Abstract
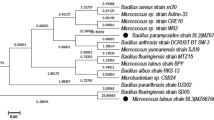
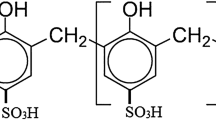
Two PCP-degrading bacterial strains, Bacillus cereus (ITRC-S6) and Serratia marcescens (ITRC-S7) were used for the treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent at conditions; 1.0% glucose and 0.5% peptone at 30 ± 1°C at 120 rpm for 168 h of incubation. These two bacterial strains effectively reduced colour (45–52%), lignin (30–42%), BOD (40–70%), COD (50–60%), total phenol (32–40%) and PCP (85–90%) within 168 h of incubation. However, the highest reduction in colour (62%), lignin (54%), BOD (70%), COD (90%), total phenol (90%) and PCP (100%) was recorded by mixed culture treatment. The bacterial mechanism for the degradation of pulp and paper mill effluent may be explained by an increase in the cells biomass using added co-substrates resulting liberation of significant amount of chloride due to bacterial dechlorination of chlorolignins and chlorophenols this showed reduction in colour, lignin and toxicity in the effluent. Further, GC-MS analysis of ethyl acetate-extractable compounds from treated pulp paper mill effluent reinforces the bacterium capability for the degradation of lignin and pentachlorophenol, as many aromatic compounds such as 2-chlorophenol, 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol and tetrachlorohydroquinone, 6-chlorohydroxyquinol and tetrachlorohydroquinone detected which were not present in the untreated effluent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonso, M. D., Geraldes, V., Rosa, M. J., & Pinho, N. M. (1992). Nanofiltration removal of chlorinated organic compounds from alkaline bleaching effluents in a pulp and paper plant. Water Research, 26, 1639–1643. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(92)90163-X.
Agneta, B., Maraha, N., & Jansson, J. K. (2004). Impact of temperature on the physiological status of potential bioremediation inoculants, Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 5, 2952–2958.
Amat, A. M., Arques, A., Miranda, M. A., & Lopez, F. (2005). Use of ozone and/or UV in the treatment of effluents from board paper industry. Chemosphere, 60(8), 1111–1117. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.062.
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed). Washington, DC.
Anandarajah, K., Kiefer, P. M., Donohoe, B. S., & Copley, S. D. (2000). Recruitment of a double bond isomerase to serve as a reductive dehalogenase during biodegradation of pentachlorophenol. Biochemical, 39, 5303–5311. doi:10.1021/bi9923813.
Andretta, C. W. S., Rosa, R. M., Tondo, E. C., Gaylarde, C. C., & Henriques, J. A. P. (2004). Identification and molecular characterization of a Bacillus subtilis IS13 strain involved in the biodegradation of 4.5,6-trichloroguaiacol. Chemosphere, 55, 631–639. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.062.
Bajpai, P., Mehna, A., & Bajpai, P. K. (1993). Decolorization of Kraft bleach plant effluent with the white rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Process Biochemistry, 28, 377–384. doi:10.1016/0032-9592(93)80024-B.
Chandra, R., Singh, S., & Raj, A. (2006a). Seasonal bacteriological analysis of Gola river water contaminated with pulp paper mill waste in Uttaranchal. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 393–406. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-1508-4.
Chandra, R., Ghosh, A., Jain, R. K., & Singh, S. (2006b). Isolation and characterization of two potential pentachlorophenol degrading aerobic bacteria from pulp paper effluent sludge. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 52, 125–130. doi:10.2323/jgam.52.125.
Chandra, R., Raj, A., Purohit, H. J., & Kapley, A. (2007). Characterisation and optimisation of three potential aerobic bacterial strains for Kraft lignin degradation from pulp paper waste. Chemosphere, 67, 839–846. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.011.
Copley, S. D. (2000). Evolution of a metabolic pathway for degradation of toxic xenobiotics, the patchwork approach. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 25, 261–265. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01562-0.
Environmental Protection Agency EPA (1987). Final determination and indent to cancel and deny applications for registrations of pesticide products containing pentachlorophenol (including but not limited to its salts and esters) for non-wood uses. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Register, 52, 2282–2293.
Environmental Protection Agency (1999). Integrated risk information system (IRSI) on pentachlorophenol. National Centre for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC.
Fahraeus-Van Ree, G. E., & Payne, J. F. (1999). Enzyme cytochemical responses of mussels (Mytilus edulis) to resin acid constituents of pulp mill effluents. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 63(4), 430–437. doi:10.1007/s001289900998.
Gaete, H., Larrain, A., Bay-Schmith, E., Baeza, J., & Rodriguez, J. (2000). Ecotoxicological assessment of two pulp mill effluent, Biobıo river Basin, Chile. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65, 183–189. doi:10.1007/s001280000113.
