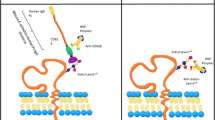
Abstract
Metastatic spreading is a dreadful complication of neoplastic diseases that is responsible for most deaths due to cancer. It consists in the formation of secondary neoplasms from cancer cells that have detached from the primary site. The formation of these secondary sites is not random and several clinical observations indicate that the metastatic colonization exhibits organ selectivity. This organ tropism relies mostly on the complementary adhesive interactions between the cancer cells and their microenvironment. In particular, several lines of evidence suggest that the organ selectivity of colon cancer cells for the liver involves the binding of the circulating cancer cells to endothelial E-selectin. The aim of this review is to make an integrative up-date of the mechanisms that govern the organ selectivity of the metastatic process focusing more especially on the role of selectins and selectin ligands.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRP:
-
Complement regulatory protein
- DR3:
-
Death receptor 3
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- MLC:
-
Myosin light chain
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Ribatti D, Mangialardi G, Vacca A (2006) Stephen Paget and the ‘seed and soil’ theory of metastatic dissemination. Clin Exp Med 6:145–149
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF, Liotta LA (1997) General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer 80:1529–1537
Chambers AF, Naumov GN, Varghese HJ et al (2001) Critical steps in hematogenous metastasis: an overview. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 10:243–255
Mehlen P, Puisieux A (2006) Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 6:449–58
Weiss L (1990) Metastatic inefficiency. Adv Cancer Res 54:159–211
Naumov GN, MacDonald IC, Weinmeister PM et al (2002) Persistence of solitary mammary carcinoma cells in a secondary site: a possible contributor to dormancy. Cancer Res 62:2162–2168
Cameron MD, Schmidt EE, Kerkvliet N et al (2000) Temporal progression of metastasis in lung: cell survival, dormancy, and location dependence of metastatic inefficiency. Cancer Res 60:2541–2546
Luzzi KJ, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE et al (1998) Multistep nature of metastatic inefficiency: dormancy of solitary cells after successful extravasation and limited survival of early micrometastases. Am J Pathol 153:865–873
Paget D (1889) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet 1:571–573
Ewing J (1928) Neoplastic diseases. Saunders Edit, Philadelphia
Fidler IJ (1996) Critical determinants of melanoma metastasis. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 1:203–208
Woltmann G, McNulty CA, Dewson G et al (2000) Interleukin-13 induces PSGL-1/P-selectin-dependent adhesion of eosinophils, but not neutrophils, to human umbilical vein endothelial cells under flow. Blood 95:3146–3152
Laferriere J, Houle F, Huot J (2002) Regulation of the metastatic process by E-selectin and stress-activated protein kinase-2/p38. Ann N Y Acad Sci 973:562–572
Vestweber D, Blanks JE (1999) Mechanisms that regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands. Physiol Rev 79:181–213
Kannagi R, Izawa M, Koike T et al (2004) Carbohydrate-mediated cell adhesion in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Cancer Sci 95:377–384
Tremblay PL, Auger FA, Huot J (2006) Regulation of transendothelial migration of colon cancer cells by E-selectin-mediated activation of p38 and ERK MAP kinases. Oncogene 25:6563–6573
Hu Y, Kiely JM, Szente BE et al (2000) E-selectin-dependent signaling via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 165:2142–2148
Bird MI, Foster MR, Priest R et al (1997) Selectins: physiological and pathophysiological roles. Biochem Soc Trans 25:1199–1206
Vestweber D, Blanks JE (1999) Mechanisms that regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands. Physiol Rev 79:181–213
Brodt P, Fallavollita L, Bresalier RS et al (1997) Liver endothelial E-selectin mediates carcinoma cell adhesion and promotes liver metastasis. Int J Cancer 71:612–619
