Abstract
Objective
To evaluate whether the association between hormone therapy (HT) and breast density differs by levels of breast cancer risk factors.
Methods
We evaluated 80,867 screening mammograms from 39,296 postmenopausal women from Washington State. We estimated odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for dense breasts (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System categories 3 “heterogeneously dense” and 4 “extremely dense”) compared to fatty breasts (categories 1 “almost entirely fat” and 2 “scattered fibroglandular”) among HT users compared to never users. We separately examined former HT use and current HT use by type (estrogen plus progestin therapy (EPT) and estrogen-only therapy (ET)). We stratified the associations by age, BMI, race, family history, and reproductive and menopausal factors.
Results
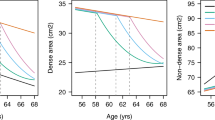
Current EPT users had a 98% (1.87–2.09) greater odds of having dense breasts and current ET users had a 71% (1.56–1.87) greater odds compared to never users. Current HT users were more likely to have dense breasts if they were older, had more children, or younger at first birth compared to never users; these associations were stronger among EPT users than ET users.
Conclusions
HT, particularly EPT, may reduce protective effects of older age, parity, and younger age at first birth on mammographic density.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd NF, Byng JW, Jong RA, et al. (1995) Quantitative classification of mammographic densities and breast cancer risk: results from the Canadian National Breast Screening Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 87(9):670–675
Harvey JA, Bovbjerg VE (2004) Quantitative assessment of mammographic breast density: relationship with breast cancer risk. Radiology 230(1):29–41
Vacek PM, Geller BM (2004) A prospective study of breast cancer risk using routine mammographic breast density measurements. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(5):715–722
Boyd NF, Lockwood GA, Byng JW, Tritchler DL, Yaffe MJ (1998) Mammographic densities and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7(12):1133–1144
Saftlas AF, Hoover RN, Brinton LA, et al. (1991) Mammographic densities and risk of breast cancer. Cancer 67(11):2833–2838
Mandelson MT, Oestreicher N, Porter PL, et al. (2000) Breast density as a predictor of mammographic detection: comparison of interval- and screen-detected cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(13):1081–1087
Ciatto S, Visioli C, Paci E, Zappa M (2004) Breast density as a determinant of interval cancer at mammographic screening. Br J Cancer 90(2):393–396
Carney PA, Miglioretti DL, Yankaskas BC, et al. (2003) Individual and combined effects of age, breast density, and hormone replacement therapy use on the accuracy of screening mammography. Ann Intern Med 138(3):168–175
Rosenberg RD, Hunt WC, Williamson MR, et al. (1998) Effects of age, breast density, ethnicity, and estrogen replacement therapy on screening mammographic sensitivity and cancer stage at diagnosis: review of 183,134 screening mammograms in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Radiology 209(2):511–518
van Gils CH, Otten JD, Verbeek AL, Hendriks JH, Holland R (1998) Effect of mammographic breast density on breast cancer screening performance: a study in Nijmegen, The Netherlands. J Epidemiol Community Health 52(4):267–271
Buist DS, Porter PL, Lehman C, Taplin SH, White E (2004) Factors contributing to mammography failure in women aged 40–49 years. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(19):1432–1440
Rutter CM, Mandelson MT, Laya MB, Seger DJ, Taplin S (2001) Changes in breast density associated with initiation, discontinuation, and continuing use of hormone replacement therapy. JAMA 285(2):171–176
Greendale GA, Reboussin BA, Slone S, Wasilauskas C, Pike MC, Ursin G (2003) Postmenopausal hormone therapy and change in mammographic density. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(1):30–37
Vachon CM, Sellers TA, Vierkant RA, Wu FF, Brandt KR (2002) Case–control study of increased mammographic breast density response to hormone replacement therapy. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11(11):1382–1388
Sendag F, Cosan Terek M, Ozsener S, et al. (2001) Mammographic density changes during different postmenopausal hormone replacement therapies. Fertil Steril 76(3):445–450
El-Bastawissi AY, White E, Mandelson MT, Taplin SH (2000) Reproductive and hormonal factors associated with mammographic breast density by age (United States). Cancer Causes Control 11(10):955–963
Vachon CM, Kuni CC, Anderson K, Anderson VE, Sellers TA (2000) Association of mammographically defined percent breast density with epidemiologic risk factors for breast cancer (United States). Cancer Causes Control 11(7):653–662
Boyd N, Martin L, Stone J, Little L, Minkin S, Yaffe M (2002) A longitudinal study of the effects of menopause on mammographic features. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11(10 Pt 1):1048–1053