Gerlach, R. W., & Emon, J. M. V. (1997). Site evaluation of field portable pentachlorophenol immunoassays. Chemosphere, 35, 2727–2749. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00331-7.
Gonzalez, J. M., Hodson, R. E., & Moran, M. A. (1999). Bacterial populations in replicate marine enrichment cultures, assessing variability in abundance using rRNA-based probes. Hydrobiologia, 401, 69–75.
Homada, M. F., Haddad, A. I., & Abd-El-Bary, M. F. (1987). Treatment of phenolic wastes in an aerated submerged fixed-film (ASFF) bioreactor. Journal of Biotechnology, 5, 279–292. doi:10.1016/0168-1656(87)90025-3.
Ito, H., & Ohnishi, Y. (1982). Escherichia coli mutants resistant to uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. Microbiology and Immunology, 226, 1079–1084.
Kannan, K. (1990). Decolorization of pulp and paper mill effluent by growth of Aspergillus niger. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 62, 114–116. doi:10.1007/BF01200929.
Knack Muss, H. J., & Hellwig, M. (1978). Utilization and co oxidation of chlorinated phenols by Pseudomonas sp. b13. Archives of Microbiology, 117, 1–7.
Koistinen, J., Lethonen, M., Tukia, K., Soimasuo, M., Lahtipera, M., & Oikari, A. (1998). Identification of lipophilic pollutants discharged from a Finnish pulp and paper mill. Chemosphere, 37, 219–235. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00041-1.
Kovacs, T. G., & Voss, R. H. (1992). Biological and chemical characterization of newsprint/specialty mill effluents. Water Research, 26, 771–780. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(92)90008-R.
Larrson, D. G. J., & Forlin, L. (2002). Male-biased sex ratios of fish embryos near a pulp mill, temporary recovery after a short-term shutdown. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110, 739–742.
Latorre, A., Malmqvist, A., Lacorte, S., Welander, T., & Barcelo, D. (2007). Evaluation of treatment efficiencies of paper mill whitewater in term of organic composition and toxicity. Environmental Pollution, 147, 648–655. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.09.015.
Livernoche, D., Jurasek, L., Desrochers, M., & Dorica, J. (1983). Removal of color from Kraft mill waste waters with cultures of white rot fungi and with immobilized mycelium of Coriolus versicolor. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 25, 2055–2065. doi:10.1002/bit.260250814.
Loh, K. C., & Chung, T. S. (2000). Immobilized-cell membrane bioreactor for high strength phenol wastewater. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 126, 75–80. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2000)126:1(75).
Malaviya, P., & Rathore, V. S. (2007). Bioremediation of pulp and paper mill effluent by a novel fungal consortium isolated from polluted soil. Bioresource Technology, 98, 3647–3651. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.021.
Martin, C., & Manzanares, P. (1994). A study of the decolorization of straw soda pulping effluents by Trametes versicolor. Bioresource Technology, 47,209–214.doi:10.1016/0960-8524(94)90182-1.
Mohn, W. W., & Kennedy, K. J. (1992). Reductive dehalogenation of chlorophenol by Desulfomonite tiedjei DCB-1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 1367–1370.
Nagarathnamma, R., Bajpai, P., & Bajpai, P. K. (1999). Studies on decolourization, degradation and detoxification of chlorinated lignin compounds in Kraft bleaching effluents by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Process Biochemistry, 34, 939–948. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(99)00021-7.
Nam, I. H., Chang, Y. S., Hong, H. B., & Lee, Y. E. (2003). A novel catabolic activity of Pseudomonas veronii in biotransformation of pentachlorophenol. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 62, 284–290. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1255-1.
Niazi, J. H., Prasad, D. T., & Karegoudar, T. B. (2001). Initial degradation of dimethylphthalate by esterases from Bacillus species. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 196(2), 201–205. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10565.xv.
Oanh, N. T. K. (1996). A comparative study of effluent toxicity for three chlorine-bleached pulp and paper mills in Southeast Asia. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 18, 87–105. doi:10.1016/S0921-3449(96)01171-8.
Palm, H., Paasivirta, J., & Lammi, R. (1995). Behaviour of chlorinated phenolic compounds in bleach-plant, treatment system and archipelago area. Chemosphere, 31, 2839–2852. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(95)00148-2.
Pearl, I. A., & Benson, H. K. (1990). The determination of lignin in sulphide pulping liquor. Paper Trade Journal, 111(18), 35–36.
Pokhrel, D., & Viraraghavan, T. (2004). Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater—A review. The Science of the Total Environment, 333, 37–58. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.05.017.
Premalatha, A., & Rajkumar, G. S. (1994). Pentachlorophenol degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 10, 334–337. doi:10.1007/BF00414874.