Witz IP (2006) The involvement of selectins and their ligands in tumor-progression. Immunol Lett 104:89–93
Sawada R, Tsuboi S, Fukuda M (1994) Differential E-selectin-dependent adhesion efficiency in sublines of a human colon cancer exhibiting distinct metastatic potentials. J Biol Chem 269:1425–1431
Khatib AM, Fallavollita L, Wancewicz EV et al (2002) Inhibition of hepatic endothelial E-selectin expression by C-raf antisense oligonucleotides blocks colorectal carcinoma liver metastasis. Cancer Res 62:5393–5398
Kobayashi K, Matsumoto S, Morishima T et al (2000) Cimetidine inhibits cancer cell adhesion to endothelial cells and prevents metastasis by blocking E-selectin expression. Cancer Res 60:3978–3984
Mannori G, Santoro D, Carter L et al (1997) Inhibition of colon carcinoma cell lung colony formation by a soluble form of E-selectin. Am J Pathol 151:233–243
Khatib AM, Kontogiannea M, Fallavollita L et al (1999) Rapid induction of cytokine and E-selectin expression in the liver in response to metastatic tumor cells. Cancer Res 59:1356–1361
Nakamura S, Ohtani H, Watanabe Y et al (1993) In situ expression of the cell adhesion molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. Evidence of immunologic activation of vascular endothelial cells. Lab Invest 69:77–85
Ye C, Kiriyama K, Mistuoka C et al (1995) Expression of E-selectin on endothelial cells of small veins in human colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 61:455–460
Kakiuchi Y, Tsuji S, Tsujii M et al (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 activity altered the cell-surface carbohydrate antigens on colon cancer cells and enhanced liver metastasis. Cancer Res 62:1567–1572
Borsig L, Wong R, Feramisco J et al (2001) Heparin and cancer revisited: mechanistic connections involving platelets, P-selectin, carcinoma mucins, and tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3352–3357
Borsig L, Wong R, Hynes RO et al (2002) Synergistic effects of L- and P-selectin in facilitating tumor metastasis can involve non-mucin ligands and implicate leukocytes as enhancers of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2193–2198
Peeters CF, Ruers TJ, Westphal JR et al (2005) Progressive loss of endothelial P-selectin expression with increasing malignancy in colorectal cancer. Lab Invest 85:248–256
Im JH, Fu W, Wang H et al (2004) Coagulation facilitates tumor cell spreading in the pulmonary vasculature during early metastatic colony formation. Cancer Res 64:8613–8619
Biggerstaff JP, Seth N, Amirkhosravi A et al (1999) Soluble fibrin augments platelet/tumor cell adherence in vitro and in vivo, and enhances experimental metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 17:723–730
Fukuda M, Hiraoka N, Yeh JC (1999) C-type lectins and sialyl Lewis X oligosaccharides. Versatile roles in cell-cell interaction. J Cell Biol 147:467–470
Zipin A, Israeli-Amit M, Meshel T et al (2004) Tumor-microenvironment interactions: the fucose-generating FX enzyme controls adhesive properties of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:6571–6578
Matsuura N, Narita T, Mitsuoka C et al (1997) Increased level of circulating adhesion molecules in the sera of breast cancer patients with distant metastases. Jpn J Clin Oncol 27:135–139
Ito K, Ye CL, Hibi K et al (2001) Paired tumor marker of soluble E-selectin and its ligand sialyl Lewis A in colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol 36:823–829
Hakomori S, Kannagi R (1983) Glycosphingolipids as tumor-associated and differentiation markers. J Natl Cancer Inst 71:231–251
Ogawa J, Inoue H, Koide S (1996) Expression of alpha-1,3-fucosyltransferase type IV and VII genes is related to poor prognosis in lung cancer. Cancer Res 56:325–329
Seko A, Nagata K, Yonezawa S et al (2002) Down-regulation of Gal 3-O-sulfotransferase-2 (Gal3ST-2) expression in human colonic non-mucinous adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:507–515
Ikeda N, Eguchi H, Nishihara S et al (2001) A remodeling system of the 3′-sulfo-Lewis a and 3′-sulfo-Lewis x epitopes. J Biol Chem 276:38588–38594