Jeffreys M, Warren R, Gunnell D, McCarron P, Smith GD (2004) Life course breast cancer risk factors and adult breast density (United Kingdom). Cancer Causes Control 15(9):947–955
El-Bastawissi AY, White E, Mandelson MT, Taplin S (2001) Variation in mammographic breast density by race. Ann Epidemiol 11(4):257–263
Chen Z, Wu AH, Gauderman WJ, et al. (2004) Does mammographic density reflect ethnic differences in breast cancer incidence rates? Am J Epidemiol 159(2):140–147
Chen CL, Weiss NS, Newcomb P, Barlow W, White E (2002) Hormone replacement therapy in relation to breast cancer. JAMA 287(6):734–741
Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative Investigators (2002) Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results from the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288(3):321–333
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer (1997) Breast cancer and hormone replacement therapy: collaborative reanalysis of data from 51 epidemiological studies of 52,705 women with breast cancer and 108,411 women without breast cancer. Lancet 350(9084):1047–1059
Chlebowski RT, Hendrix SL, Langer RD, et al. (2003) Influence of estrogen plus progestin on breast cancer and mammography in healthy postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Trial. JAMA 289(24):3243–3253
Buist DS, Newton KM, Miglioretti DL, et al. (2004) Hormone therapy prescribing patterns in the United States. Obstet Gynecol 104(5 Pt 1):1042–1050
Majumdar SR, Almasi EA, Stafford RS (2004) Promotion and prescribing of hormone therapy after report of harm by the Women’s Health Initiative. JAMA 292(16):1983–1988
Taplin SH, Thompson RS, Schnitzer F, Anderman C, Immanuel V (1990) Revisions in the risk-based breast cancer screening program at Group Health Cooperative. Cancer 66(4):812–818
Thompson RS, Taplin SH, Carter AP, Schnitzer F (1989) Cost effectiveness in program delivery. Cancer 64(12 Suppl):2682–2689
Taplin SH, Ichikawa L, Buist DS, Seger D, White E (2004) Evaluating organized breast cancer screening implementation: the prevention of late-stage disease? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(2):225–234
American College of Radiology (ACR) (1998) Illustrated breast imaging reporting, data system (BI-RADS), 3rd ed. American College of Radiology, Reston, VA
Lundstrom E, Wilczek B, von Palffy Z, Soderqvist G, von Schoultz B (2001 ) Mammographic breast density during hormone replacement therapy: effects of continuous combination, unopposed transdermal and low-potency estrogen regimens. Climacteric 4(1):42–48
Erel CT, Seyisoglu H, Senturk ML, et al. (1996) Mammographic changes in women on hormonal replacement therapy. Maturitas 25(1):51–57
Panpanit A, Muttarak M, Pongsatha S, et al. (2004) Mammographic change in hysterectomized women on 0.625 mg/day of conjugated equine estrogen. J Med Assoc Thai 87(2):126–130
Laya MB, Gallagher JC, Schreiman JS, Larson EB, Watson P, Weinstein L (1995) Effect of postmenopausal hormonal replacement therapy on mammographic density and parenchymal pattern. Radiology 196(2):433–437
Ziv E, Shepherd J, Smith-Bindman R, Kerlikowske K (2003) Mammographic breast density and family history of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(7):556–558
Boyd NF, Dite GS, Stone J, et al. (2002) Heritability of mammographic density, a risk factor for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347(12):886–894
Sala E, Warren R, McCann J, Duffy S, Luben R, Day N (1999) High-risk mammographic parenchymal patterns and anthropometric measures: a case-control study. Br J Cancer 81(7):1257–1261
Boyd NF, Lockwood GA, Byng JW, Little LE, Yaffe MJ, Tritchler DL (1998) The relationship of anthropometric measures to radiological features of the breast in premenopausal women. Br J Cancer 78(9):1233–1238
Lukanova A, Lundin E, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, et al. (2004) Body mass index, circulating levels of sex-steroid hormones, IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-3: a cross-sectional study in healthy women. Eur J Endocrinol 150(2):161–171
Ursin G, Tseng CC, Paganini-Hill A, et al. (2002) Does menopausal hormone replacement therapy interact with known factors to increase risk of breast cancer? J Clin Oncol 20(3):699–706
Brisson J, Diorio C, Masse B (2003) Wolfe’s parenchymal pattern and percentage of the breast with mammographic densities: redundant or complementary classifications? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12(8):728–732
Acknowledgments
We thank Melissa Anderson, MS, for her statistical review of this manuscript. This study was supported by Grant CA063731 from the National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aiello, E.J., Buist, D.S.M. & White, E. Do breast cancer risk factors modify the association between hormone therapy and mammographic breast density? (United States). Cancer Causes Control 17, 1227–1235 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-006-0073-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-006-0073-z