Abstract
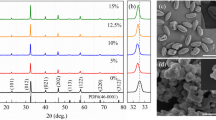
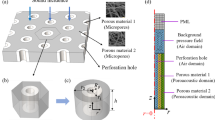
Porous ceramics are of interest for ultrasonic transducer applications. Porosity allows to decrease acoustical impedance, thus improving transfer of acoustical energy to water or biological tissues. For underwater applications, the dhgh figure of merit can also be improved as compared to dense materials. In the case of high frequency transducers, namely for high resolution medical imaging, thick film technology can be used. The active films are generally porous and this porosity must be controlled. An unpoled porous PZT substrate is also shown to be an interesting solution since it can be used in a screen-printing process and as a backing for the transducer. This paper describes the fabrication process to obtain such materials, presents microstructure analysis as well as functional properties of materials. Modelling is also performed and results are compared to measurements. Finally, transducer issues are addressed through modelling and design of several configurations. The key parameters are identified and their effect on transducer performance is discussed. A comparison with dense materials is performed and results are discussed to highlight in which cases porous piezoceramics can improve transducer performance, and improvements are quantified.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Newnham, D.P. Skinner, L.E. Cross, Mater. Res. Bull. 13, 525–536 (1978)
D.P. Skinner, R.E. Newnham, L.E. Cross, Mater. Res. Bull. 13, 599–607 (1978)
E.K. Akdogan, M. Allahverdi, A. Safari, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 52(5), 746–775 (2005)
C. Galassi, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24(14), 2951–2958 (2006)
O. Lyckfeldt, J.M.F. Ferreira, Eur. Ceram. Soc. 184, 134–140 (1998)
W.J. Chao, K.S. Chou, Key Eng. Mater. 113, 96–108 (1996)
D. Piazza, C. Capiani, C. Galassi, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 3075–3078 (2005)
T. Zeng, X.L. Dong, S.T. Chen, H. Yang, Ceram. Int. 33(3), 395–399(2006)
R. Krimholtz, D.A. Leedom, G.L. Matthei, Electronic Letters 38, 338–339 (1970)
S. Van Kervel, J.M. Thijssen, Ultrasonics 21, 134–140 (1983)
M. Lethiecq, F. Levassort, L.P. Tran Huu-Hue, M. Alguero, L. Pardo, T. Bove, E. Ringgaard, W. Wolny, New low acoustic impedance piezoelectric material for broadband transducer applications. IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings 1153–1156 (2004)
M. Lukacs, T. Olding, M. Sayer, R. Tasker, S. Sherrit, J. Appl. Phys. 85(5), 2835–2843 (1999)
F. Levassort, L.P. Tran-Huu-Hue, J. Holc, T. Bove, M. Kosec, M. Lethiecq, High performance piezoceramic films on substrates for high frequency imaging. IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings 1035–1038 (2001)
P. Maréchal, F. Levassort, J. Holc, L.P. Tran-Huu-Hue, M. Kosec, M. Lethiecq, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 53(8), 1524–1533 (2006)
W.F. Deeg, The Analysis of Dislocation, Crack, and Inclusion Problems in Piezoelectric Solids. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University (1980)
M.L. Dunn, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 32(1), 119–131 (1994)
J.D. Eshelby, The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 376–396 (1957)
M.L. Dunn, M. Taya, An analysis of piezoelectric composite materials containing ellipsoidal inhomogeneities. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 265–287 (1993)
M.L. Dunn, M. Taya, Int. J. Solids Struct. 30(2), 161–175 (1993)
M.L. Dunn, M. Taya, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 1697–1706 (1993)
C.W. Nan, F.S. Jin, Phys. Rev., B 48(12), 8578–8582 (1993)
C.W. Nan, J. Appl. Phys. 76(2), 1155–1163 (1994)
B. Wang, Int. J. Solids Struct. 29(3), 293–308 (1992)
B. Wang, S. Du, Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mater. 3, 289–295 (1993)
T.E. Gomez Alvarez-Arenas, F. Montero de Espinosa, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102(6), 3507–3515 (1997)
A. Perry, C.R. Bowen, Scripta Materiala 41(9),1001–1007 (1999)
F. Levassort, M. Lethiecq, D. Certon, F. Patat, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 44(2), 445–452 (1997)
F. Levassort, M. Lethiecq, C.E. Millar, L. Pourcelot, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 45(6), 1497–1505 (1998)
F. Levassort, M. Lethiecq, R. Desmare, L.P. Tran-Huu-Hue, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 46(4), 1028–1034 (1999)
K.Y. Hashimoto, M. Yamaguchi, Elastic, Piezoelectric and Dielectric Properties of Composite Materials. IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings 697–702 (1986)
H. Banno, Ferroelectrics 50, 3–12 (1983)
K. Rittenmeyer, T. Shrout, W.A. Schulze, R.E. Newnham, Ferroelectrics 41, 189–195 (1982)
H. Banno, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 4214–4217 (1993)
C.R. Bowen, A. Perry, H. Kara, S.W. Mahon, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1463–1467 (2001)
S.M. Pilgrim, R.E. Newnham, Mater. Res. Bull. 21, 1447–1454 (1986)
C.R. Bowen, H. Kara, Mater. Chem. Phys. 75, 45–49 (2002)
M.J. Creedom, W.A. Schulze, Ferroelectrics 153, 333–339 (1994)
M.J. Creedom, W.A. Schulze, Large area piezoelectric composite arrays from distorted reticulated ceramics. IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings 527–530 (1996)
R.Y. Ting, Ferroelectrics 67, 143–157 (1986)
T. Arai, K. Ayusawa, H. Sato, T. Miyata, K. Kawamura, K. Kobayashi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2253–2255 (1991)
P. Guillaussier, C.A.D. Boucher, Ferroelectrics 187, 121–128 (1996)
S. Marselli, V. Pavia, C. Galassi, E. Roncari, F. Craciun, G. Guidarelli, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106(2), 733–738 (1999)
H. Kara, R. Ramesh, R. Stevens, C.R. Bowen, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Contr. 50(3), 289–296 (2003)
V.Yu. Topolov, A.V. Turik, Tech. Phys. 46(9), 1093–1100 (2001)
V.Yu. Topolov, A.V. Turik, Tech. Phys. Lett. 27(1), 81–83 (2001)
C.R. Bowen, V.Yu. Topolov, Acta Mater. 51, 4965–4976 (2003)
R. Desmare, L.P. Tran-Huu-Hue, F. Levassort, M. Lethiecq, Journal Revista de Acustica 33 (2003)
F.S. Foster, C.J. Pavlin, K.A. Harasiewicz, D.A. Christopher, D.H. Turnbull, Ultrasound Med. Biol. 26(1), 1–27 (2000)
Acknowledgement
This work was performed in the frame of the Piramid FP5 European project (contract no. G5RD-CT-2001-456) and MIND FP6 Network of Excellence (contract no. 515757-2). The authors thank C. Galassi for discussion and bibliography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levassort, F., Holc, J., Ringgaard, E. et al. Fabrication, modelling and use of porous ceramics for ultrasonic transducer applications. J Electroceram 19, 127–139 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9117-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9117-3