, Loube DI. Home diagnosis of sleep apnea: a systematic review of the literature. An evidence review cosponsored by the american academy of sleep medicine, the american college of chest physicians, and the american thoracic society. Chest. 2003;124:1543–79.
Ahmed M, Patel NP, Rosen I. Portable monitors in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 2007;132:1672–7.
Michael H, Andreas S, Thomas B, Beatrice H, Werner H, Holger K. Analysed snoring sounds correlate to obstructive sleep disordered breathing. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2008;265:105–113.
Saunders NC, Tassone P, Wood G, Norris A, Harries M, Kotecha B. Is acoustic analysis of snoring an alternative to sleep nasendoscopy? Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2004;29:242–6.
Alshaer H, Garcia M, Radfar MH, Fernie GR, Bradley TD. Detection of upper airway narrowing via classification of LPC coefficients: implications for obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 2011. pp. 681–4.
Alshaer H, Fernie GR, Bradley TD. Phase tracking of the breathing cycle in sleeping subjects by frequency analysis of acoustic data. Int J Healthcare Technol Manag. 2010;11:163–75.
Alshaer H, Fernie G, Bradley TD. Development and validation of an algorithm for detection of apneas and hypopneas using overnight breath sound recordings. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:A6317.
Alshaer H, Fernie GR, Sejdic E, Bradley TD. Adaptive segmentation and normalization of breathing acoustic data of subjects with obstructive sleep apnea. In: Science and technology for humanity (TIC-STH), 2009 IEEE Toronto International Conference, pp. 279–84.
Alshaer H et al (2013) Validation of an automated algorithm for detecting apneas and hypopneas by acoustic analysis of breath sounds. Sleep Med. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.12.015
Duckitt WD, Tuomi SK, Niesler TR. Automatic detection, segmentation and assessment of snoring from ambient acoustic data. Physiol Meas. 2006;27:1047–56.
Ng AK, Zhi Jie H, Tong San K. Effects of microphone position on snore signal quality and patient comfort. In: Signal processing, 2008. ICSP 2008. 9th International conference on, pp. 2130–3.
Yadollahi A, Moussavi Z. Automatic breath and snore sounds classification from tracheal and ambient sounds recordings. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32:985–90.
Collop NA, Anderson WM, Boehlecke B, Claman D, Goldberg R, Gottlieb DJ, Hudgel D, Sateia M, Schwab R. Clinical guidelines for the use of unattended portable monitors in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adult patients. Portable monitoring task force of the american academy of sleep medicine. J Clin Sleep Med. 2007;3:737–47.
Chediak AD, Acevedo-Crespo JC, Seiden DJ, Kim HH, Kiel MH. Nightly variability in the indices of sleep-disordered breathing in men being evaluated for impotence with consecutive night polysomnograms. Sleep. 1996;19:589–92.
Bliwise DL, Benkert RE, Ingham RH. Factors associated with nightly variability in sleep-disordered breathing in the elderly. Chest. 1991;100:973–6.
EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples: a preliminary report from the sleep disorders atlas task force of the american sleep disorders association. Sleep. 1992;15:173–84. http://www.journalsleep.org/ViewAbstract.aspx?pid=23917
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Los Angeles: UCLA Brain Information Service/Brain Research Institute; 1968.
Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep. 1999;22:667–89. http://www.journalsleep.org/ViewAbstract.aspx?pid=24156
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan S. The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology, and technical specifications, 1st edn. Westchester, IL: The American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2007.
Redolfi S, Yumino D, Ruttanaumpawan P, Yau B, Su MC, Lam J, Bradley TD. Relationship between overnight rostral fluid shift and obstructive sleep apnea in nonobese men. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:241–6.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the contributions of Inas Kadri in developing the illustrations and to Azadeh Yadollahi for her editorial input. This work might result in a commercializable device and patent applications have been filed. This project has been supported by the Ministry of Research and Innovation of Ontario, MaRS Innovation, Ontario Centre of Excellence, Johnson and Johnson Inc., and FedDev via the Ontario Brain Institute. Toronto Rehabilitation Institute receives funding from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Dr Alshaer is a recipient NSERC scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshaer, H., Levchenko, A., Bradley, T.D. et al. A system for portable sleep apnea diagnosis using an embedded data capturing module. J Clin Monit Comput 27, 303–311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-013-9435-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-013-9435-8