Raj, A., Chandra, R., & Patel, D. K. (2005). Physico-chemical characterization of pulp and paper mill effluent and toxicity assessment by a Tubificid worm, Tubifex tubifex. Toxicology International, 12, 109–188.
Raj, A., Reddy, M. M. K., & Chandra, R. (2007a). Identification of low molecular weight aromatic compounds by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) from Kraft lignin degradation by three Bacillus sp. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 59, 292–296. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.09.006.
Raj, A., Reddy, M. M. K., & Chandra, R. (2007b). Decolourisation and treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by lignin degrading Bacillus sp. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire: 1986), 82, 399–406. doi:10.1002/jctb.1683.
Raj, A., Reddy, M. M. K., Chandra, R., Purohit, H. J., & Kapley, A. (2007c). Biodegradation of kraft-lignin by Bacillus sp isolated from sludge of pulp and paper mill. Biodegradation, 18, 783–792. doi:10.1007/s10532-007-9107-9.
Rheinheimer, G. (1998). Pollution in the Baltic Sea. Naturwissenschaften, 85, 318–329. doi:10.1007/s001140050508.
Saber, D. L., & Crawford, R. L. (1985). Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 50, 1512–1518.
Sahoo, D. K., & Gupta, R. (2005). Evaluation of ligninolytic microorganisms for efficient decolorization of a small pulp and paper mill effluent. Process Biochemistry, 40, 1573–1578. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.05.013.
Schnell, A., Stell, P., Melcer, H., Hudson, P. V., & Carey, J. H. (2000). Enhanced biological treatment of bleached Kraft mill effluents removal of chlorinated organic compounds and toxicity. Water Research, 34, 493–500. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00160-8.
Shah, S., & Thakur, I. S. (2003). Enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by Pseudomonas fluorescens of the Microbial community from tannery effluent. Current Microbiology, 47, 65–70. doi:10.1007/s00284-002-3927-y.
Sibley, P. K., Legler, J., Dixon, D. G., & Barton, D. R. (1997). Environmental health assessment of the benthic habitat adjacent to a pulp mill discharge, I. Acute and chronic toxicity of sediments to benthic macro invertebrates. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32, 274–284. doi:10.1007/s002449900185.
Singh, P., & Thakur, I. S. (2006). Colour removal of anaerobically treated pulp and paper mill effluent by microorganisms in two steps bioreactor. Bioresource Technology, 97, 218–223. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.022.
Sobral, O., Ribeiro, R., Goncalves, F., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (1998). Ecotoxicity of pulp mill effluents from different prebleaching processes. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 738–745. doi:10.1007/s001289900823.
Steinle, P., Stucki, G., Stettler, R., & Hanselmann, K. W. (1998). Aerobic mineralization of 2,6 diphenol by Ralstonia sp. strain RK1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2566–2571.
Suegara, J., Lee, B. D., & Espino, M. P. (2005). Photodegradation of pentachlorophenol and its degradation pathways predicted using functional theory. Chemosphere, 61, 341–346. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.090.
Suntio, L. R., Shiu, W. Y., & Mackay, D. (1988). Review of the nature and properties of chemical present in pulp mill effluents. Chemosphere, 17, 1249–1290. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(88)90080-X.
Thakur, I. S., Verma, P. K., & Upadhaya, C. K. (2002). Molecular cloning and characterization of pentachlorophenol-degrading Monooxygenase genes of Pseudomonas sp. from a chemostat. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 290, 770–774. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.6239.
Vallecillo, A., Garcia-Encia, P. A., & Peana, M. (1999). Anaerobic biodegradability and toxicity of chlorophenols. Water Science and Technology, 40, 161–168. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00622-8.
Xun, L., Bohuslavek, J., & Cai, M. (1999). Characterization of 2,6-dichloro-P-hydroquinone 1,2-dioxygenase (PcpA) of sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC 39723. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 266, 322–325. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1805.
Yeber, M. C., Freer, J., Martinez, M., & Mansilla, H. D. (2000). Bacterial response to photolytic degradation of 6-chlorovanillin. Chemosphere, 41, 12257–12261.
Yen, N. T., Oanh, N. T. K., Reutergardh, L. B., Wise, D. L., & Lan, N. T. T. (1996). An integrated waste survey and environmental effects of COGIDO, a bleached pulp and paper mill in Vietnam, on the receiving waterbody. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 18, 161–173. doi:10.1016/S0921-3449(96)01177-9.
Zimmermann, W. (1990). Degradation of lignin by bacteria. Journal of Biotechnology, 13, 119–130. doi:10.1016/0168-1656(90)90098-V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, R., Raj, A., Yadav, S. et al. Reduction of pollutants in pulp paper mill effluent treated by PCP-degrading bacterial strains. Environ Monit Assess 155, 1–11 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0413-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0413-4