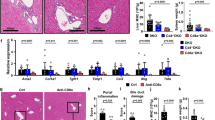
Abstract
Primary sclerosing cholangitis is often complicated by ulcerative colitis. Recently, we reported on Th1-dominant cholangitis associated with experimental colitis, and natural killer T (NKT) cells might play an important role in this model. The aim of this study was to clarify the immunopathogenic role of NKT cells in this model using α-galactosylceramide. CD-1 mice were administered 2.0% dextran sulfate sodium for 29 days and injection of α-galactosylceramide was performed every 5 days, then inflammation was assessed. Mononuclear cells from the liver were analyzed with respect to cytokine production and the surface marker. α -Galactosylceramide improved survival rate, weight gain, and inflammation score. Also, interferon-γ release from MNC, CD4/CD8 ratio, NKT cell population, and NK cell population were decreased by this treatment. These findings indicate that repeated stimulation of NKT cells modifies the Th1/Th2 balance to reduce Th1 dominance, and this may be a mechanism by which α -galactosylceramide has a therapeutic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee YM, Kaplan MM: Management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 97:528–534, 2002
Bambha K, Kim WR, Talwalkar J, Torgerson H, Benson JT, Therneau TM, Loftus EV Jr, Yawn BP, Dickson ER, Melton LJ 3rd: Incidence, clinical spectrum, and outcomes of primary sclerosing cholangitis in a United States community. Gastroenterology 125:1364–1369, 2003
Numata Y, Tazuma S, Nishioka T, Ueno Y, Chayama K: Immune response in mouse experimental cholangitis associated with colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19:910–915, 2004
Farrant JM, Hayllar KM, Wilkinson ML, Karani J, Portmann BC, Westaby D, Williams R: Natural history and prognostic variables in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 100:1710–1717, 1991
Broome U, Olsson R, Loof L, Bodemar G, Hultcrantz R, Danielsson A, Prytz H, Sandberg-Gertzen H, Wallerstedt S, Lindberg G: Natural history and prognostic factors in 305 Swedish patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 38:610–615, 1996
Boberg KM, Lundin KE, Schrumpf E: Etiology and pathogenesis in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 204(Suppl):47–58, 1994
Nakanuma Y, Harada K, Katayanagi K, Tsuneyama K, Sasaki M: Definition and pathology of primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 6:333–342, 1999
Vierling JM: Animal models for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 15:591–610, 2001
Orth T, Neurath M, Schirmacher P, Galle PR, Mayet WJ: A novel rat model of chronic fibrosing cholangitis induced by local administration of a hapten reagent into the dilated bile duct is associated with increased TNF-alpha production and autoantibodies. J Hepatol 33:862–872, 2000
Lichtman SN, Keku J, Clark RL, Schwab JH, Sartor RB: Biliary tract disease in rats with experimental small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Hepatology 13:766–772, 1991
Ueno Y, Phillips JO, Ludwig J, Lichtman SN, LaRusso NF: Development and characterization of a rodent model of immune-mediated cholangitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U A 93:216–220, 1996
Kawano T, Cui J, Koezuka Y, Toura I, Kaneko Y, Motoki K, Ueno H, Nakagawa R, Sato H, Kondo E, Koseki H, Taniguchi M: CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides. Science 278:1626–1629, 1997
Taniguchi M, Harada M, Kojo S, Nakayama T, Wakao H: The regulatory role of Valpha14 NKT cells in innate and acquired immune response. Annu Rev Immunol 21:483–513, 2003
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 69:238–249, 1993
Kamiyasu M, Watanabe Y, Miura T, Masuda K, Nakanishi T, Kajiyama G, Gershwin ME: Experimental hepatitis in neonatally thymectomized mice: transfer of disease and the role of T cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 83:302–309, 1997
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL: Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 96:795–803, 1989
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R: A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702, 1990
Nakagawa R, Nagafune I, Tazunoki Y, Ehara H, Tomura H, Iijima R, Motoki K, Kamishohara M, Seki S: Mechanisms of the antimetastatic effect in the liver and of the hepatocyte injury induced by α–galactosylceramide in mice. J Immunol 166: 6578–6584, 2001
Smyth MJ, Crowe NY, Pellicci DG, Kyparissoudis K, Kelly JM, Takeda K, Yagita H, Godfrey DI: Sequential production of interferon-α by NK1.1+ T cells and natural killer cells is essential for the antimetastatic effect of α-galactosylceramide. Blood 99:1259–1266, 2002
Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, de Oliveira C, Tomaska M, Hong S, Bruna-Romero O, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M, Bendelac A, Van Kaer L, Koezuka Y, Tsuji M: ?-galactosylceramide-activated V?14 natural killer T cells mediate protection against murine malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 8461–8466, 2000
Kawakami K, Kinjo Y, Yara S, Koguchi Y, Uezu K, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M, Saito A: Activation of Vα14+ natural killer T cells by α–galactosylceramide results in development of Th1 response and local host resistance in mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun 69:213–220, 2001
Roberts TJ, Lin Y, Spence PM, Van Kaer L, Brutkiewicz RR: CD1d1-dependent control of the magnitude of an acute antiviral immune response. J Immunol 172:3454–3461, 2004
Singh N, Hong S, Scherer DC, Serizawa I, Burdin N, Kronenberg M, Koezuka Y, Van Kaer L: Cutting edge: activation of NK T cells by CD1d and α–galactosylceramide directs conventional T cells to the acquisition of a Th2 phenotype. J Immunol 163:2373–2377, 1999
Burdin N, Brossay L, Kronenberg M: Immunization with α–galactosylceramide polarizes CD1–reactive NK T cells towards Th2 cytokine synthesis. Eur J Immunol 29: 2014–2025, 1999
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Van Kaer L, Matsuda H, Yagita H, Okumura K: Critical contribution of liver natural killer T cells to a murine model of hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5498–5503, 2000
Eberl G, MacDonald HR: Selective induction of NK cell proliferation and cytotoxicity by activated NKT cells. Eur J Immunol 30:985–992, 2000
Osman Y, Kawamura T, Naito T, Takeda K, Van Kaer L, Okumura K, Abo T: Activation of hepatic NKT cells and subsequent liver injury following administration of alpha-galactosylceramide. Eur J Immunol 30:1919–1928, 2000
Chen H, Huang H, Paul WE: NK1.1+ CD4+ T cells lose NK1.1 expression upon in vitro activation. J Immunol 158:5112–5119, 1997
Wilson MT, Johansson C, Olivares-Villagomez D, Singh AK, Stanic AK, Wang CR, Joyce S, Wick MJ, Van Kaer L: The response of natural killer T cells to glycolipid antigens is characterized by surface receptor down-modulation and expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10913–10918, 2003
Matsuda JL, Gapin L, Baron JL, Sidobre S, Stetson DB, Mohrs M, Locksley RM, Kronenberg M: Mouse Vα14i natural killer T cells are resistant to cytokine polarization in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8395–8400, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Numata, Y., Tazuma, S., Ueno, Y. et al. Therapeutic Effect of Repeated Natural Killer T Cell Stimulation in Mouse Cholangitis Complicated by Colitis. Dig Dis Sci 50, 1844–1851 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2949-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2949-2