Lenter M, Levinovitz A, Isenmann S et al (1994) Monospecific and common glycoprotein ligands for E- and P-selectin on myeloid cells. J Cell Biol 125:471–81
Steegmaier M, Levinovitz A, Isenmann S et al (1995) The E-selectin-ligand ESL-1 is a variant of a receptor for fibroblast growth factor. Nature 373:615–20
Zou X, Shinde Patil VR, Dagia NM et al (2005) PSGL-1 derived from human neutrophils is a high-efficiency ligand for endothelium-expressed E-selectin under flow. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289: C415–424
Dimitroff CJ, Descheny L, Trujillo N et al (2005) Identification of leukocyte E-selectin ligands, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 and E-selectin ligand-1, on human metastatic prostate tumor cells. Cancer Res 65:5750–5760
Gout S, Morin C, Houle F et al (2006) Death receptor-3, a new E-Selectin counter-receptor that confers migration and survival advantages to colon carcinoma cells by triggering p38 and ERK MAPK activation. Cancer Res 66:9117–9124
Napier SL, Healy ZR, Schnaar RL et al (2007) Selectin ligand expression regulates the initial vascular interactions of colon carcinoma cells: the roles of CD44V and alternative sialofucosylated selectin ligands. J Biol Chem 282:3433–3441
Tomlinson J, Wang JL, Barsky SH et al (2000) Human colon cancer cells express multiple glycoprotein ligands for E-selectin. Int J Oncol 16:347–353
Mackay CR, Terpe HJ, Stauder R et al (1994) Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol 124:71–82
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M et al (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303–1313
Haynes BF, Liao HX, Patton KL (1991) The transmembrane hyaluronate receptor (CD44): multiple functions, multiple forms. Cancer Cells 3:347–350
Heider KH, Dammrich J, Skroch-Angel P et al (1993) Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in intestinal- and diffuse-type human gastric carcinomas and normal gastric mucosa. Cancer Res 53:4197–4203
Rall CJ, Rustgi AK (1995) CD44 isoform expression in primary and metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 55:1831–1835
Penno MB, August JT, Baylin SB et al (1994) Expression of CD44 in human lung tumors. Cancer Res 54:1381–1387
Terpe HJ, Storkel S, Zimmer U et al (1996) Expression of CD44 isoforms in renal cell tumors. Positive correlation to tumor differentiation. Am J Pathol 148:453–463
Reeder JA, Gotley DC, Walsh MD et al (1998) Expression of antisense CD44 variant 6 inhibits colorectal tumor metastasis and tumor growth in a wound environment. Cancer Res 58:3719–3726
Hanley WD, Burdick MM, Konstantopoulos K et al (2005) CD44 on LS174T colon carcinoma cells possesses E-selectin ligand activity. Cancer Res 65:5812–5817
Burdick MM, Chu JT, Godar S et al (2006) HCELL is the major E- and L-selectin ligand expressed on LS174T colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 281:13899–13905
Bodmer JL, Burns K, Schneider P et al (1997) TRAMP, a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor with sequence homology to tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and Fas(Apo-1/CD95). Immunity 6:79–88
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Yu GL et al (1996) Signal transduction by DR3, a death domain-containing receptor related to TNFR-1 and CD95. Science 274:990–992
Screaton GR, Xu XN, Olsen AL et al (1997) LARD: a new lymphoid-specific death domain containing receptor regulated by alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4615–4619
Lohi O, Lehto VP (1998) ITAM motif in an apoptosis-receptor. Apoptosis 3:335–336
Laferriere J, Houle F, Taher MM et al (2001) Transendothelial migration of colon carcinoma cells requires expression of E-selectin by endothelial cells and activation of stress-activated protein kinase-2 (SAPK2/p38) in the tumor cells. J Biol Chem 276:33762–33772
Ohana-Malka O, Benharroch D, Isakov N et al (2003) Selectins and anti-CD15 (Lewis x/a) antibodies transmit activation signals in Hodgkin’s lymphoma-derived cell lines. Exp Hematol 31:1057–1065
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM et al (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436:518–524
Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D (2006) Preparing the “soil”: the premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 66:11089–11093
Hiratsuka S, Nakamura K, Iwai S et al (2002) MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2:289–300
Nicolson GL (1988) Cancer metastasis: tumor cell and host organ properties important in metastasis to specific secondary sites. Biochim Biophys Acta 948:175–224
Khatib AM, Auguste P, Fallavollita L et al (2005) Characterization of the host proinflammatory response to tumor cells during the initial stages of liver metastasis. Am J Pathol 167:749–759
Haier J, Nicolson GL (2001) The role of tumor cell adhesion as an important factor in formation of distant colorectal metastasis. Dis Colon Rectum 44:876–884
Walzog B, Gaehtgens P (2000) Adhesion Molecules: The Path to a New Understanding of Acute Inflammation. News Physiol Sci 15:107–113
Narita T, Kawakami-Kimura N, Kasai Y et al (1996) Induction of E-selectin expression on vascular endothelium by digestive system cancer cells. J Gastroenterol 31:299–301
Auguste P, Fallavollita L, Wang N et al (2007) The host inflammatory response promotes liver metastasis by increasing tumor cell arrest and extravasation. Am J Pathol 170:1781–1792
Wang HH, Qiu H, Qi K et al (2005) Current views concerning the influences of murine hepatic endothelial adhesive and cytotoxic properties on interactions between metastatic tumor cells and the liver. Comp Hepatol 4:8
Carrascal MT, Mendoza L, Valcarcel M et al (2003) Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces b16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelium. Cancer Res 63:491–497
Kitakata H, Nemoto-Sasaki Y, Takahashi Y et al (2002) Essential roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55 in liver metastasis of intrasplenic administration of colon 26 cells. Cancer Res 62:6682–6687
Araki M, Araki K, Biancone L et al (1997) The role of E-selectin for neutrophil activation and tumor metastasis in vivo. Leukemia 11(Suppl 3):209–212
Gotsch U, Jager U, Dominis M et al (1994) Expression of P-selectin on endothelial cells is upregulated by LPS and TNF-alpha in vivo. Cell Adhes Commun 2:7–14
Kneuer C, Ehrhardt C, Radomski MW et al (2006) Selectins–potential pharmacological targets? Drug Discov Today 11:1034–1040
He XY, Xu Z, Melrose J et al (1998) Humanization and pharmacokinetics of a monoclonal antibody with specificity for both E- and P-selectin. J Immunol 160:1029–1035
Hosono J, Narita T, Kimura N et al (1998) Involvement of adhesion molecules in metastasis of SW1990, human pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Oncol 67:77–84
Nakashio T, Narita T, Sato M et al (1997) The association of metastasis with the expression of adhesion molecules in cell lines derived from human gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 17:293–299
O I, Otvos L, Kieber-Emmons T et al (2002) Role of SA-Le(a) and E-selectin in metastasis assessed with peptide antagonist. Peptides 23:999–1010
Weston BW, Hiller KM, Mayben JP et al (1999) Expression of human alpha(1,3)fucosyltransferase antisense sequences inhibits selectin-mediated adhesion and liver metastasis of colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 59:2127–2135
Matsumoto S, Imaeda Y, Umemoto S et al (2002) Cimetidine increases survival of colorectal cancer patients with high levels of sialyl Lewis-X and sialyl Lewis-A epitope expression on tumour cells. Br J Cancer 86:161–167
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Cancer Research Society Inc and the Canadian Cancer Society. SG holds a Post-Doctoral Fellowship from MEQ/FRSQ and PLT holds a PhD studentship from FRSQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stéphanie Gout and Pierre-Luc Tremblay are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gout, S., Tremblay, PL. & Huot, J. Selectins and selectin ligands in extravasation of cancer cells and organ selectivity of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 25, 335–344 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9096-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9096-4